Abstract
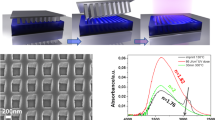
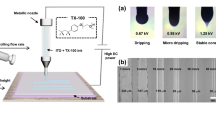
Indium tin oxide (ITO) is one of the few materials available that display a high transparency in the visible wavelength region and at the same time can conduct electrical currents. Thus it is widespread in many optoelectronic applications such as displays or solar cells. Layers of this material are commonly deposited by vacuum deposition methods which are not compatible with inexpensive production methods such as roll-to-roll processing or printed electronics in general. In this work, we demonstrate the generation of arbitrarily shaped ITO layers by laser induced forward transfer of ITO nanoparticles. The transferred particle ink volumes range in the sub picoliter regime. Feature sizes as small as 20 μm are produced without any outward flow or “coffee-stain” effects. Furthermore, the feasibility of excimer laser consolidation of these nanoparticulate layers in ambient air for the generation of dense ITO films is shown. Conductivities of over 4000 Ω−1 m−1 were achieved. The presented methods are a promising alternative for the generation of transparent conducting layers for the inexpensive production of optoelectronics.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
J.C. Manifacier, Thin metallic oxides as transparent conductors. Thin Solid Films 90, 287 (1982)
M. Groß, Druckbare, nanopartikiläre Indiumzinnoxidschichten für optoelektronische Anwendungen. Dissertation, Friedrich-Alexander-Universität Erlangen-Nuremberg, 2009, p. 33
T. Maruyama, K. Fukui, Indium tin oxide thin films prepared by chemical vapour deposition. Thin Solid Films 203, 297 (1991)
M. Penza, S. Cozzi, M.A. Tagliente, L. Mirenghi, C. Martucci, A. Quirini, Characterization of transparent and conductive electrodes of indium tin oxide thin films by sequential reactive evaporation. Thin Solid Films 349, 71 (1999)
A. Kachouane, M. Addou, A. Bougrine, B. El Idrissi, R. Messoussi, M. Regragui, J.C. Bérnede, Preparation and characterisation of tin-doped indium oxide films. Mater. Chem. Phys. 70, 285 (2001)
K.K. Banger, Y. Yamashita, K. Mori, R.L. Peterson, T. Leedham, J. Rickard, H. Sirringhaus, Low-temperature, high-performance solution-processed metal oxide thin-films transistors formed by a ‘sol-gel on chip’ process. Nat. Mater. 10, 45 (2011)
M. Kim, M.G. Kanatzidis, A. Facchetti, T.J. Marks, Low temperature fabrication of high-performance metal oxide thin-film electronics via combustion procession. Nat. Mater. 10, 382 (2011)
J.-S. Lee, M.V. Kovalenko, J. Huang, D.S. Chung, D.V. Talapin, Band-like transport, high electron mobility and high photoconductivity in all-inorganic nanocrystal arrays. Nat. Nanotechnol. 6, 348 (2011)
S. Walther, S. Schäfer, M.P.M. Jank, H. Thiem, W. Peukert, L. Frey, H. Ryssel, Influence of annealing temperature and measurement ambient on TFTs based on gas phase synthesized ZnO nanoparticles. Microelectron. Eng. 87, 2312 (2010)
M. Hwang, B. Jeong, J. Moon, S.-K. Chun, J. Kim, Inkjekt-printing of indium tin oxide (ITO) thin films for transparent conducting electrodes. Mater. Sci. Eng. B 176, 1128 (2011)
A. Piqué, R.C.Y. Auyeung, H. Kim, K.M. Metkus, S.A. Mathews, Digital microfabrication by laser decal transfer. J. Laser Micro Nanoeng. 3, 163 (2008)
H. Kim, R.c.Y. Auyeung, S.H. Lee, A.L. Huston, A. Piqué, Laser printed interdigitated Ag electrodes for organic thin-film transistors. J. Phys. D, Appl. Phys. 43, 085101 (2010)
H. Kim, J.S. Melinger, A. Khachatrian, N.A. Charipar, R.C.Y. Auyeung, A. Piqué, Fabrication of Terahertz metamaterials by laser printing. Opt. Lett. 35, 4039 (2010)
C.T. Lynch, CRC Handbook of Materials Science, vol. 1 (CRC, Boca Raton, 1974), p. 348
M. Baum, S. Polster, M.P.M. Jank, I. Alexeev, L. Frey, M. Schmidt, Efficient laser induced consolidation of nanoparticulate ZnO thin films with reduced thermal budget. Appl. Phys. A 107, 269 (2012)
M. Mahajeri, A. Schneider, M. Baum, T. Rechtenwald, M. Voigt, M. Schmidt, W. Peukert, Production of dispersions with small particle size from commercial indium tin oxide powder for the deposition of highly conductive and transparent films. Thin Solid Films 520, 5741 (2012)
Y. Noguchi, T. Sekitani, T. Yokota, T. Someya, Direct inkjet printing of silver electrodes on organic semiconductors for thin-film transistors with top contact geometry. Appl. Phys. Lett. 93, 043303 (2008)
M. Duocastella, H. Kim, P. Serra, A. Piqué, Optimization of laser printing of nanoparticles suspensions for microelectronic applications. Appl. Phys. A 106, 471 (2012)
G. Legeay, X. Castel, R. Benzerga, J. Pinel, Excimer laser beam/ITO interaction: from laser processing to surface reaction. Phys. Status Solidi C 5, 3248 (2008)
Acknowledgements
The support of the Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft (DFG, Graduiertenkolleg 1161/2) is gratefully acknowledged. Additionally, we are thankful for the support by Evonik Industries AG and also for the production of the particle suspensions by Daniel Kilian at the Institute of Particle Technology at the University of Erlangen. Moreover, the authors gratefully acknowledge funding of the Erlangen Graduate School in Advanced Optical Technologies (SAOT) by the German Research Foundation (DFG) in the framework of the German excellence initiative as well as the support from the Office of Naval Research (ONR).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Baum, M., Kim, H., Alexeev, I. et al. Generation of transparent conductive electrodes by laser consolidation of LIFT printed ITO nanoparticle layers. Appl. Phys. A 111, 799–805 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-013-7646-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-013-7646-y