Abstract
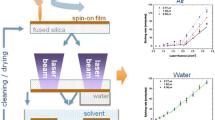
The backside ablation of a absorbing carbon layer onto fused silica is studied in air and water confinement in comparison. The confinement influences the etch rate and the laser fluence dependence of the etch rate significantly while the threshold fluence is almost the same. The different confinement of the laser induced plasma results in the observed rate saturation in the case of air and in a linear growing rate in the case of water confinement at medium laser fluences. The less dense air confinement permits a faster plasma expansion of the laser plume than in the case of water confinement and effects consequently the interaction time and interaction strength of the laser plume with the fused silica surface. The differences in the laser-plasma-substrate interaction cause the observed rate saturation at weak interaction (air) and the growing etch rate at strong interaction (water). Thus, the confinement situation controls the interaction process in the case of backside ablation and should be considered in indirect material processing methods such as LIBWE and LESAL, too.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bäuerle D (2000) Laser Processing and Chemistry, 3. Ed. Springer, Berlin Heidelberg New York
Ihlemann J, Wolff-Rottke B (1996) Appl. Surf. Sci. 106:282
Dyer PE, Maswadi SM, Walton CD, Ersoz M, Fletcher PDI, Paunov VN (2003) Appl. Phys. A 77:391
Ben-Yakar A, Byer RL (2004) J. Appl. Phys. 96:5316
Wang J, Niino H, Yabe A (1999) Appl. Phys. A 68:111
Böhme R, Braun A, Zimmer K (2002) Appl. Surf. Sci. 186:276
Zimmer K, Böhme R, Rauschenbach B (2004) Appl. Phys. A 79:1883
Böhme R, Spemann D, Zimmer K (2004) Thin Solid Films 453:127
Shin JK, Lee CS, Lee KR, Eun KY (2001) Appl. Phys. Lett. 78:631
Dupont A, Caminat P, Bournot P, Gauchon JP (1995) J. Appl. Phys. 78:2022
Kane DM, Halfpenny DR (2000) J. Appl. Phys. 87:4548
Zhao J, Sullivan J, Zayac J, Bennett TD (2004) J. Appl. Phys. 95:5475
Kolomenskii AA, Lomonosov AM, Kuschnereit R, Hess P, Gusev VE (1997) Phys. Rev. Lett. 79:1325
Allcock G, Dyer PE, Elliner G, Snelling HV (1995) J. Appl. Phys. 78:7295
Haverkamp J, Mayo RM, Bourham MA, Narayan J, Jin C, Duscher G (2003) J. Appl. Phys. 93:3627
Claeyssens F, Ashfold MNR, Sofoulakis E, Ristoscu CG, Anglos D, Fotakis C (2002) J. Appl. Phys. 91:6162
Andreic Z, Gracin D, Aschke L, Kunze HJ (2001) Vacuum 61:385
Loiseleur P, Hansen TN, Larour J, Lunney JG (2002) Appl. Surf. Sci. 197:164
Sugioka K, Wada S, Tashiro H, Toyoda K, Ohnuma Y, Nakamura A (1995) Appl. Phys. Lett. 67:2789
Dickinson JT (1991) Simultaneous bombardement of wide bandgap materials with UV excimer laser irradiation and KeV electrons. Springer, Berlin
Zhang J, Sugioka K, Midorikawa K (1998) Opt. Lett. 23:1486
Makimura T, Mitani S, Kenmotsu Y, Murakami K, Mori M, Kondo K (2004) Appl. Phys. Lett. 85:1274
Berthe L, Fabbro R, Peyre P, Tollier L, Bartnicki E (1997) J. Appl. Phys. 82:2826
Zhu S, Lu YF, Hong MH, Chen XY (2001) J. Appl. Phys. 89:2400
Saito K, Sakka T, Ogata YH (2003) J. Appl. Phys. 94:5530
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
PACS
81.65.C; 81.05.K; 79.20.D; 61.80.B; 42.55.L; 68.45.D
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Böhme, R., Zimmer, K. & Rauschenbach, B. Laser backside etching of fused silica due to carbon layer ablation. Appl. Phys. A 82, 325–328 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-005-3387-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-005-3387-x