Abstract
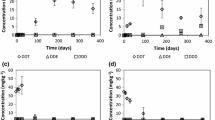
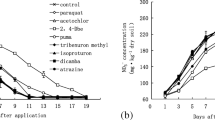
The persistence of DDT [1,1,1-trichloro-2,2-bis(p-chlorophenyl)ethane] and its metabolites in soil, their toxicity to soil algae, and effects on microbial activities were studied in laboratory microcosms for 45 days. In non-sterile soils, removal of DDD [1,1-dichloro-2,2-bis(p-chlorophenyl)ethane] and DDE [1,1-dichloro-2,2-bis(p-chlorophenyl)ethylene] was less than 3%, while 4–8% of applied DDMU [1-chloro-2,2-bis(p-chlorophenyl)ethylene], DDA [2,2-bis(p-chlorophenyl)acetic acid] and DDT were lost. Added DDOH [2,2-bis(p-chlorophenyl)ethanol] was more labile, as 60% was degraded during the same period. Soil microalgae were not measurably affected by the compounds tested at 10–50 mg kg–1, but at 100 mg kg–1 soil, DDD, DBP (p,p′-dichlorobenzophenone) and DDA significantly reduced their growth. Phosphatase activity was not affected by DDT and its metabolites at the concentrations tested (≤50 mg kg–1), but all compounds inhibited dehydrogenase activity at concentrations of 50 mg kg–1 soil. The toxic effects of DDT and its metabolites were dose-related.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Received: 9 January 1998
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Megharaj, M., Boul, H. & Thiele, J. Effects of DDT and its metabolites on soil algae and enzymatic activity. Biol Fertil Soils 29, 130–134 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1007/s003740050534
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s003740050534