Abstract
Submarine groundwater discharge in coastal settings can massively modify the hydraulic and geochemical conditions of the seafloor. Resulting local anomalies in the morphology and physical properties of surface sediments are usually explored with seismo-acoustic imaging techniques. Controlled source electromagnetic imaging offers an innovative dual approach to seep characterization by its ability to detect pore-water electrical conductivity, hence salinity, as well as sediment magnetic susceptibility, hence preservation or diagenetic alteration of iron oxides. The newly developed electromagnetic (EM) profiler Neridis II successfully realized this concept for a first time with a high-resolution survey of freshwater seeps in Eckernförde Bay (SW Baltic Sea). We demonstrate that EM profiling, complemented and validated by acoustic as well as sample-based rock magnetic and geochemical methods, can create a crisp and revealing fingerprint image of freshwater seepage and related reductive alteration of near-surface sediments. Our findings imply that (1) freshwater penetrates the pore space of Holocene mud sediments by both diffuse and focused advection, (2) pockmarks are marked by focused freshwater seepage, underlying sand highs, reduced mud thickness, higher porosity, fining of grain size, and anoxic conditions, (3) depletion of Fe oxides, especially magnetite, is more pervasive within pockmarks due to higher concentrations of organic and sulfidic reaction partners, and (4) freshwater advection reduces sediment magnetic susceptibility by a combination of pore-water injection (dilution) and magnetite reduction (depletion). The conductivity vs. susceptibility biplot resolves subtle lateral litho- and hydrofacies variations.

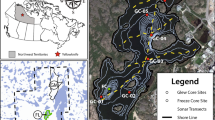
Freshwater advection within pockmarks reduces the magnetic susceptibility of near-surface Eckernförde Bay sediments, traced by electromagnetic mapping complemented by rock magnetic and geochemical methods











Similar content being viewed by others
References
Archie GE (1942) The electrical resistivity log as an aid in determining some reservoir characteristics. J Petrol Technol 5:1–8
Benech C, Marmet E (1999) Optimum depth of investigation and conductivity response rejection of the different electromagnetic devices measuring apparent magnetic susceptibility. Archaeol Prospection 6:31–45
Berner RA (1981) A new geochemical classification of sedimentary environments. J Sed Petrol 51:359–365. doi:10.1306/212F7C7F-2B24-11D7-8648000102C1865D
Bloemendal J, King JW, Hall FR, Doh SJ (1992) Rock magnetism of late Neogene and Pleistocene deep-sea sediments: relationship to sediment source, diagenetic processes, and sediment lithology. J Geophys Res 97:4361–4375. doi:10.1029/91JB03068
Booth CA, Walden J, Neal A, Smith JP (2005) Use of mineral magnetic concentration data as a particle size proxy: a case study using marine, estuarine and fluvial sediments in the Carmarthen Bay area, South Wales, U.K. Sci Total Environ 347:241–253. doi:10.1029/91JB03068
Burnett WC, Taniguchi M, Oberdorfer J (2001) Measurement and significance of the direct discharge of groundwater into the coastal zone. J Sea Res 46:109–116. doi:10.1016/S1385-1101(01)00075-2
Burnett WC, Aggarwal PK, Aureli A et al (2006) Quantifying submarine groundwater discharge in the coastal zone via multiple methods. Sci Total Environ 367:498–543. doi:10.1016/j.scitotenv.2006.05.009
Day R, Fuller M, Schmidt VA (1977) Hysteresis properties of titanomagnetites: grain-size and compositional dependence. Phys Earth Planet Interiors 13:260–266. doi:10.1016/0031-9201(77)90108-X
Dekkers MJ, Schoonen MAA (1996) Magnetic properties of hydrothermally synthesized greigite (Fe3S4) - I. Rock magnetic parameters at room temperature. Geophys J Int 126:360–368
Dillon M, Bleil U (2006) Rock magnetic signatures in diagenetically altered sediments from the Niger deep-sea fan. J Geophys Res 111:B03105. doi:10.1029/2004JB003540
Dunlop DJ, Özdemir Ö (1997) Rock magnetism: fundamentals and frontiers. Cambridge Studies in Magnetism. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge
Ellwood BB, Balsam WL, Roberts HH (2006) Gulf of Mexico sediment sources and sediment transport trends from magnetic susceptibility measurements of surface samples. Mar Geol 230:237–248. doi:10.1016/j.margeo.2006.05.008
Emiroglu S, Petersen N, Rey D (2004) Magnetic properties of sediment in the Ría de Arousa (Spain): dissolution of iron oxides and formation of iron sulphides. Phys Earth Planet Interiors 29:947–959. doi:10.1016/j.pce.2004.03.012
Evans ME, Heller F (2003) Environmental magnetism. Principles and applications of enviromagnetics. Academic, New York
Farquharson CG, Oldenburg DW, Routh PS (2003) Simultaneous 1D inversion of loop–loop electromagnetic data for magnetic susceptibility and electrical conductivity. Geophysics 68:1857–1869
Fu Y, von Dobeneck T, Franke C, Heslop D, Kasten S (2008) Rock magnetic identification and geochemical process models of greigite formation in Quaternary marine sediments from the Gulf of Mexico (IODP Hole U1319A). Earth Planet Sci Lett 275:233–245. doi:10.1016/j.epsl.2008.07.034
Funk JA, von Dobeneck T, Reitz A (2004) Integrated rock magnetic and geochemical quantification of redoxomorphic iron mineral diagenesis in Late Quaternary sediments from the Equatorial Atlantic. In: Wefer G, Mulitza S, Ratmeyer V (eds) The South Atlantic in the Late Quaternary: reconstruction of material budget and current systems. Springer, Berlin Heidelberg, pp 237–260
Gay SP (2004) Glacial till: a troublesome source of near-surface magnetic anomalies. Lead Edge 23:542–547
Harrington PK (1985) Formation of pockmarks by pore-water escape. Geo-Mar Lett 5(3):193–197. doi:10.1007/BF02281638
Hoefel FG, Evans RL (2001) Impact of low salinity pore water on seafloor electromagnetic data: a means of detecting submarine ground water discharge? Estuarine Coastal Shelf Sci 52:179–189. doi:10.1006/ecss.2000.0718
Housen BA, Moskowitz BM (2006) Depth distribution of magnetofossils in near-surface sediments from the Blake/Bahama Outer Ridge, western North Atlantic Ocean, determined by low-temperature magnetism. J Geophys Res 111:G01005. doi:10.1029/2005JG000068
Housen BA, Musgrave RJ (1996) Rock-magnetic signature of gas hydrates in accretionary prism sediments. Earth Planet Sci Lett 139:509–519. doi:10.1016/0012-821X(95)00245-8
Hovland M (2003) Geomorphological, geophysical, and geochemical evidence of fluid flow through the seabed. J Geochem Explor 78(79):287–291. doi:10.1016/S0375-6742(03)00091-8
Hussenoeder SA, Tivey MA, Schouten H (1995) Direct inversion of potential fields from an uneven track with application to the Mid-Atlantic Ridge. Geophys Res Lett 22:3131–3134. doi:10.1029/95GL03326
Jensen JB, Kuijpers A, Bennike O, Laier T, Werner F (2002) New geological aspects for freshwater seepage and formation in Eckernförde Bay, western Baltic. Cont Shelf Res 22:2159–2173. doi:10.1016/S0278-4343(02)00076-6
Karpen V, Thomsen L, Suess E (2004) A new ‘schlieren’ technique application for fluid flow visualization at cold seep sites. Mar Geol 204:145–159. doi:10.1016/S0025-3227(03)00370-0
King JW, Channell JET (1991) Sedimentary magnetism, environmental magnetism, and magnetostratigraphy. Rev Geophys 29:358–370
King J, Banerjee SK, Marvin J, Özdemir Ö (1982) A comparison of different magnetic methods for determining the relative grain size of magnetite in natural materials: some results from lake sediments. Earth Planet Sci Lett 59:404–419. doi:10.1016/0012-821X(82)90142-X
Larrasoaña JC, Roberts AP, Musgrave RJ, Gracia E (2007) Diagenetic formation of greigite and pyrrhotite in gas hydrate marine sedimentary systems. Earth Planet Sci Lett 261:350–366. doi:10.1016/j.epsl.2007.06.032
Maher BA, Thompson R (1999) Quaternary climates, environments and magnetism. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge
Marczinek S, Piotrowski JA (2002) Groundwater transport and composition in the Eckernforder Bay catchment area, Schleswig-Holstein. Grundwasser 7(2):101–107
Moore WS (1996) Large groundwater inputs to coastal waters revealed by 226Ra enrichment. Nature 380:612–614
Müller H (2010) Characterization of marine near-surface sediments by electromagnetic profiling. Dissertation, Universität Bremen, Bremen
Nehmiz W (2007) Umweltmagnetische und geochemische Untersuchungen an Grundwasseraustritten in der Eckernförder Bucht. Diplomarbeit, Universität Bremen, Bremen
Novosel I, Spence GD, Hyndman RD (2005) Reduced magnetization produced by increased methane flux at a gas hydrate vent. Mar Geol 216:265–274. doi:10.1016/j.margeo.2005.02.027
Oldfield F, Yu L (1994) The influence of particle-size variations on the magnetic properties of sediments from the N.E. Irish Sea. Sedimentology 41:1093–1108
Rey D, Mohamed KJ, Bernabeu A, Rubio B, Vilas F (2005) Early diagenesis of magnetic minerals in marine transitional environments: geochemical signatures of hydrodynamic forcing. Mar Geol 215:215–236. doi:10.1016/j.margeo.2004.12.001
Rey D, Müller H, Rubio B (2008) Using electromagnetic sensors to estimate physical properties and environmental quality of surface sediments in the marine environment. Preliminary results. Geotemas 10:651–654
Roberts AP, Weaver R (2005) Multiple mechanisms of remagnetization involving sedimentary greigite (Fe3S4). Earth Planet Sci Lett 231:263–277. doi:10.1016/j.epsl.2004.11.024
Rowan CJ, Roberts AP (2006) Magnetite dissolution, diachronous greigite formation, and secondary magnetizations from pyrite oxidation: unravelling complex magnetizations in Neogene marine sediments from New Zealand. Earth Planet Sci Lett 241:119–137. doi:10.1016/j.epsl.2005.10.017
Rowan CJ, Roberts AP, Broadbent T (2009) Reductive diagenesis, magnetite dissolution, greigite growth and paleomagnetic smoothing in marine sediments: a new view. Earth Planet Sci Lett 277:223–235. doi:10.1016/j.epsl.2008.10.016
Schlüter M, Sauter EJ, Andersen CE, Dahlgaard H, Dando PR (2004) Spatial distribution and budget for submarine groundwater discharge in Eckernforde Bay (western Baltic Sea). Limnol Oceanogr 49:157–167
Seeberg-Elverfeldt J, Schlüter M, Feseker T, Kölling M (2005) Rhizon sampling of porewaters near the sediment-water interface of aquatic systems. Limnol Oceanogr 3:361–371
Siemon B (2006) Airborne techniques. In: Kirsch R (ed) Groundwater geophysics—A tool for hydrogeology. Springer, Berlin Heidelberg, pp 348–362
Steuer A, Siemon B, Auken E (2007) A comparison of helicopter-borne electromagnetics in frequency- and time-domain at the Cuxhaven valley in Northern Germany. J Appl Geophys 67:194–205
Thompson R, Oldfield F (1986) Environmental magnetism. Allen & Unwin, Sydney
Thompson R, Bloemendal J, Dearing JA (1980) Environmental applications of magnetic measurements. Science 207:481–486
Tivey MA, Johnson HP (2002) Crustal magnetization reveals subsurface structure of Juan de Fuca Ridge hydrothermal vent fields. Geology (Boulder, CO) 30:979–982
Tribovillard N, Averbuch O, Bialkowski A, Deconinck JF (2002) Early diagenesis of marine organic-matter and magnetic properties of sedimentary rocks: the role of iron limitation and organic-matter source organisms. Bull Soc Géol France 173:295–306
Van Dongen BE, Roberts AP, Schouten S, Jiang WT, Florindo F, Pancost RD (2007) Formation of iron sulfide nodules during anaerobic oxidation of methane. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 71:5155–5167. doi:10.1016/j.gca.2007.08.019
Verosub KL, Roberts AP (1995) Environmental magnetism: past, present, and future. J Geophys Res 100:2175–2192
Verwey EJW (1939) Electronic conduction of magnetite (Fe3O4) and its transition point at low temperatures. Nature 144:327–328
Whiticar MJ (2002) Diagenetic relationships of methanogenesis, nutrients, acoustic turbidity, pockmarks and freshwater seepages in Eckernförde Bay. Mar Geol 182:29–53. doi:10.1016/S0025-3227(01)00227-4
Whiticar MJ, Werner F (1981) Pockmarks: submarine vents of natural gas or freshwater seeps? Geo-Mar Lett 1(3/4):193–199. doi:10.1007/BF02462433
Won IJ, Huang H (2004) Magnetometers and electro-magnetometers. Lead Edge 23:448–451
Won IJ, Keiswetter DA, Hanson DR, Novikova E, Hall TM (1997) GEM-3: a monostatic broadband electromagnetic induction sensor. J Environ Eng Geophys 2:53–64
Zhang W, Yu L, Hutchinson SM (2001) Diagenesis of magnetic minerals in the intertidal sediments of the Yangtze Estuary, China, and its environmental significance. Sci Total Environ 266:160–175. doi:10.1016/S0048-9697(00)00735-X
Acknowledgements
Four survey campaigns with the RB Polarfuchs in the Western Baltic Sea were granted by IfM GEOMAR in Kiel and Center for Marine Environmental Sciences (MARUM) at the University of Bremen. We thank the ship’s crew members H. Meier and H. Schramm for their great support. We also thank C. Hilgenfeldt and T. Frederichs for technical assistance, and D. Rey, B. Rubio, G. Bohrmann, F. Abegg, I.J. Won, B. SanFilipo, and M. Schlüter for thoughtful suggestions and comments. The authors would like to thank A. Roberts and B. Housen for helpful comments in their detailed reviews of the manuscript. Research, development, and implementation of the electromagnetic seafloor profiler Neridis II was jointly funded by MARUM incentive funding and two research grants of the Marine and Environmental Geology Group (MARGO) at the University of Vigo (Spain), PGDIT06TAM31201PR (XUGA) and CTM 2007-61227/MAR (micinn). This work contributes to MARUM projects C1 and SD2 on sediment dynamics.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Müller, H., von Dobeneck, T., Nehmiz, W. et al. Near-surface electromagnetic, rock magnetic, and geochemical fingerprinting of submarine freshwater seepage at Eckernförde Bay (SW Baltic Sea). Geo-Mar Lett 31, 123–140 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00367-010-0220-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00367-010-0220-0