Abstract
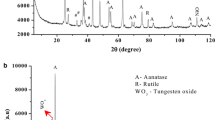
Due to the importance of the WO3–TeO2 binary compounds, the characterization of their compounds plays an important role in the study of the properties of these materials. In this paper, WO3–TeO2 nanostructured binary compound was prepared using chemical reduction method with different precursors. In this study, three synthesis processes (A, B, C) of WO3–TeO2 compounds were studied and the chemical reduction conditions were investigated on binary components. Sodium hydroboride (NaBH4) and hydrazine as reduction agents were used in processes. The nano-powders were characterized by XRD analysis, FE-SEM, EDAX elemental analysis, FTIR and UV–vis spectroscopy. The results of X-ray diffraction showed that, before the annealing in the presence of hydrazine, the peaks of diffraction of TeO2 and WO3 binary compounds were independently formed. The first stage of chemical reduction with sodium borohydrate (NaBH4) in synthesis C led to the formation of a WTe2 compound, and the chemical reduction of the second stage with hydrazine significantly reduced the amount of oxygen in various compounds of WO3–TeO2. In addition, after annealing in the presence of hydrazine, tellurium (Te) phase in XRD patterns are increased. The images of the FE-SEM showed that the morphology of the nanoparticles was uniformly spherical. The energy gap of the nanoparticles varied in the range 3.23–3.92 eV with two separated phases of WO3 and TeO2. The bond structure of the nanoparticle is also studied by FT-IR and UV–vis spectroscopy.













Similar content being viewed by others
References
M.N. Ali, J. Xiong, S. Flynn, J. Tao, Q.D. Gibson, L.M. Schoop, T. Liang, N. Haldolaarachchige, M. Hirschberger, N.P. Ong, R.J. Cava, Large, non-saturating magnetoresistance in WTe2. Lett. Res. Nat. 514, 205 (2014)
H. Zeng, G.-B. Liu, J. Dai, Y.Y.B. Zhu, R. He, Lu Xie, S. Xu, X. Chen, W. Yao, X. Cui. Optical signature of symmetry variations and spin-valley coupling in atomically thin tungsten dichalcogenides. Sci. Rep. (2013). https://doi.org/10.1038/srep01608
X. Qian, J. Liu, L. Fu, J. Li, Quantum spin Hall effect in two-dimensional transition metal dichalcogenides. Mater. Methods 346(6215), 1256815 (2014)
G.R. Bhimanapati, Z. Lin, V. Meunier et al., Recent advances in two-dimensional materials beyond graphene. ACS Nano. (2015). https://doi.org/10.1021/acsnano.5b05556
M. Chhowalla, H.S. Shin, G. Eda, L.-J. Li, K.P. Loh, H. Zhang, The chemistry of two-dimensional layered transition metal dichalcogenide nanosheets. Nat. Chem. 5, 263 (2013)
H. Nurhafizah, M. Rohani, S. Ghoshal, Self-cleanliness of Er3+/Nd3+ Co-doped lithium niobate tellurite glass containing silver nanoparticles. J. Non-Cryst. Solids 455, 62–69 (2017)
N. Berwal, S. Dhankhar, P. Sharma, R.S. Kundu, R. Punia, N. Kishore, Physical, structural and optical characterization of silicate modified bismuth-borate-tellurite glasses. J. Mol. Struct. 1127, 636–644 (2017)
I.Z. Hager, R. El-Mallawany, A. Bulou, Luminescence spectra and optical properties of TeO2–WO3–Li2O glasses doped with Nd, Sm and Er rare earth ions. Phys. B 406, 972–980 (2011)
C. Yu, Z. Yang, A. Huang, Z. Chai, J. Qiu, Z. Song, D. Zhou, Photoluminescence properties of tellurite glasses doped Dy3+ and Eu3+ for the UV and blue converted WLEDs. J. Non-Cryst. Solids 457, 1–8 (2017)
M. Sidkey, R. El Mallawany, A. Abousehly, Y. Saddeek, Relaxation of longitudinal ultrasonic waves in some tellurite glasses. Mater. Chem. Phys. 74(2), 222–229 (2002)
I. Hager, R. El-Mallawany, Preparation and structural studies in the (70-x) TeO2–20WO3–10Li2O–xLn2O3 glasses. J Mater Sci. 45, 897–905 (2010).
M. Celikbiek, A.E. Ersundu, N. Solak, S. Aydin, Investigation on thermal and microstructural characterization of TeO2–WO3 system. J. Alloys Compd. 509, 5646–5654 (2011)
A.N. Moiseev et al., Production and properties of high purity TeO2–ZnO–Na2OBi2O3 and TeO2–WO3–La2O3–MoO3. J. Opt. Mater. 33, 1858–1861 (2011)
V.V. Dorofeev et al., High-purity TeO2–WO3–(La2O3,-Bi2O3). J. Opt. Mater. 33, 1911–1915 (2011)
G. Upender, S. Ramesh, M. Prasad, V.G. Sathe, V.C. Mouli, Optical band gap, glass transition temperature and structural studies of (100-x) TeO2-xAg2OxWO3. J. Alloys Compd. 504, 468–474 (2010)
M. I. Sayyed, S.I. Qashou, Z.Y. Khattari, Radiation shielding competence of newly developed TeO2–WO3 Glasses. J. Alloys Compd. 696, 632–638 (2017)
V.V. Dorofeev, A.N. Moiseev, M.F. Churbanov, G.E. Snopatin, A.V. Chilyasov, I.A. Kraev, A.S. Lobanov, T.V. Kotereva, L.A. Ketkova, A.A. Pushkin, V.V. Gerasimenko, V.G. Plotnichenko, A.F. Kosolapov, E.M. Dianov, High-purity TeO2–WO3–(La2O3, Bi2O3) glasses for fiber-optics. Opt Mater 33, 1911–1915 (2011)
J.H. Pan, W.I. Lee, Preparation of highly ordered cubic mesoporous WO3/TiO2 films and their photocatalytic properties. Chem. Mater. 18, 847 (2006)
K.R. Reyes-Gil, Z.D. Stephens, V. Stavila, D.B. Robinson, Composite WO3/TiO2 nanostructures for high electrochromic activity. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 7, 2202 (2015)
P.S. Archana, A. Gupta, M.M. Yusoff, R. Jose, Tungsten doped titanium dioxide nanowires for high efficiency dye-sensitized solar cells. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 16, 7448–7454 (2014)
B. Pal, B.L. Vijayan, et al., Hydrothermal syntheses of tungsten doped TiO2 and TiO2/WO3 composite using metal oxide precursors for charge storage applications. J. Alloys Compd. (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2018.01.065
V.D.D. Cacho, A.L. Siarkowski, N.I. Morimoto, B.-H.V. Borges, L.R.P. Kassab, Fabrication and characterization of TeO2-ZnO rib waveguides. ECS Trans. 31(1), 225–229 (2010)
M.S. Choi, J.H. Bang, A. Mirzaei, H.W. Kim, S.S. Kim, Modification of SnO2 nanowires with TeO2 branches and their enhanced gas sensing. In: XXXI conference of Eurosensors Paris, September 3–6 (2017)
R. El-Mallawany, Y.S. Rammah, A. El Adawy, Z. Wasses, Optical and thermal properties of some tellurite glasses. Am. J. Opt. Photon. 5(2), 11–18 (2017)
M.Celikbilek,A. E.Ersundu, S. Aydin, Glass Formation and characterization studies in the TeO2–WO3–Na2O System. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 96(5), 1470–1476 (2013)
N. Elkhoshkhany, R. Abbas, R. El-Mallawany, A. J. Fraih, Optical properties of quaternary TeO2–ZnO–Nb2O5–Gd2O3 glasses. Ceram. Int. 40, 14477–14481 (2014)
H. Fares, I. Jlassi, H. Elhouichet, M. Férid. Investigations of thermal, structural and optical properties of tellurite glass withWO3 adding. J. Non-Cryst. Solids 396–397, 1–7 (2014)
J.H. Kim, K.-Y. Yoo, S. Shin, S.H. Youn, J.-H. Moon. Preparation and characterization of 70TeO2-30WO3 glass thin films by radio-frequency magnetron sputtering method. Solid State Phenom. 124–126, 487–490 (2007)
R.R. Kharade, S.S. Mali, S.S. Mohite, V.V. Kondalkar, P.S. Patil, P.N. Bhosale, Hybrid physicochemical synthesis and electrochromic performance of WO3/MoO3 thin films. Electroanalysis 26, 2388–2397 (2014)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shirpay, A., Mohagheghi, M.M.B. The effect of chemical reduction conditions on the structural and optical properties of WO3–TeO2 binary compounds by controlled synthesis from oxide precursors. Appl. Phys. A 124, 627 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-018-2047-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-018-2047-x