Abstract
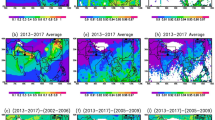
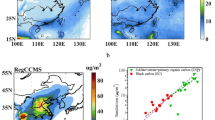
Quantitative assessment of the seasonal variations in the direct radiative effect (DRE) of composite aerosols as well as the constituent species over the Indian sub continent has been carried out using a synergy of observations from a dense network of ground based aerosol observatories and modeling based on chemical transport model simulations. Seasonal variation of aerosol constituents depict significant influence of anthropogenic aerosol sources in winter and the dominance of natural sources in spring, even though the aerosol optical depth doesn’t change significantly between these two seasons. A significant increase in the surface cooling and atmospheric warming has been observed as season changes from winter (DRESUR = −28 ± 12 W m−2 and DREATM = +19.6 ± 9 W m−2) to spring (DRESUR = −33.7 ± 12 W m−2 and DREATM = +27 ± 9 W m−2). Interestingly, springtime aerosols are more absorptive in nature compared to winter and consequently the aerosol induced diabatic heating of the atmosphere goes as high as ~1 K day−1 during spring, especially over eastern India. The atmospheric DRE due to dust aerosols (+14 ± 7 W m−2) during spring overwhelms that of black carbon DRE (+11.8 ± 6 W m−2) during winter. The DRE at the top of the atmosphere is mostly governed by the anthropogenic aerosols during all the seasons. The columnar aerosol loading, its anthropogenic fraction and radiative effects shows a steady increase with latitude across Indian mainland leading to a larger aerosol-induced atmospheric warming during spring than in winter.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ackerman AS, Toon OB, Stevens DE, Heymsfield AJ, Ramanathan V, Welton EJ (2000) Reduction of tropical cloudiness by soot. Science 288:1042–1047
Babu SS, Satheesh SK, Moorthy KK (2002) Aerosol radiative forcing due to enhanced black carbon at an urban site in India. Geophys Res Lett 29(18):1880. doi:10.1029/2002GL015826
Babu SS, Moorthy KK, Satheesh SK (2007) Temporal heterogeneity in aerosol characteristics and the resulting radiative impacts at a tropical coastal station—Part 2: direct short wave radiative forcing. Ann Geophys 25:2309–2320
Babu SS, Manoj MR, Moorthy KK, Gogoi MM, Nair VS, Kompalli SK, Satheesh SK, Niranajan K, Gopal R, Bhuyan PK, Singh D (2013) Trends in aerosol optical depth over Indian region: potential causes and impact indicators. J Geophys Res Atmos 118:11794–11806. doi:10.1002/2013JD020507
Babu SS, Nair VS, Gogoi MM, Moorthy KK (2016) Seasonal variation of vertical distribution of aerosol single scattering albedo over Indian sub-continent: RAWEX aircraft observations. Atmos Environ 125:312–323
Beegum SN, Moorthy KK, Nair VS, Babu SS, Satheesh SK, Vinoj V, Reddy RR, Gopal KR, Badarinath KVS, Niranjan K, Pandey SK, Behera M, Jeyaram A, Bhuyan PK, Gogoi MM, Singh S, Pant P, Dumka UC, Kant Y, Kuniyal JC, Singh D (2008) Characteristics of spectral aerosol optical depths over India during ICARB. J Earth Syst Sci 117(S1):303–313
Bollasina M, Ming Y, Ramaswamy V (2011) Anthropogenic aerosols and the weakening of the South Asian summer monsoon. Science 334:502–505. doi:10.1126/science.1204994
Chin M, Ginoux P, Kinne S, Torres O, Holben BN, Duncan BN, Martin RV, Logan JA, Higurashi A, Nakajima T (2002) Tropospheric aerosol optical thickness from the GOCART model and comparisons with satellite and sunphotometer measurements. J Atmos Sci 59:461–483
Chin M, Diehl T, Dubovik O, Eck TF, Holben BN, Sinyuk A, Streets DG (2009) Light absorption by pollution, dust, and biomass burning aerosols: a global model study and evaluation with AERONET measurements. Ann Geophys 27:3439–3464
Chin M, Diehl T, Tan Q, Prospero JM, Kahn RA, Remer LA, Yu H, Sayer AM, Bian H, Geogdzhayev IV, Holben BN, Howell SG, Huebert BJ, Hsu NC, Kim D, Kucsera TL, Levy RC, Mishchenko MI, Pan X, Quinn PK, Schuster GL, Streets DG, Strode SA, Torres O, Zhao X-P (2014) Multi-decadal variations of atmospheric aerosols from 1980 to 2009: a perspective from observations and a global model. Atmos Chem Phys 14:3657–3690
Chung CE, Zhang GJ (2004) Impact of absorbing aerosol on precipitation: dynamic aspects in association with convective available potential energy and convective parameterization closure and dependence on aerosol heating profile. J Geophys Res 109:D22103. doi:10.1029/2004JD004726
D’Errico M, Cagnazzo C, Gogli PG, Lau WKM, Hardenberg J, Fierli F, Cherchi A (2015) Indian monsoon and the elevated heat pump mechanism in a coupled aerosol-climate model. J Geophys Res. doi:10.1002/2015JD023346
Deepshikha S, Satheesh SK, Srinivasan J (2006) Dust aerosols over India and adjacent continents retrieved using METEOSAT infrared radiance Part II: quantification of wind dependence and estimation of radiative forcing. Annales Geophysicae 24(1):63–79
Dey S, Tripathi SN (2007) Estimation of aerosol optical properties and radiative effects in the Ganga basin, northern India, during the wintertime. J Geophys Res 112:D03203
Dey S, Tripathi SN (2008) Aerosol direct radiative effects over Kanpur in the Indo-Gangetic basin, northern India: long-term (2001–2005) observations and implications to regional climate. J Geophys Res 113:D04212. doi:10.1029/2007JD009029
Ding AJ, Huang X, Nie W, Sun JN, Kerminen V-M et al (2016) Enhanced haze pollution by black carbon in megacities in China. Geophys Res Lett 43:2873–2879. doi:10.1002/2016GL067745
Dubovik O, Smirnov A, Holben BN, King MD, Kaufman YJ, Eck TF, Slutsker I (2000) Accuracy assessment of aerosol optical properties retrieval from AERONET sun and sky radiance measurements. J Geophys Res 105:9791–9806
Flanner MG, Zender CS, Randerson JT, Rasch PJ (2007) Present-day climate forcing and response from black carbon in snow. J Geophys Res 112:D11202. doi:10.1029/2006JD008003
Ganguly D, Jayaraman A (2006) Physical and optical properties of aerosols over an urban location in western India: implications for shortwave radiative forcing. J Geophys Res 111:D24207. doi:10.1029/2006JD007393
Ganguly D, Jayaraman A, Gadhavi H (2006) Physical and optical properties of aerosols over an urban location in western India: seasonal variabilities. J Geophys Res 111:D24206
Ganguly D, Rasch PJ, Wang H, Yoon J-H (2012) Climate response of the South Asian monsoon system to anthropogenic aerosols. J Geophys Res 117:D13209
Hansen J, Sato M, Ruedy R, Nazarenko L et al (2005) Efficacy of climate forcings. J Geophys Res 110:D18104. doi:10.1029/2005JD005776
Haywood J, Boucher O (2000) Estimates of the direct and indirect radiative forcing due to tropospheric aerosols: a review. Rev Geophys 38(4):513–543
Haywood JM, Shine KP (1995) The effect of anthropogenic sulfate and soot aerosol on the clear sky planetary radiation budget. Geophys Res Lett 22(5):603–606
Hess M, Koepke P, Schult I (1998) Optical properties of aerosols and clouds: the software package OPAC. Bull Am Meteorol Soc 79:831–844
Holben BN, Eck TF, Slutsker I, Tanre D et al (1998) AERONET—a federated instrument network and data archive for aerosol characterization. Remote Sens Environ 66:1–16
Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC) (2007) Climate change 2007: the physical science basis. In: Solomon S, Qin D, Manning M, Chen Z, Marquis M, Averyt KB, Tignor M, Miller HL (eds) Contribution of working group I to the fourth assessment report of the IPCC. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge and New York
Jethva H, Satheesh SK, Srinivasan J, Moorthy KK (2009) How good is the assumption about visible surface reflectance in MODIS aerosol retrieval over land? A comparison with aircraft measurements over an urban site in India. IEEE Trans Geosci Remote Sens 47:1990–1998. doi:10.1109/TGRS.2008.2010221
Kaufman YJ, Boucher O, Tanre D, Chin M, Remer L, Takemura T (2005) Aerosol anthropogenic component estimated from satellite data. Geophys Res Lett 32:L17804. doi:10.1029/2005GL023125
Kim MK, Lau WKM, Kim K-M, Sang J, Kim Y-H, Lee W-S (2015) Amplification of ENSO effects on Indian summer monsoon by absorbing aerosols. Clim Dyn. doi:10.1007/s00382-015-2722-y
Kompalli SK, Babu SS, Moorthy KK (2010) Inter-comparison of aerosol optical depth from the multi-wavelength solar radiometer with other radiometric measurements. Ind J Radio Space Phys 39:364–371
Lau WKM (2014) Desert dust and monsoon rainfall. Nat Geosci 7:255–256. doi:10.1038/ngeo2115
Lau WKM (2016) The aerosol-monsoon climate system of Asia: a new paradigm. J Meteorol Res. doi:10.1007/s13351-015-5999-1
Lau KM, Kim MK, Kim KM (2006) Asian summer monsoon anomalies induced by aerosol direct forcing: the role of the Tibetan Plateau. Clim Dyn 26:855–864
Lawrence MG, Lelieveld J (2010) Atmospheric pollutant outflow from southern Asia: a review. Atmos Chem Phys 10:11017–11096. doi:10.5194/acp-10-11017-2010
Lohmann U, Feichter J (2005) Global indirect aerosol effects: a review. Atmos Chem Phys 5:715–737
Mani A, Chacko O, Hariharan S (1969) A study of Ångström turbidity parameters from solar radiation measurements in India. Tellus 21:829–843
McComiskey A, Schwartz SE, Schmid B, Guan H, Lewis ER, Ricchiazzi P, Ogren JA (2008) Direct aerosol forcing: calculation from observables and sensitivities to inputs. J Geophys Res 113:D09202. doi:10.1029/2007JD009170
Meehl GA, Arblaster JM, Collins WD (2008) Effects of black carbon aerosols on the Indian Monsoon. J Climate 21:2869–2882
Menon S, Hansen J, Nazarenko L, Luo Y (2002) Climate effects of black carbon aerosols in China and India. Science 297:2250–2253
Moorthy KK, Satheesh SK, Krishna Murthy BV (1997) Investigations of marine aerosols over the tropical Indian Ocean. J Geophys Res 102:18827–18842
Moorthy KK, Babu SS, Badarinath KVS, Sunilkumar SV, Kiranchand TR, Ahmed YN (2007) Latitudinal distribution of aerosol black carbon and its mass fraction to composite aerosols over peninsular India during winter season. Geophys Res Lett 34:L08802. doi:10.1029/2006GL029150
Moorthy KK, Nair VS, Babu SS, Satheesh SK (2009) Spatial and vertical heterogeneities of aerosol radiative forcing over the oceanic regions surrounding the Indian peninsula: climate implications. Q J R Meteorol Soc 135:2131–2145
Moorthy KK, Beegum SN, Srivastava N, Satheesh SK, Chin M, Blond N, Babu SS, Singh S (2013) Performance evaluation of chemistry transport models over India. Atmos Environ 71:210–225
Nair VS, Satheesh SK, Moorthy KK, Babu SS, George SK, Nair PR (2010) Surprising observation of large anthropogenic aerosol fraction over the near-pristine southern Bay of Bengal: climate implications. J Geophys Res Atmos 115:D21201. doi:10.1029/2010JD013954
Nair VS, Solmon F, Giorgi F, Mariotti L, Babu SS, Moorthy KK (2012) Simulation of South Asian aerosols for regional climate studies. J Geophys Res Atmos. doi:10.1029/2011JD016711
Nair VS, Babu SS, Moorthy KK, Sharma AK, Marinoni A, Ajai (2013a) Black carbon aerosols over the Himalayas: direct and surface albedo forcing. Tellus B 65:19738
Nair VS, Babu SS, Moorthy KK, Prijith SS (2013b) Spatial gradients in aerosol-induced atmospheric heating and surface dimming over the oceanic regions around India: anthropogenic or natural? J Clim 26:7611–7621
Nair VS, Babu SS, Moorthy KK, Satheesh SK (2014) Implications of multiple scattering on the assessment of black carbon aerosol radiative forcing. J Quant Spectrosc Radiat Transf 148:134–140
Nigam S, Bollasina M (2010) The ‘elevated heat pump’ hypothesis for the aerosol-monsoon hydroclimate link: ‘‘grounded’’ in observations? J Geophys Res 115:D16201
Novakov T, Kirchstetter TW, Menon S, Aguiar J (2008) Response of California temperature to regional anthropogenic aerosol changes. Geophys Res Lett 35:L19808. doi:10.1029/2008GL034894
Pant P, Hegde P, Dumka UC, Sagar R, Satheesh SK, Moorthy KK (2006) Aerosol characteristics at a high altitude location in central Himalayas: optical properties and radiative forcing. J Geophys Res 111:D17206. doi:10.1029/2005JD006768
Pathak B, Kalita G, Bhuyan K, Bhuyan PK, Moorthy KK (2010) Aerosol temporal characteristics and its impact on shortwave radiative forcing at a location in the northeast of India. J Geophys Res 115:D19204. doi:10.1029/2009JD013462
Peng J et al (2016) Markedly enhanced direct radiative forcing of black carbon particles under polluted urban environments. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 113(16):4266–4271
Porter JN, Miller M, Pietras C, Motell C (2001) Ship-based sun photometer measurements using Microtops sun photometers. J Atmos Ocean Technol 18:765–774
Ramachandran S, Kedia S (2010) Black carbon aerosols over an urban region: radiative forcing and climate impact. J Geophys Res 115:D10202. doi:10.1029/2009JD013560
Ramanathan V, Crutzen PJ, Lelieveld J, Mitra AP, Althausen D, Anderson J, Andreae MO, Cantrell W, Cass GR, Chung CE, Clarke AD, Coakley JA, Collins WD, Conant WC, Dulac F, Heintzenberg J, Heymsfield AJ, Holben B, Howell S, Hudson J, Jayaraman A, Kiehl JT, Krishnamurti TN, Lubin D, McFarquhar G, Novakov T, Ogren JA, Podgorny IA, Prather K, Priestley K, Prospero JM, Quinn PK, Rajeev K, Rasch P, Rupert S, Sadourny R, Satheesh SK, Shaw GE, Sheridan PJ, Valero FPJ (2001) Indian Ocean experiment: an integrated analysis of the climate forcing and effects of the great Indo-Asian haze. J Geophys Res 106:28371–28398
Ramanathan V, Chung C, Kim D, Bettge T, Buja L, Kiehl JT, Washington WM, Fu Q, Sikka DR, Wild M (2005) Atmospheric brown clouds: impacts on South Asian climate and hydrological cycle. Proc Natl Acad Sci 102:5326–5333
Ricchiazzi P, Yang S, Gautier C, Sowle D (1998) SBDART: a research and teaching software tool for plane-parallel radiative transfer in the Earth’s atmosphere. Bull Am Meteorol Soc 79:2101–2114
Satheesh SK, Srinivasan J (2006) A method to estimate aerosol radiative forcing from spectral optical depths. J Atmos Sci 63:1082–1092
Satheesh SK, Moorthy KK, Kaufman YJ, Takemura T (2006) Aerosol optical depth, physical properties and radiative forcing over the Arabian Sea. Meteorol Atmos Phys 91:45–62. doi:10.1007/s00703-004-0097-4
Satheesh SK, Moorthy KK, Babu SS, Vinoj V, Dutt CBS (2008) Climate implications of large warming by elevated aerosols over India. Geophys Res Lett 35:L19809. doi:10.1029/2008GL034944
Satheesh SK, Torres O, Remer LA, Babu SS, Vinoj V, Eck TF, Kleidman RG, Holben BN (2009) Improved assessment of aerosol absorption using OMI-MODIS joint retrieval. J Geophys Res. doi:10.1029/2008JD011024
Schulz M, Textor C, Kinne S, Balkanski Y, Bauer S, Berntsen T, Berglen T, Boucher O, Dentener F, Guibert S, Isaksen ISA, Iversen T, Koch D, Kirkevag A, Liu X, Montanaro V, Myhre G, Penner JE, Pitari G, Reddy S, Seland Stier P, Takemura T (2006) Radiative forcing by aerosols as derived from the AeroCom present-day and pre-industrial simulations. Atmos Chem Phys 6:5225–5246
Soni VK, Attri SD, Taneja K, Peshin SK (2014) Assessment of aerosol radiative properties in India. Met Monograph IMD, No: ESSO/IMD/EMRC/01/2014
Vinoj V, Rasch PJ, Wang H, Yoon J, Ma PL, Landu K, Singh B (2014) Short-term modulation of Indian summer monsoon rainfall by West Asian dust. Nat Geosci 7:308–313. doi:10.1038/ngeo2107
Wang S-H, Lin N-H, Chou M-D, Woo J-H (2007) Estimate of radiative forcing of Asian biomass-burning aerosols during the period of TRACE-P. J Geophys Res 112:D10222. doi:10.1029/2006JD007564
Wang Y, Khalizov A, Levy M, Zhang R (2013) New directions: light absorbing aerosols and their atmospheric impacts. Atmos Environ 81:713–715
Wang Y, Lee K-H, Lin Y, Levy M, Zhang R (2014) Distinct effects of anthropogenic aerosols on tropical cyclones. Nat Clim Change 4:368–373
Wang Y, Jiang J, Su H (2015) Atmospheric responses to the redistribution of anthropogenic aerosols. J Geophys Res Atmos 120(18):9625–9641
Yu H, Dickinson RE, Chin M, Kaufman YJ, Zhou M, Zhou L, Tian Y, Dubovik O, Holben BN (2004) Direct radiative effect of aerosols as determined from a combination of MODIS retrievals and GOCART simulations. J Geophys Res 109:D03206. doi:10.1029/2003JD003914
Zhang R, Wang G, Guo S, Zamora M, Lin Y, Wang W, Hu M, Wang Y (2015) Formation of urban fine particulate matter. Chem Rev 115(10):3803–3855
Acknowledgments
This study has been carried out as a part of ARFI project of the ISRO-Geosphere Biosphere program. We thank the seamless effort made by the each and every ARFINET PIs for their interest and dedication to support the program, which resulted in such long term aerosol data over the region. Details of ARFINET are available at: http://spl.gov.in. We also acknowledge NASA AERONET and IMD for providing aerosol data over the Indian region. The authors acknowledge the NASA Giovanni for GOCART data, MODIS and TOMS data made available.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nair, V.S., Babu, S.S., Manoj, M.R. et al. Direct radiative effects of aerosols over South Asia from observations and modeling. Clim Dyn 49, 1411–1428 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00382-016-3384-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00382-016-3384-0