Abstract
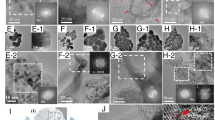
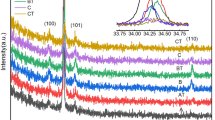
Aluminium nitride thin films were deposited on n-Si <100> substrates by RF plasma activated reactive pulsed laser deposition (PLD). An ArF excimer pulsed laser, 10 Hz and 2.5 J/cm2 energy fluence, has been used to ablate a pure Al target in a reactive atmosphere of N2 plasma (generated by a RF source), at varying processing parameters (substrate temperature, time, and N2 plasma configuration). We studied the dependence and correlation of structural and electronic properties with the experimental conditions. The chemical composition of deposited material has been determined by both Raman and X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS). Electrical resistivity has been evaluated by the sheet resistance method. Both spectroscopic characterizations (Raman and XPS) show a strong dependence in the formation of AlN on the deposition temperature. At low temperatures, there is little formation of nitride, with a prevalence of aluminium oxide, while at higher temperatures the N uptake increases, with AlN formation. Raman analysis also highlights the formation of nano-structures, for temperatures ≥400∘C. These material characteristics have a fundamental influence on the electronic properties. Indeed, electrical resistivity properties have been found to be strongly dependent on the film structure, nitrogen incorporation, and presence of mixed oxide compounds, closely related to deposition temperature.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
B. Liu, J. Gao, K.M. Wu, C. Liu, Solid State Commun. 149, 715 (2009)
Y. Lu, X. Liu, X. Wang, D.C. Lu, D. Li, X. Han, G. Cong, Z. Wang, J. Cryst. Growth 263, 4 (2004)
M. Clement, E. Iborra, J. Sangrador, A. Sanz-Hervas, L. Vergara, M. Aguilar, J. Appl. Phys. 94, 1495 (2003)
P. Kung, A. Saxler, X. Zhang, D. Walker, T.C. Wang, I. Ferguson, M. Razeghi, Appl. Phys. Lett. 66, 2958 (1995)
K.S. Stevens, A. Ohtani, M. Kinniburgh, R. Beresford, Appl. Phys. Lett. 65, 321 (1994)
W.J. Meng, J. Heremans, Y.T. Chang, Appl. Phys. Lett. 59, 2097 (1991)
R.D. Vispute, J. Narayan, H. Wu, K. Jagannadham, J. Appl. Phys. 77, 4724 (1995)
G.K. Hubler, in Pulsed Laser Deposition of Thin Films, ed. by D.B. Chrisey, G.K. Hubler (Wiley-Interscience, New York, 1994), p. 327
J.D. Wu, J. Sun, Z.F. Ying, W. Shi, H. Ling, F.M. Li, Z.Y. Zhou, K.L. Wang, X.M. Ding, J. Vac. Sci. Technol. A 19, 299 (2001)
K. Jagannadham, A.K. Sharma, Q. Wei, R. Kalyanraman, J. Narayan, J. Vac. Sci. Technol. A 16, 2804 (1998)
P. Verardi, M. Dinescu, C. Gerardi, L. Mirenghi, V. Sandu, Appl. Surf. Sci. 109–110, 371 (1997)
A.G. Guidoni, A. Mele, T.M. Di Palma, C. Flamini, S. Orlando, R. Teghil, Thin Solid Films 295, 77 (1997)
A. Basillais, R. Benzerga, H. Sanchez, E. Le Menn, C. Boulmer-Leborgne, J. Perrier, Appl. Phys. A 80, 851 (2005)
E. Cappelli, S. Orlando, D.M. Trucchi, A. Bellucci, V. Valentini, A. Mezzi, S. Kaciulis, Appl. Surf. Sci. 257, 5175 (2011)
E. Cappelli, D.M. Trucchi, S. Kaciulis, S. Orlando, A. Zanza, A. Mezzi, Thin Solid Films 519, 4059 (2011)
S. Kaciulis, L. Pandolfi, R. White, Surf. Interface Anal. 36, 845 (2004)
J.F. Moulder, W.F. Stickle, P.E. Sobol, K.D. Bomben, Handbook of X-ray Photoelectron Spectroscopy (Physical Electronics, Eden Prairie, 1995), p. 20
I. Bertoti, Surf. Coat. Technol. 151–152, 194 (2002)
Y.G. Cao, X.L. Chen, Y.C. Lan, J.Y. Li, Y.P. Xu, T. Xu, Q.L. Liu, J.K. Liang, J. Cryst. Growth 213, 198 (2000)
V.Yu. Davydov, Yu.E. Kitaev, I.N. Goncharuk, A.N. Smirnov, J. Graul, O. Semchinova, D. Uffmann, M.B. Smirnov, A.P. Mirgorodsky, R.A. Evarestov, Phys. Rev. B 58, 12899 (1998)
N. Laidani, L. Vanzetti, M. Anderle, A. Basillais, C. Boulmer-Leborgne, J. Perriere, Surf. Coat. Technol. 122, 242 (1999)
O. Elmazria, M.B. Assouar, P. Renard, P. Alnot, Phys. Status Solidi A 196, 416 (2003)
J. Borges, N. Martin, N.P. Barradas, E. Alves, D. Eyidi, M.F. Beaufort, J.P. Riviere, F. Vaz, L. Marques, Thin Solid Films 520, 6709 (2012)
Acknowledgements
The authors are very grateful to P. Piciacchia for the excimer laser maintenance and to N. Vitulano for the RF plasma confined design and realization.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cappelli, E., Trucchi, D.M., Orlando, S. et al. AlN thin films prepared by ArF plasma assisted PLD. Role of process conditions on electronic and chemical–morphological properties. Appl. Phys. A 114, 611–617 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-013-7632-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-013-7632-4