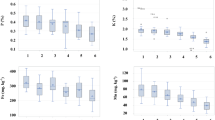
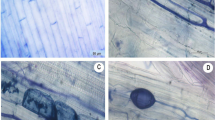
Abstract
Heavy metals (HM) are a unique class of toxicants because they cannot be broken up into nontoxic forms. Excess HM causes stunted growth, upsets mineral nutrition, and affects membrane structure and permeability. High tolerance to HM toxicity is based on reduced metal uptake or increased internal sequestration in a genotype. Arbuscular mycorrhizal (AM) fungi are important rhizospheric microorganisms that occur in metal-contaminated soils and perhaps detoxify the potential effects of metals. The aim of this work was to study the role of the AM fungus Glomus mosseae in the alleviation of cadmium (Cd) and lead (Pb) toxicities in Cajanus cajan (L.) Millsp. (pigeonpea) genotypes. The effects of interactions between Cd (25 and 50 mg/kg) and Pb (500 and 800 mg/kg) on plant dry mass, nitrogen metabolism, and production of phytochelatins (PCs) and glutathione (GSH) were monitored with and without AM fungus in genotypes Sel-85N (relatively tolerant) and Sel-141-97 (sensitive). Cd treatments were more toxic than Pb, and their combinations led to synergistic inhibitions to growth and nitrogen-fixing potential (acetylene reduction activity [ARA]) in both genotypes. However, the effects were less deleterious in Sel-85N than in Sel-141-97. Exposure to Cd and Pb significantly increased the levels of PCs in a concentration- and genotype-dependent manner, which could be directly correlated with the intensity of mycorrhizal infection (MI). Stimulation of GSH production was observed under Cd treatments, although no obvious effects on GSH levels were observed under Pb treatments. The metal contents (Cd, Pb) were higher in roots and nodules when compared with that in shoots, which was significantly reduced in the presence of AM fungi. The results indicated that PCs and GSH might function as potential biomarkers for metal toxicity, and microbial inoculations showed bioremediation potential by helping pigeonpea plants to grow in multimetal contaminated soils.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abou-Shanab RA, Ghanem K, Ghanem N, Al-Kolaibe A (2008) The role of bacteria on heavy metal extraction and uptake by plants growing on multi-metal-contaminated soils. World J Microbiol Biotechnol 24:253–262
Ahmed A, Tajmir-Riahi HA (1993) Interaction of toxic metals ions Cd2+, Hg2+ and Pb2+ with light-harvesting proteins of chloroplast thylakoid membranes: an FTIR spectroscopic study. J Inorg Biochem 40:235–243
Alcantara E, Romera FJ, Canete M, De La Guardia MD (1994) Effects of heavy metals on both induction and function of root Fe (III) reductase in Fe-deficient cucumber (Cucumis sativus L.) plants. J Exp Bot 45:1893–1898
Al-Raddad A (1991) Response of bean, broad bean and chickpea plants to inoculation with Glomus species. Sci Hortic 146:195–200
An YJ (2004) Soil ecotoxicity assessment using cadmium sensitive plants. Environ Sci Technol 127:21–26
Anderson ME (1985) Determination of glutathione and glutathione disulfides in biological samples. Meth Enzymol 113:548–570
Andrade SAL, Abreu CA, Abreu MF, Silveira APD (2004) Influence of lead additions on arbuscular mycorrhiza and Rhizobium symbiosis under soybean plants. Appl Soil Ecol 26:123–131
Andrade SAL, Jorge RA, da Silveira APD (2005) Cadmium effect on the association of jackbean (Canavalia ensiformis) and arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi. Sci Agric 62(4):389–394
Anjum NA, Umar S, Ahmad A, Iqbal M (2008) Responses of components of antioxidant system in moongbean (Vigna radiata L. Wilezek) genotypes to cadmium. Common Soil Sci Plant Anal 39:2469–2483
Azcón R, Perálvarez Mdel C, Roldán A, Barea JM (2009) Arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi, Bacillus cereus and Candida parapsilosis, from a multicontaminated soil alleviate metal toxicity in plants. Microb Ecol 59(4):668–677
Baker AJM, Ewart K, Hendry GAF, Thorpe PC, Walker PL (1990) The evolutionary basis of cadmium tolerance in higher plants. In: 4th international conference on environmental contamination, Barcelona, pp 23–29
Balestrasse KB, Gallego SM, Tomaro ML (2004) Cadmium induced senescence in nodules of soybean (Glycine max. L.) plants. Plant Soil 262:373–381
Balestrasse KB, Gallego SM, Tomaro ML (2006) Oxidation of the enzymes involved in nitrogen assimilation plays an important role in the cadmium-induced toxicity in soybean plants. Plant Soil 284:187–194
Banaszak A, Napieralska A, Wozny A (2001) Inhibition of greening of Lemna minor by Pb2+. Biology 56:111–116
Belimov AA, Safronova VI, Tsyganov VE, Borisov AY, Kozhemyakov AP, Tikhonovich IA, Stepanok VV, Martenson AM, Gianinazzi–Pearson V (2003) Genetic variability in tolerance to cadmium and accumulation of heavy metals in pea (Pisum sativum L.). Euphytica 131:25–35
Bell MJ, Mclaughlin MJ, Wright GC, Cruickshank J (1997) Inter and intra-specific variation in accumulation of cadmium by peanut, soybean, and navybean. Aus J Agr Res 48:1151–1160
Bhargava P, Srivastava AK, Urmil S, Rai LC (2005) Phytochelatin plays a role in UV-B tolerance in N2-fixing cyanobacterium Anabaena doliolum. J Plant Physiol 162:1220–1225
Bidar G, Garcon G, Pruvot C, Dewaele D, Cazier F, Douay F, Shirali P (2007) Behavior of Trifolium repens and Lolium perenne growing in a heavy metal contaminated field: Plant metal concentration and phytotoxicity. Environ Pollut 147:546–553
Bidar G, Pruvot C, Garcon G, Verdin A, Shirali P, Douay F (2009) Seasonal and annual variations of metal uptake, bioaccumulation, and toxicity in Trifolium repens and Lolium perenne growing in a heavy metal-contaminated field. Environ Sci Pollut Res 16:42–53
Blum R, Beck A, Korte A, Stengel A, Letzel T, Lendzian K, Grill E (2007) Function of phytochelatin synthase in catabolism of glutathione-conjugates. Plant J 49:740–749
Boucher N, Carpentier R (1999) Hg2+, Cu2+, and Pb2+ induced changes in photosystem-II photochemical yield and energy storage in isolated thylakoid membranes: a study using simultaneous and photoacoustic measurements. Photosynth Res 59:167–174
Brekken A, Stennes E (2004) Seasonal concentrations of cadmium and zinc in native pasture plants: consequences for grazing animals. Sci Total Environ 326:181–195
Brennan MA, Shelley ML (1999) A model of the uptake, translocation and accumulation of lead (Pb) by maize for the purpose of phytoextraction. Ecol Eng 12:271–297
Burzynski M (1987) The influence of lead and cadmium on the absorption and distribution of potassium, calcium, magnesium and iron in cucumber seedlings. Acta Physiol Plant 9:229–238
Burzynski M, Buczek J (1998) Uptake and assimilation of ammonium ions by cucumber seedlings from solutions with different pH and addition of heavy metals. Acta Soc Bot Pol 67(2):197–200
Carpena RO, Vazquez S, Esteban E, Fernandez-Pascual M, de Felipe MR, Zornoza P (2003) Cadmium-stress in white lupin: effects on nodule structure and functioning. Plant Physiol Biochem 41:911–919
Chen J, Zhou J, Goldsbrough PB (1997) Characterization of phytochelatin synthase from tomato. Physiol Plant 101:165–172
Chen YX, He YF, Yang Y, Yu YL, Zhen SJ, Tian GM, Luo YM, Wong MH (2003) Effect of cadmium on nodulation and N2 fixation of soybean in contaminated soils. Chemosphere 50:781–787
Chen S, Sun T, Chao L, Guo G (2007) Interaction between cadmium, lead and potassium fertilizer (K2SO4) in a soil-plant system. Environ Geochem Health 29:435–446
Clark RB, Zeto SK (2000) Mineral acquisition by arbuscular mycorrhizal plants. J Plant Nutr 23:867–902
Comba ME, Benavides MP, Tomaro ML (1998) Effect of salt stress on antioxidant defence system in soybean root nodules. Aust J Plant Physiol 25:665–671
Czuba M, Kraszewski A (1994) Long term cadmium exposure accelerates oxidant injury: significance of bound/free water states during long-term metal stress. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 29(3):330–348
Dakora FD (1995) A functional relationship between leghemoglobin and nitrogenase based on novel measurements of the two proteins in legume root nodules. Ann Bot 75:49–54
de Andrade SAL, da Silveira APD, Jorge RA, de Abreu MF (2008) Cadmium accumulation in sunflower plants influenced by arbuscular mycorrhiza. Int J Phytoremed 10(1):1–13
Del Longo OT, Gonzalez CA, Pastori GM, Tripps VS (1993) Antioxidant defences under hyperoxygenic and hyperosmotic conditions in leaves of two lines of maize with differential sensitivity to drought. Plant Cell Physiol 34:1023–1028
Del Val C, Barea JM, Azcon-Aguilar C (1999) Diversity of arbuscular mycorrhizal fungus populations in heavy metal contaminated soils. Appl Environ Microbiol 65:718–723
Dixit V, Pandey V, Shyam R (2001) Differential oxidative responses to cadmium in roots and leaves of pea (Pisum sativum L. cv. Azad). J Exp Bot 52:1101–1109
Dong J, Wu FB, Zhang GP (2006) Influence of cadmium on antioxidant capacity and four microelement concentrations in tomato seedlings (Lycopersicon esculentum). Chemosphere 64:1659–1666
Duman F, Cicek M, Sezen G (2007) Seasonal changes of metal accumulation and distribution in common club rush (Schoenoplectus lacustris) and common reed (Phragmites australis). Ecotoxicology 16:457–463
Eun SO, Youn HS, Lee Y (2000) Lead disturbs microtubule organization in the root meristem of Zea mays. Physiol Plant 110:357–365
Foyer CH, Lopez-Delgado H, Dat JF, Scott IM (1997) Hydrogen peroxide and glutathione-associated mechanisms of acclamatory stress tolerance and signaling. Physiol Plant 100:241–254
Freedman JH, Ciriolo MR, Peisach J (1989) The role of glutathione in copper metabolism and toxicity. J Biol Chem 264:5598–5605
Galli U, Schuepp H, Brunold C (1994) Heavy metal binding by mycorrhizal fungi. Physiol Plant 92:364–368
Gaur A, Adholeya A (2004) Prospects of arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi in phytoremediation of heavy metal contaminated soils. Curr Sci 86:528–534
Gisbert C, Ros R, de Haro A, Walker DJ, Bernal MP, Serrano R, Navarro-Avino J (2003) A plant genetically modified that accumulates Pb is especially promising for phytoremediation. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 303:440–445
Gong H, Zhu X, Chen K, Wang S, Zhang C (2005) Silicon alleviates oxidative damage of wheat plants in pots under drought. Plant Sci 169:313–321
Grill E, Winnacker EL, Zenk MH (1987) Phytochelatins, a class of heavy metal binding peptides from plants are functionally analogous to metallothioneins. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 84:439–443
Hagemeyer J, Kahle H, Breckle SW, Waisel Y (1986) Cadmium in Fagus sylvatica L. trees and seedlings: leaching, uptake and interconnection with transpiration. Water Air Soil Pollut 29:347–359
Hajduch M, Rakwal R, Agrawal GK, Yonekura M, Petrova A (2001) High-resolution two-dimensional electrophoresis separation of proteins from metal-stressed rice (Oryza sativa L.) leaves: drastic reduction/fragmentation of ribulose-1,5-biphosphate carboxylase/oxygenase and induction of stress-related proteins. Electrophoresis 22:2824–2831
Hassan JM, Wang Z, Zhang G (2005) Sulphur alleviates growth inhibition and oxidative stress caused by cadmium toxicity in rice. J Plant Nutr 28:1785–1800
Hildebrandt U, Kaldorf M, Bothe H (1999) The zinc violet and its colonization by arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi. J Plant Physiol 154:709–717
Inouhe M, Ninomiya S, Tohoyama H, Joho M, Murayama T (1994) Differential characteristics of root in the cadmium-tolerance and Cd-binding complex formation between mono- and dicotyledonous plants. J Plant Res 107:201–207
Jabeen R, Ahmad A, Iqbal M (2009) Phytoremediation of heavy metals: physiological and molecular mechanisms. Bot Rev 75:339–364
Jamal A, Ayub N, Usman M, Khan AG (2002) Arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi enhance zinc and nickel uptake from contaminated soil by soybean and lentil. Int J Phytorem 4:205–221
John R, Gadgil K, Ahmad P, Sharma S (2008) Effect of cadmium and lead on growth, biochemical parameters and uptake in Lemna polyrrhiza L. Plant Soil Environ 54(6):262–270
Joner EJ, Leyval C (1997) Uptake of 109Cd by roots and hyphae of a Glomus mosseae/Trifolium subterraneum mycorrhiza from soil amended with high and low concentrations of cadmium. New Phytol 135:352–360
Joner EJ, Briones R, Leyval C (2000) Metal-binding capacity of arbuscular mycorrhizal mycelium. Plant Soil 226:227–234
Kahle H (1993) Response of roots of trees to heavy metals. Environ Exp Bot 33:99–119
Kang SH, Singh S, Kim JY, Lee W, Mulchandani A, Chen W (2007) Bacteria metabolically engineered for enhanced phytochelatin production and cadmium accumulation. Appl Environ Microbiol 73:6317–6320
Khade SW, Adholeya A (2007) Feasible bioremediation through arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi imparting heavy metal tolerance: a retrospective. Bioremed J 11:1–33
Kim YY, Yang YY, Lee Y (2002) Pb and Cd uptake in rice roots. Physiol Plant 116:368–372
Kunert KJ, Foyer CH (1993) Thiol/disulfide exchange in plants. In: De Kok LJ (ed) Sulphur nutrition and assimilation in higher plants. SPB Academic Publishing, The Hague, pp 139–151
Labri A, Morales F, Abadia A, Gogorcena Y, Lucena JJ, Abadia J (2002) Effects of Cd and Pb in sugarbeet plants grown in nutrient solution: induced Fe deficiency and growth inhibition. Funct Plant Biol 29:1453–1464
Li J, Guo J, Xu W, Ma M (2006) Enhanced cadmium accumulation in transgenic tobacco expressing the phytochelatin synthase gene of Cynodon dactylon L. J Integr Plant Biol 48:928–937
Lima AI, Pereria SI, Figueira EM, Caldeira GC, Caldiera HD (2006) Cadmium detoxification in roots of Pisum sativum seedlings: relationship between toxicity levels, thiol pool alterations and growth. Environ Exp Bot 55:149–162
Lin RZ, Wang XR, Luo Y, Du WC, Guo HY, Yin DQ (2007) Effects of soil cadmium on growth, oxidative stress and antioxidant system in wheat seedlings (Triticum aestivum L.). Chemosphere 69:89–98
LiQin C, YiFei G, LiMin Y, QinQuan W (2008) Synergistic defensive mechanism of phytochelatins and antioxidative enzymes in Brassica chinensis L. against Cd stress. Chin Sci Bull 53(10):1503–1511
Lopez-Millan A, Sagardoy R, Solonas M, Abadia A, Abadia J (2009) Cadmium toxicity in tomato (Lycopersicon esculentum) plants grown in hydroponics. Environ Exp Bot 65:376–385
Lozano-Rodriguez E, Hernandez LE, Bonay P, Carpena-Ruiz RO (1997) Distribution of cadmium in shoot and root tissues of maize and pea plants: physiological disturbances. J Exp Bot 306:123–128
Maitani T, Kubota H, Sato K, Yamada T (1996) The composition of metals bound to class III metallothionein (phytochelatin and its desglycyl peptide) induced by various metals in root cultures of Rubia tinctorum. Plant Physiol 110:1145–1150
May MJ, Vernoux T, Leaver C, Van-Montagu M, Inze D (1998a) Glutathione homeostatis in plants: implications for environmental sensing and plant development. J Exp Bot 49:649–667
May MJ, Vernoux T, Sanchez-Fernandez R, Van Montagu M, Inze D (1998b) Evidence for posttranscriptional activation of γ-glutamylcysteine synthetase during plant stress responses. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 95:12049–12054
Mazen AMA (1995) Assessment of heavy metal accumulation and performance of some physiological parameters in Zea mays L. and Vicia faba L. grown on soil amended by sewage sludge resulting from sewage water treatment in the state of Qatar. Qatar Univ Sci J 15:353–359
Meharg AA, Cairney JWG (2000) Co-evolution of mycorrhiza symbionts and their host to metal contaminated environments. Adv Ecol Res 30:69–112
Miranda MG, Ilangiovan K (1996) Uptake of lead by Lemna gibba L. influence on specific growth rate and basic biochemical changes. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 56:1000–1007
Mishra A, Choudhari MA (1998) Amelioration of lead and mercury effects on germination and rice seedling growth by antioxidants. Biol Plant 41:469–473
Mishra S, Srivastava S, Tripathi RD, Govindarajan R, Kuriakose SV, Prasad MN (2006) Phytochelatin synthesis and response of antioxidants during cadmium stress in Bacopa monnieri L. Plant Physiol Biochem 44(1):25–37
Mobin M, Khan NA (2007) Photosynthetic activity, pigment composition and antioxidative response of two mustard (Brassica juncea) cultivars differing in photosynthetic capacity subjected to cadmium stress. J Plant Physiol 164:601–610
Munzuroglu O, Geckil H (2002) Effects of metals on seed germination, root elongation, and coleoptiles and hypocotyls growth in Triticum aestivum and Cucumis sativus. Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 43:203–213
Nikiforova V, Freitag J, Kempa S, Adamik M, Hesse H, Hoefgen R (2003) Transcriptome analysis of sulphur depletion in Arabidopsis thaliana: interlacing of biosynthetic pathways provides response specificity. Plant J 33:633–650
Noctor G, Gomez LA, Vanacker H, Foyer CH (2002) Interactions between biosynthesis, compartmentation and transport in the control of glutathione homeostasis and signaling. J Exp Bot 53:1283–1304
Obroucheva NV, Bystrova EI, Ivanov VB, Anupova OV, Seregin IV (1998) Root growth responses to lead in young maize seedlings. Plant Soil 200:55–61
Ouariti O, Boussama N, Zarrouk M, Cherif A, Ghorbal MH (1997) Cadmium and copper induced changes in tomato membrane lipids. Phytochemistry 45:1343–1350
Paivoke AEA (2002) Soil lead alters phytase activity and mineral nutrient balance of Pisum sativum. Environ Exp Bot 48:61–73
Pal R, Rai JPN (2010) Phytochelatins: peptides involved in heavy metal detoxification. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 160:945–963
Paradiso A, Berardino R, de Pinto MC, Sanita di Toppi L, Storelli MM, Tommasi F, Gara LG (2008) Increase in ascorbate- glutathione metabolism as local and precocious systemic responses induced by cadmium in durum wheat plants. Plant Cell Physiol 49(3):362–374
Pawlowska TE, Blaszkowski J, Ruhling A (1996) The mycorrhizal status of plants colonizing a calamine spoil mound in southern Poland. Mycorrhiza 6:499–505
Phillips JM, Hayman DS (1970) Improved procedures for clearing and staining parasitic and vesicular-arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi for rapid assessment of infection. Trans Br Mycol Soc 55:158–161
Pitschke A, Forzani C, Hirt H (2006) Reactive oxygen species signaling in plants. Antioxid Redox Signal 8:1757–1764
Plenchette C, Furlan V, Fortin JA (1983) Responses of endomycorrhizal plants grown in a calcined montmollironite clay to different levels of soluble phosphorus. II. Effect on nutrient uptake. Can J Bot 61:1384–1391
Poskuta JW, Parys E, Romanowaska E (1996) Toxicity of lead to photosynthesis, accumulation of chlorophyll, respiration and growth of Chlorella pyrenoidosa. Protective role of dark respiration. Acta Physiol Plant 18:165–171
Prasad MNV (1995) Cadmium toxicity and tolerance in vascular plants. Environ Exp Bot 35:525–545
Rabie GH (2005) Contribution of arbuscular mycorrhizal fungus to red kidney and wheat plants tolerance grown in heavy metal-polluted soil. Afr J Biotechnol 4(4):332–345
Rashid A, Camm EL, Ekramoddoullah KM (1994) Molecular mechanism of action of Pb and Zn2+ on water oxidizing complex of photosystem II. FEBS Lett 350:296–298
Repetto O, Bestel-Corre G, Dumas-Gaudot E, Berta G, Gianinazzi-Pearson V, Gianinazzi S (2003) Targeted proteomics to identify cadmium-induced protein modification in Glomus mosseae-inoculated pea roots. New Phytol 157:555–567
Rivera-Becerril F, Calantzis C, Turnau K, Caussanel JP, Belimov AA, Gianinazzi S, Strasser JR, Gianinazzi-Pearson V (2002) Cadmium accumulation and buffering of cadmium-induced stress by arbuscular mycorrhiza in three Pisum sativum L. genotypes. J Exp Bot 371:1177–1185
Rivera-Becerril F, van Tuinen D, Martin-Laurent F, Metwally A, Dietz KJ, Gianinazzi S, Gianinazzi-Pearson V (2005) Molecular changes in Pisum sativum L. roots during arbuscular mycorrhiza buffering of cadmium stress. Mycorrhiza 16:51–60
Rivetta A, Negrini N, Cocucci M (1997) Involvement of Ca2+ calmodulin in Cd2+ toxicity during the early phases of radish (Raphanus sativus L.) seed germination. Plant Cell Environ 20:600–608
Robinson NJ, Urwin PE, Robinson PJ, Jackson PJ (1994) Gene expression in relation to metal toxicity and tolerance. In: Basra AJ (ed) Stress induced gene expression in plants. Harwood Academic Publishers, Amsterdam, pp 209–248
Rodriguez-Ortiz JC, Valdez-Cepeda RD, Lara-Mireles JL, Rodriguez-Fuentes H, Vazquez-Alvarado RE, Magallanes-Quintanar R, Garcia-Hernandez JL (2006) Soil nitrogen fertilization effects on phytoextraction of cadmium and lead by tobacco (Nicotiana tabaccum L.). Biorem J 10(3):105–114
Romanowsk E, Igamberdiev U, Parys E, Gardestron P (2002) Stimulation of respiration by Pb2+ in detached leaves and mitochondria of C3 and C4 plants. Physiol Plant 116:148–154
Saito K, Kurosawa M, Tatsuguchi K, Takagi Y, Murakoshi I (1994) Modulation of cysteine biosynthesis in the chloroplasts of transgenic tobacco overexpressing cysteine synthesis (O-acetylserine(thiol)lyase). Plant Physiol 106:887–895
Salt DEM, Blaylock NP, Kumar V, Dushenkov BD, Ensley I, Chet RI (1995) Phytoremediation: a novel strategy for the removal of toxic metals from the environment using plants. Biotechnology 13:468–474
Sanita di Toppi L, Gabbrielli R (1999) Response of cadmium in higher plants. Environ Exp Bot 41:105–130
Saxena KB (2008) Genetic improvement of pigeon pea—a review. Trop Plant Biol 1:159–178
Scheublin TR, van der Heijden MGA (2006) Arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi colonize non-fixing nodules of several legume species. New Phytol 172:732–738
Seregin IV, Ivanov VB, Shpigun LK (2003) Distribution and toxic effects of cadmium and lead on maize roots. Russ J Plant Physiol 51(4):525–533
Shalaby AM (2003) Responses of arbuscular mycorrhizal fungal spores isolated from heavy metal-polluted and unpolluted soil to Zn, Cd, Pb and their interactions in vitro. Pak J Biol Sci 6(16):1416–1422
Shvaleva A, de La Peña TC, Rincón A, Morcillo CN, de la Torre VSG, Lucas MM, Pueyo JJ (2010) Flavodoxin overexpression reduces cadmium-induced damage in alfalfa root nodules. Plant Soil 326:109–121
Singh S, Anjum NA, Khan NA, Nazar R (2008) Metal-binding peptides and antioxidant defence system in plants: significance in cadmium tolerance. In: Khan NA, Singh S (eds) Abiotic stress and plant responses. IK International, New Delhi, pp 159–189
Singhal RK, Anderson ME, Meister A (1987) Glutathione, a first line defence against cadmium toxicity. FASEB J 1:220–223
Smeets K, Cuypers A, Lambrechts A, Semane B, Hoet P, Van Laere A, Vangronsveld J (2005) Induction of oxidative stress and antioxidant mechanisms in Phaseolus vulgaris after Cd application. Plant Physiol Biochem 43:437–444
Szalai G, Kellos T, Galiba G, Kocsy G (2009) Glutathione as an antioxidant and regulatory molecule in plants under abiotic stress conditions. J Plant Growth Regul 28:66–80
Ting YP, Lawson F, Prince IG (1991) Uptake of cadmium and zinc by alga Chlorella vulgaris: multiion situation. Biotechnol Bioeng 37:445–455
Trivedi S, Erdei L (1992) Effects of cadmium and lead on the accumulation of Ca2+ and K+ and on the influx and translocation of K+ in wheat of low and high K+ status. Physiol Plant 84:94–100
Tudoreanu L, Phillips CJC (2004) Modeling cadmium uptake and accumulation in plants. Adv Agron 84:121–157
Turnau K, Kottke I, Oberwinkler F (1993) Element localization in mycorrhizal roots of Pteridium aquinilium L. Kuhn collected from experimental plots treated with cadmium dust. New Phytol 123:313–324
Uveges JL, Corbett AL, Mal TK (2002) Effects of Pb contamination on the growth of Lythrum salicaria. Environ Pollut 120:319–323
Van der Maesen LJG (1980) India is the native home of the pigeonpea. In: Arends JC, Boelama G, de Grant CT, Leeuwenberg A (eds) Libergratulatorious in Honerem HCD de Wit. Agricultural University Miscellaneous Paper 19. Wageningen, The Netherlands, pp 257–262
Vange V, Hevchand I, Vandvik V (2004) Does seed mass and family affect germination and juvenile performance in Knautia arvensis? A study using failure time methods. Acta Oecol 25(3):169–178
Vassilev A (2002) Physiological and agroecological aspects of cadmium interactions with barley plants: an overview. J Central Eur Agric 4:65–75
Vivas A, Azcon R, Biro B, Barea JM, Ruiz-Lozano JM (2003) Influence of bacterial strains isolated from lead-polluted soil and their interactions with arbuscular mycorrhizae on the growth of Trifolium pretense L. under lead toxicity. Can J Microbiol 49:577–588
Vogel-Mikus K, Drobne D, Regvar M (2005) Zn, Cd and Pb accumulation and arbuscular mycorrhizal colonization of pennycress Thalaspi praecox Wulf. (Brassicaceae) from the vicinity of a lead mine and smelter in Slovenia. Environ Pollut 133:233–242
Vosatka M, Rydlova J, Sudova R, Vohnik M (2006) Mycorrhizal fungi as helping agents in phytoremediation of degraded and contaminated soils. In: Mackova M, Dowling DN, Maeck T (eds) Phytoremediation Rhizoremediation, 1st ed. Springer-Verlag, Berlin, pp 237–257
Walker WM, Miller JE, Hassett JJ (1977) Effect of lead and cadmium upon the calcium, magnesium, potassium and phosphorus concentration in young corn plants. Soil Sci 124:145–151
Wang X, Zhou QX (2003) Distribution of forms for cadmium, lead, copper and zinc in soil land its influences by modifier. J Agr Environ Sci 22:541–545
Wang FY, Lin XG, Yin R (2007) Effect of arbuscular mycorrhizal fungal inoculation on heavy metal accumulation of maize grown in a naturally contaminated soil. Int J Phytorem 9(4):345–353
Wei SH, Zhou QX (2004) Identification of weed species with hyperaccumulative characteristics of heavy metals. Prog Nat Sci 14:495–503
Weissenhorn I, Leyval C (1995) Root colonization of maize by a Cd-sensitive and a Cd-tolerant Glomus mosseae and cadmium uptake in sand culture. Plant Soil 175:233–238
Wierzbicka M (1994) Resumption of mitotic activity in Allium cepa root tips during treatment with lead salts. Environ Exp Bot 34:173–180
Yen CL, Mar MH, Zeisel SH (1999) Choline deficiency-induced apoptosis in PC12 cells is associated with diminished membrane phosphatidylcholine and activation of a caspase. FASEB J 13:135–142
Younis M (2007) Responses of Lablab purpureus-Rhizobium symbiosis to heavy metals in pot and field experiments. World J Agric Sci 3(1):111–122
Yu X, Cheng J, Wong MH (2005) Earthworm-mycorrhiza interaction on Cd uptake and growth of ryegrass. Soil Biol Biochem 37:195–201
Zenk MH (1996) Heavy metal detoxification in higher plants: a review. Gene 179:21–30
Zornoza P, Vazquez S, Esteban E, Fernandez-Pascual M, Carpena R (2002) Cadmium-stress in nodulated white lupin: strategies to avoid toxicity. Plant Physiol Biochem 40:1003–1009
Acknowledgment
The financial support provided by the University Grant Commission, New Delhi, India, is gratefully acknowledged.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Garg, N., Aggarwal, N. Effects of Interactions Between Cadmium and Lead on Growth, Nitrogen Fixation, Phytochelatin, and Glutathione Production in Mycorrhizal Cajanus cajan (L.) Millsp.. J Plant Growth Regul 30, 286–300 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00344-010-9191-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00344-010-9191-7