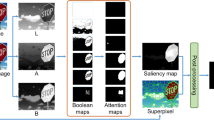
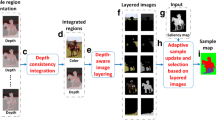
Abstract
Detecting salient objects in challenging images attracts increasing attention as many applications require more robust method to deal with complex images from the Internet. Prior methods produce poor saliency maps in challenging cases mainly due to the complex patterns in the background and internal color edges in the foreground. The former problem may introduce noises into saliency maps and the later forms the difficulty in determining object boundaries. Observing that depth map can supply layering information and more reliable boundary, we improve salient object detection by integrating two features: color information and depth information which are calculated from stereo images. The two features collaborate in a two-stage framework. In the object location stage, depth mainly helps to produce a noise-filtered salient patch, which indicates the location of the object. In the object boundary inference stage, boundary information is encoded in a graph using both depth and color information, and then we employ the random walk to infer more reliable boundaries and obtain the final saliency map. We also build a data set containing 100+ stereo pairs to test the effectiveness of our method. Experiments show that our depth-plus-color based method significantly improves salient object detection compared with previous color-based methods.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Achanta, R., Hemami, S., Estrada, F., Susstrunk, S.: Frequency-tuned salient region detection. In: IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), pp. 1597–1604 (2009)
Alexe, B., Deselaers, T., Ferrari, V.: Measuring the objectness of image windows. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 34(11), 2189–2202 (2012)
Backer, G., Mertsching, B., Bollmann, M.: Data-and model-driven gaze control for an active-vision system. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 23(12), 1415–1429 (2001)
Borji, A., Ahmadabadi, M.N., Araabi, B.N., Hamidi, M.: Online learning of task-driven object-based visual attention control. Image Vis. Comput. 28(7), 1130–1145 (2010)
Bruce, N., Tsotsos, J.: Saliency based on information maximization. Adv. Neural. Inf. Process. Syst. 18, 155 (2006)
Chang, K.Y., Liu, T.L., Chen, H.T., Lai, S.H.: Fusing generic objectness and visual saliency for salient object detection. In: IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), pp. 914–921 (2011)
Chen, T., Cheng, M.M., Tan, P., Shamir, A., Hu, S.M.: Sketch2photo: internet image montage. ACM Trans. Graph. 28(5), 124:1–124:10 (2009)
Cheng, M.M., Mitra, N.J., Huang, X., Hu, S.M.: Salientshape: group saliency in image collections. Vis. Comput. 30(4), 1–11 (2013)
Cheng, M.M., Mitra, N.J., Huang, X., Torr, P.H.S., Hu, S.M.: Global contrast based salient region detection. IEEE TPAMI (2014). doi:10.1109/TPAMI.2014.2345401
Cheng, M.M., Warrell, J., Lin, W.Y., Zheng, S., Vineet, V., Crook, N.: Efficient salient region detection with soft image abstraction. In: IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), pp. 1529–1536 (2013)
Cheng, M.M., Zhang, G.X., Mitra, N.J., Huang, X., Hu, S.M.: Global contrast based salient region detection. In: IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), pp. 409–416 (2011)
Ciptadi, A., Hermans, T., Rehg, J.M.: An in depth view of saliency. In: BMVC, pp. 1–11 (2013)
Desingh, K., Krishna, K.M., Rajan, D., Jawahar, C.: Depth really matters: improving visual salient region detection with depth. In: BMVC, pp. 1–11 (2013)
Donoser, M., Urschler, M., Hirzer, M., Bischof, H.: Saliency driven total variation segmentation. In: IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), pp. 817–824 (2009)
Du, S.P., Hu, S.M., Martin, R.R.: Changing perspective in stereoscopic images. IEEE Trans. Vis. Comput. Graph. 19(8), 1288–1297 (2013)
Du, S.P., Masia, B., Hu, S.M., Gutierrez, D.: A metric of visual comfort for stereoscopic motion. ACM Trans. Graph. 32(6), 222 (2013)
Fang, Y., Wang, J., Narwaria, M., Le Callet, P., Lin, W.: Saliency detection for stereoscopic images. In: Visual Communications and Image Processing (VCIP), pp. 1–6. IEEE (2013)
Felzenszwalb, P.F., Huttenlocher, D.P.: Efficient graph-based image segmentation. Int. J. Comput. Vis. 59(2), 167–181 (2004)
Garcia-Diaz, A., Fdez-Vidal, X.R., Pardo, X.M., Dosil, R.: Decorrelation and distinctiveness provide with human-like saliency. In: Advanced Concepts for Intelligent Vision Systems, pp. 343–354. Springer, Berlin (2009)
Goferman, S., Zelnik-Manor, L., Tal, A.: Context-aware saliency detection. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 34(10), 1915–1926 (2012)
Grady, L.: Random walks for image segmentation. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 28(11), 1768–1783 (2006)
Han, J., Ngan, K.N., Li, M., Zhang, H.J.: Unsupervised extraction of visual attention objects in color images. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. Video Technol. 16(1), 141–145 (2006)
Harel, J., Koch, C., Perona, P., et al.: Graph-based visual saliency. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 19, 545 (2007)
Hou, X., Zhang, L.: Saliency detection: a spectral residual approach. In: IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), pp. 1–8 (2007)
Hou, X., Zhang, L.: Dynamic visual attention: searching for coding length increments. In: NIPS, vol. 5, p. 7 (2008)
Hu, S.M., Chen, T., Xu, K., Cheng, M.M., Martin, R.: Internet visual media processing: a survey with graphics and vision applications. Vis. Comput. 29(5), 393–405 (2013)
Itti, L., Koch, C., Niebur, E., et al.: A model of saliency-based visual attention for rapid scene analysis. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 20(11), 1254–1259 (1998)
Jiang, H., Wang, J., Yuan, Z., Liu, T., Zheng, N., Li, S.: Automatic salient object segmentation based on context and shape prior. In: BMVC, vol. 3, p. 7 (2011)
Ko, B.C., Nam, J.Y.: Object-of-interest image segmentation based on human attention and semantic region clustering. JOSA A 23(10), 2462–2470 (2006)
Lang, C., Nguyen, T.V., Katti, H., Yadati, K., Kankanhalli, M., Yan, S.: Depth matters: influence of depth cues on visual saliency. In: ECCV, pp. 101–115. Springer, Berlin (2012)
Li, H., Ngan, K.N.: A co-saliency model of image pairs. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 20(12), 3365–3375 (2011)
Li, N., Ye, J., Ji, Y., Ling, H., Yu, J.: Saliency detection on light field. In: IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR) (2014)
Liu, H., Zhang, L., Huang, H.: Web-image driven best views of 3d shapes. Vis. Comput. 28(3), 279–287 (2012)
Liu, T., Yuan, Z., Sun, J., Wang, J., Zheng, N., Tang, X., Shum, H.Y.: Learning to detect a salient object. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 33(2), 353–367 (2011)
Liu, Z., Xue, Y., Shen, L., Zhang, Z.: Nonparametric saliency detection using kernel density estimation. In: IEEE International Conference on Image Processing (ICIP), pp. 253–256 (2010)
Margolin, R., Tal, A., Zelnik-Manor, L.: What makes a patch distinct? In: IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), pp. 1139–1146 (2013)
Margolin, R., Zelnik-Manor, L., Tal, A.: Saliency for image manipulation. Vis. Comput. 29(5), 381–392 (2013)
Mu, T.J., Sun, J.J., Martin, R.R., Hu, S.M.: A response time model for abrupt changes in binocular disparity. Vis. Comput. 1–13 (2014)
Mu, T.J., Wang, J.H., Du, S.P., Hu, S.M.: Stereoscopic image completion and depth recovery. Vis. Comput. 30(6–8), 833–843 (2014)
Niu, Y., Geng, Y., Li, X., Liu, F.: Leveraging stereopsis for saliency analysis. In: IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), pp. 454–461 (2012)
Peng, H., Li, B., Xiong, W., Hu, W., Ji, R.: Rgbd salient object detection: a benchmark and algorithms. In: ECCV, pp. 92–109 (2014)
Perazzi, F., Krähenbühl, P., Pritch, Y., Hornung, A.: Saliency filters: contrast based filtering for salient region detection. In: IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), pp. 733–740 (2012)
Rosenholtz, R., Dorai, A., Freeman, R.: Do predictions of visual perception aid design? ACM Trans. Appl. Percept. (TAP) 8(2), 12 (2011)
Rutishauser, U., Walther, D., Koch, C., Perona, P.: Is bottom-up attention useful for object recognition? In: IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), vol. 2, pp. II-37. IEEE (2004)
Seo, H.J., Milanfar, P.: Static and space–time visual saliency detection by self-resemblance. J. Vis. 9(12), 15 (2009)
Shen, X., Wu, Y.: A unified approach to salient object detection via low rank matrix recovery. In: IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), pp. 853–860 (2012)
Shi, Y., Yi, Y., Yan, H., Dai, J., Zhang, M., Kong, J.: Region contrast and supervised locality-preserving projection-based saliency detection. Vis. Comput. 1–15 (2014)
Siagian, C., Itti, L.: Biologically inspired mobile robot vision localization. IEEE Trans. Robot. 25(4), 861–873 (2009)
Smith, B.M., Zhang, L., Jin, H.: Stereo matching with nonparametric smoothness priors in feature space. In: IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), pp. 485–492 (2009)
Tong, R., Zhang, Y., Cheng, K.L.: Stereopasting: interactive composition in stereoscopic images. IEEE Trans. Vis. Comput. Graph. 19(8), 1375–1385 (2013)
Yan, Q., Xu, L., Shi, J., Jia, J.: Hierarchical saliency detection. In: IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), pp. 1155–1162 (2013)
Yang, C., Zhang, L., Lu, H., Ruan, X., Yang, M.H.: Saliency detection via graph-based manifold ranking. In: IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), pp. 3166–3173 (2013)
Zhai, Y., Shah, M.: Visual attention detection in video sequences using spatiotemporal cues. In: Proceedings of the 14th Annual ACM International Conference on Multimedia, pp. 815–824. ACM (2006)
Zhang, J., Sclaroff, S.: Saliency detection: a boolean map approach. In: IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), pp. 153–160 (2013)
Acknowledgments
We thank Prof. Jianjun Zhang and Jian Chang from Bournemouth University for their valuable discussion. We also thank all anonymous reviewers for their valuable comments. This work was supported by National High-Tech Research and Development Program of China (No. 2013AA013903), National Basic Research Program of China (No. 2011CB302205), the People Programme (Marie Curie Actions) of the European Union’s Seventh Framework Programme FP7/2007-2013/ under REA Grant agreement No. [612627]- ’AniNex’, Zhejiang Provincial Natural Science Foundation of China (No. LY14F020050).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tang, Y., Tong, R., Tang, M. et al. Depth incorporating with color improves salient object detection. Vis Comput 32, 111–121 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00371-014-1059-6
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00371-014-1059-6