Abstract
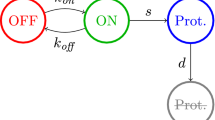
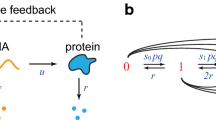
This paper considers adiabatic reduction in a model of stochastic gene expression with bursting transcription considered as a jump Markov process. In this model, the process of gene expression with auto-regulation is described by fast/slow dynamics. The production of mRNA is assumed to follow a compound Poisson process occurring at a rate depending on protein levels (the phenomena called bursting in molecular biology) and the production of protein is a linear function of mRNA numbers. When the dynamics of mRNA is assumed to be a fast process (due to faster mRNA degradation than that of protein) we prove that, with appropriate scalings in the burst rate, jump size or translational rate, the bursting phenomena can be transmitted to the slow variable. We show that, depending on the scaling, the reduced equation is either a stochastic differential equation with a jump Poisson process or a deterministic ordinary differential equation. These results are significant because adiabatic reduction techniques seem to have not been rigorously justified for a stochastic differential system containing a jump Markov process. We expect that the results can be generalized to adiabatic methods in more general stochastic hybrid systems.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bardet JB, Christen A, Guillin A, Malrieu F, Zitt PA (2013) Total variation estimates for the TCP process. Electron J Probab 18(10):1–21
Berglund N, Gentz B (2006) Noise-induced phenomena in slow-fast dynamical systems, a sample-paths approach. Springer, Berlin
Buckwar E, Riedler MG (2011) An exact stochastic hybrid model of excitable membranes including spatio-temporal evolution. J Math Biol 63(6):1051–1093
Crudu A, Debussche A, Muller A, Radulescu O (2012) Convergence of stochastic gene networks to hybrid piecewise deterministic processes. Ann Appl Probab 5:1822–1859
Davis MHA (1984) Piecewise-deterministic Markov processes: a general class of non-diffusion stochastic models. J R Stat Soc Ser B 46(3):353–388
Elf J, Li GW, Xie XS (2007) Probing transcription factor dynamics at the single-molecule level in a living cell. Science 316(5828):1191–1194. doi:10.1126/science.1141967
Fenichel N (1979) Geometric singular perturbation theory for ordinary differential equations. J Differ Equ 31(1):53–98. doi:10.1016/0022-0396(79)90152-9
Friedman N, Cai L, Xie XS (2006) Linking stochastic dynamics to population distribution: an analytical framework of gene expression. Phys Rev Lett 97(16):168–302. doi:10.1103/PhysRevLett.97.168302
Gardiner CW (1985) Handbook of stochastic methods. Springer, Berlin
Golding I, Paulsson J, Zawilski SM, Cox EC (2005) Real-time kinetics of gene activity in individual bacteria. Cell 123(6):1025–1036
Hasty J, Pradines J, Dolnik M, Collins J (2000) Noise-based switches and amplifiers for gene expression. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 97(5):2075–2080
Kang HW, Kurtz TG (2013) Separation of time-scales and model reduction for stochastic reaction networks. Ann App Probab 23:529–583
Lasota A, Mackey MC (1985) Probabilistic properties of deterministic systems. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge
Lei J (2009) Stochasticity in single gene expression with both intrinsic noise and fluctuation in kinetic parameters. J Theor Biol 256:485–492
Mackey MC, Tyran-Kamińska M (2008) Dynamics and density evolution in piecewise deterministic growth processes. Ann Pol Math 94(2):111–129. doi:10.4064/ap94-2-2
Mackey MC, Tyran-Kamińska M, Yvinec R (2011) Molecular distributions in gene regulatory dynamics. J Theor Biol 274(1):84–96. doi:10.1016/j.jtbi.2011.01.020
Ozbudak EM, Thattai M, Kurtser I, Grossman AD, van Oudenaarden A (2002) Regulation of noise in the expression of a single gene. Nat Genet 31(1):69–73. doi:10.1038/ng869
Pakdaman K, Thieullen M, Wainrib G (2012) Fluid limit theorems for stochastic hybrid systems with application to neuron models. Adv Appl Probab 42(3):761–794
Raj A, van Oudenaarden A (2009) Single-molecule approaches to stochastic gene expression. Annu Rev Biophys 38(1):255–270. doi:10.1146/annurev.biophys.37.032807.125928
Raj A, Peskin CS, Tranchina D, Vargas DY, Tyagi S (2006) Stochastic mRNA synthesis in mammalian cells. PLoS Biol 4(10):e309. doi:10.1371/journal.pbio.0040309
Riedler MG, Thieullen M, Wainrib G (2012) Limit theorems for infinite-dimensional piecewise deterministic Markov processes. Applications to stochastic excitable membrance models. Electron J Probab 17(55): 1–48
Santillán M, Qian H (2011) Irreversible thermodynamics in multiscale stochastic dynamical systems. Phys Rev E 83:1–8
Schwanhäusser B, Busse D, Li N, Dittmar G, Schuchhardt J, Wolf J, Chen W, Selbach M (2011) Global quantification of mammalian gene expression control. Nature 473:337–342
Shahrezaei V, Swain PS (2008) Analytical distributions for stochastic gene expression. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 105(45):17256–17261. doi:10.1073/pnas.0803850105
Stratonovich R (1963) Topics in the theory of random noise, vol 1. General theory of random processes. Nonlinear transformations of signals and noise, revised English edition. Translated from the Russian by Richard A. Silverman edn. Gordon and Breach Science Publishers, New York
Suter DM, Molina N, Gatfield D, Schneider K, Schibler U, Naef F (2011) Mammalian genes are transcribed with widely different bursting kinetics. Science 332(6028):472–474. doi:10.1126/science.1198817
Taniguchi Y, Choi PJ, Li GW, Chen H, Babu M, Hearn J, Emili A, Xie XS (2010) Quantifying E. coli proteome and transcriptome with single-molecule sensitivity in single cells. Science 329:533–538
Tikhonov AN (1952) Systems of differential equations containing small parameters in the derivatives. Mat Sb (NS) 31(73):575–586
Titular U (1978) A systematic solution procedure for the Fokker–Planck equation of a Brownian particle in the high-friction case. Phys A 91:321–344
Tyran-Kamińska M (2009) Substochastic semigroups and densities of piecewise deterministic Markov processes. J Math Anal Appl 357(2):385–402
Wilemski G (1976) On the derivation of Smoluchowski equations with corrections in the classical theory of Brownian motion. J Stat Phys 14:153–169
Xie XS, Choi PJ, Li GW, Lee NK, Lia G (2008) Single-molecule approach to molecular biology in living bacterial cells. Annu Rev Biophys 37(1):417–444. doi:10.1146/annurev.biophys.37.092607.174640
Zeiser S, Franz U, Wittich O, Liebscher V (2008) Simulation of genetic networks modelled by piecewise deterministic Markov processes. IET Syst Biol 2(3):113–135
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the Natural Sciences and Engineering Research Council (NSERC, Canada), the Mathematics of Information Technology and Complex Systems (MITACS, Canada), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (NSFC 11272169, China) and the région Rhône-Alpes (mobility fellowship), and carried out in Montréal, Lyon and Beijing. We thank our colleague M. Tyran-Kamińska for valuable discussions.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
This research was supported by the Ecole Normale Superieure Lyon (ENS Lyon, France), the National Natural Science Foundation of China, and the Natural Sciences and Engineering Research Council of Canada.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yvinec, R., Zhuge, C., Lei, J. et al. Adiabatic reduction of a model of stochastic gene expression with jump Markov process. J. Math. Biol. 68, 1051–1070 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00285-013-0661-y
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00285-013-0661-y
Keywords
- Adiabatic reduction
- Piecewise deterministic Markov process
- Stochastic bursting gene expression
- Quasi-steady state assumption
- Scaling limit