Abstract
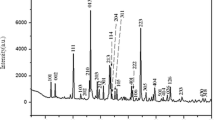
In this paper, we report some physical properties of AgAlP2O7 compound obtained through the standard solid-state reaction technique. AgAlP2O7 has been studied by X-ray diffraction, Raman spectroscopy and impedance spectroscopy. The title compound crystallized at room temperature (T = 300 K) in the monoclinic system with P21/c space group. The electrical properties were studied over a wide range of temperature (440–640 K) in the frequency range of 40 Hz–10 MHz. Study of frequency dependence of AC conductivity suggests that the material obeys the Jonscher’s universal dynamic law. The conductivity is equal to 9.37 × 10−5 Ω cm−1 at 640 K, and it is thermally activated with activation energy of 0.76 eV. The variation of DC conductivity with temperature follows the Arrhenius behavior. The calculated values of s decreased with temperature. This behavior reveals that the conduction mechanism is correlated with barrier hopping. The binding energy W m and the hopping distance R ω were deduced.













Similar content being viewed by others
References
E.J. Baran, R.C. Mercader, A. Massaferro, E. Kremer, Spectrochim. Acta A 60, 1001 (2004)
M.E. Hagerman, K.R. Poppelmeyer, Chem. Mater. 7, 602 (1995)
H. Aono, E. Sugimoto, Y. Sadaoka, N. Amanaka, G. Adaki, Solid State Ionics 62, 309 (1993)
J.P. Boilot, G. Collin, P. Colomban, J. Solid State Chem. 73, 160 (1988)
S. Villain, E. Nigrelli, G. Nihoul, Solid State Ionics 116, 73 (1999)
F. Sanz, C. Parada, J.M. Rojo, C. Ruiz-Valero, R. Saez-Puche, J. Solid State Chem. 145, 604 (1999)
C. Delmas, A. Nadini, J.L. Subeyrou, Solid State Ionics 28, 419 (1988)
A. Clearfeld (ed.), Inorganic ionic exchange materials (CRC Press, Boca Raton, 1982)
S. Arsalane, M. Ziyad, G. Coudurier, J.C. Vedrine, J. Catal. 159, 162 (1996)
Y. Hizhnyi, O. Gomenyuk, S. Nedilko, A. Oliynyk, B. Okhrimenko, V. Bojko, Radiat. Meas. 42, 719 (2007)
Y. Ben Taher, A. Oueslati, M. Gargouri (2014) Ionics. doi: 10.1007/s11581-014-1288-8
Y. Ben Taher, R. Hajji A. Oueslati, M. Gargouri (2014) J. Clust. Sci. doi: 10.1007/s10876-014-0812-3
S. Nasri, M. Megdiche, M. Gargouri, K. Guidara, Ionics (2013). doi:10.1007/s11581-013-0969-z
H.Y.P. Hong, Mater. Res. Bull. 11, 173 (1976)
Goodenough JB (1980) Fast ionic conductors, in UNESCO Course in Materials Science, Erice, Italy
A. Daidouh, M.L. Veiga, C.P. Marin, M. Martinez-Ripoll, Acta Crystallogr. C 53, 167 (1997)
S.R.S. Prabaharan, M.S. Michael, S. Radhakrishna, C. Julien, J. Mater. Chem. 7, 1791 (1997)
J.P. Gamaondes, F. d’Yvoire, A. Boulle, C R Acad. Sci. (Paris) 272, 49 (1971)
J. Belkouch, L. Monceaux, E. Bordes, P. Courtine, Mater. Res. Bull. 30, 149 (1995)
B.S. ParajÓn-Costa, R.C. Mercaderb, E.J. Baran, J. Phys. Chem. Solids 74, 354 (2013)
G.T. Stranford, R.A. Condrate Sr, B.C. Cornilsen, J. Mol. Struct. 73, 231 (1981)
A.R. West, D.C. Sinclair, N. Hirose, J. Electroceram. 1, 65 (1997)
C.G. Koops, Phys. Rev. 83, 121 (1951)
H. Rahmouni, M. Nouiri, R. Jemai, N. Kallel, N. Rzigua, A. Selmi, K. Khirouni, S. Alaya, J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 316, 23 (2007)
Moti Ram, Solid State Sci. 12, 350 (2010)
K. Srinivas, P. Sarah, S.V. Suryanarayana, Bull. Mater. Sci. 26, 247 (2003)
Okutan M, Basaran E, Bakan HI, Yakuphanoglu F (2005) J Phys B 364:300
A.R. Long, Adv. Phys. 31, 553 (1982)
A. Ghosh, Phys. Rev. B 42, 5665 (1990)
M. Pollak, Phil. Mag. 23, 519 (1971)
V. Chithambaram, S. Jerome Das, S. Krishnan, J. Alloys Compd. 509, 4543 (2011)
K.H. Mahmoud, F.M. Abdel-Rahim, K. Atef, Y.B. Saddeek, Curr. Appl. Phys. 11, 55 (2011)
I.A. Niel, Proc SPIE 237, 422 (1980)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ben Taher, Y., Oueslati, A., Maaloul, N.K. et al. Conductivity study and correlated barrier hopping (CBH) conduction mechanism in diphosphate compound. Appl. Phys. A 120, 1537–1543 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-015-9353-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-015-9353-3