Abstract
Purpose
Recent epidemiological studies have shown that habitual consumption of extra virgin olive oil (EVOO), the characteristic culinary fat of the Mediterranean area, is effective in the prevention of diverse types of digestive disorders such as inflammatory bowel disease. Many of these benefits are, in addition to its high proportion of oleic acid, due to the high content of phenolic compounds.
Methods
Six-week-old mice were randomized into three dietary groups: standard, EVOO and hydroxytyrosol-enriched EVOO. After 30 days, mice that were exposed to 3% DSS for 5 days developed acute colitis that progressed to severe chronic inflammation during a regime of 21 days of water.
Results
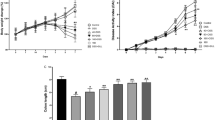
Diets enriched with EVOO significantly attenuated the clinical and histological signs of damage, improving results from disease activity index and reducing about 50% the mortality caused by DSS. Moreover, hydroxytyrosol supplement showed better results. Cytokines study showed that TNF-α was maintained near to sham control and IL-10 levels were significantly improved in EVOO and EVOO plus hydroxytyrosol diet-DSS groups. In the same way, COX-2 and iNOS were downregulated, and the activation of p38 MAPK was reduced. We also observed a higher significant reduction in iNOS in hydroxytyrosol-enriched EVOO compared with EVOO alone.
Conclusions
EVOO diets exerted a noteworthy beneficial effect in chronic DSS-induced colitis by cytokine modulation and COX-2 and iNOS reduction via downregulation of p38 MAPK. In addition to the beneficial effect by EVOO, supplementation of the diet with hydroxytyrosol may improve chronic colitis through iNOS downregulation plus its antioxidant capacity.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Braus NA, Elliott DE (2009) Advances in the pathogenesis and treatment of IBD. Clin Immunol 132:1–9
Wei J, Feng J (2010) Signaling pathways associated with inflammatory bowel disease. Recent Pat Inflamm Allergy Drug Discov 4:105–117
Ortega RM (2006) Importance of functional foods in the Mediterranean diet. Public Health Nutr 9:1136–1140
Sirtori CR, Galli C, Anderson JW, Arnoldi A (2009) Nutritional and nutraceutical approaches to dyslipidemia and atherosclerosis prevention: focus on dietary proteins. Atherosclerosis 203:8–17
Servili M, Esposto S, Fabiani R, Urbani S, Taticchi A, Mariucci F, Selvaggini R, Montedoro GF (2009) Phenolic compounds in olive oil: antioxidant, health and organoleptic activities according to their chemical structure. Inflammopharmacol 17:76–84
Quiles JL, Ramirez-Tortosa MC, Yaqoob P (2006) Olive oil and health. CABI Publishing, Oxford
Sánchez-Fidalgo S, Villegas I, Cárdeno A, Talero E, Sánchez-Hidalgo M, Motilva V, Alarcón de la Lastra C (2010) Extra-virgin olive oil-enriched diet modulates DSS-colitis-associated colon carcinogenesis in mice. Clin Nutr 29:663–673
Vissers MN, Zock PL, Katan MB (2004) Bioavailability and antioxidant effects of olive oil phenols in humans: a review. Eur J Clin Nutr 58:955–965
Visioli F, Galli C (2002) Biological properties of olive oil phytochemicals. Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr 42:209–221
Granados-Principal S, Quiles JL, Ramirez-Tortosa CL, Sanchez-Rovira P, Ramirez-Tortosa MC (2010) Hydroxytyrosol: from laboratory investigations to future clinical trials. Nutr Rev 68:191–206
Melgar S, Karlsson L, Rehnström E, Karlsson A, Utkovic H, Jansson L, Michaëlsson E (2008) Validation of murine dextran sulfate sodium-induced colitis using four therapeutic agents for human inflammatory bowel disease. Int Immunopharmacol 8:836–844
González-Correa JA, Navas MD, Muñoz-Marín J, Trujillo M, Fernández-Bolaños J, de la Cruz JP (2008) Effects of hydroxytyrosol and hydroxytyrosol acetate administration to rats on platelet function compared to acetylsalicylic acid. J Agric Food Chem 56:7872–7876
Sánchez-Fidalgo S, Cárdeno A, Villegas I, Talero E, de la Lastra CA (2010) Dietary supplementation of resveratrol attenuates chronic colonic inflammation in mice. Eur J Pharmacol 633:78–84
Okayasu I, Hatakeyama S, Yamada M, Ohkusa T, Inagaki Y, Nakaya R (1990) A novel method in the induction of reliable experimental acute and chronic ulcerative colitis in mice. Gastroenterology 98:694–702
Motilva V, Sánchez-Fidalgo S, Calvo JR, Talero E (2008) Mechanism of increased gastric protection after NSAID-administration in rats consuming virgin olive oil diets. ESPEN 3:e9–e16
Perona JS, Montero E, Sánchez-Domínguez JM, Cañizares J, Garcia M, Ruiz-Gutiérrez V (2009) Evaluation of the effect of dietary virgin olive oil on blood pressure and lipid composition of serum and low-density lipoprotein in elderly type 2 diabetic subjects. J Agric Food Chem 57:11427–11433
Razquin C, Martinez JA, Martinez-Gonzalez MA, Mitjavila MT, Estruch R, Marti A (2009) A 3 years follow-up of a Mediterranean diet rich in virgin olive oil is associated with high plasma antioxidant capacity and reduced body weight gain. Eur J Clin Nutr 63:1387–1393
Konstantinidou V, Covas MI, Muñoz-Aguayo D, Khymenets O, de la Torre R, Saez G, Tormos Mdel C, Toledo E, Marti A, Ruiz-Gutiérrez V, Ruiz Mendez MV, Fito M (2010) In vivo nutrigenomic effects of virgin olive oil polyphenols within the frame of the Mediterranean diet: a randomized controlled trial. FASEB J 24:2546–2557
Barceló F, Perona JS, Prades J, Funari SS, Gomez-Gracia E, Conde M, Estruch R, Ruiz-Gutiérrez V (2009) Mediterranean-style diet effect on the structural properties of the erythrocyte cell membrane of hypertensive patients: the prevencion con dieta Mediterranea study. Hypertension 54:1143–1150
Khymenets O, Fitó M, Touriño S, Muñoz-Aguayo D, Pujadas M, Torres JL, Joglar J, Farré M, Covas MI, de la Torre R (2010) Antioxidant activities of hydroxytyrosol main metabolites do not contribute to beneficial health effects after olive oil ingestion. Drug Metab Dispos 38:1417–1421
Nieto N, Torres MI, Ríos A, Gil A (2002) Dietary polyunsaturated fatty acids improve histological and biochemical alterations in rats with experimental ulcerative colitis. J Nutr 132:11–19
Camuesco D, Gálvez J, Nieto A, Comalada M, Rodríguez-Cabezas ME, Concha A, Xaus J, Zarzuelo A (2005) Dietary olive oil supplemented with fish oil, rich in EPA and DHA (n−3) polyunsaturated fatty acids, attenuates colonic inflammation in rats with DSS-induced colitis. J Nutr 135:687–694
Hegazi RA, Saad RS, Mady H, Matarese LE, O’Keefe S, Kandil HM (2006) Dietary fatty acids modulate chronic colitis, colitis-associated colon neoplasia and COX-2 expression in IL-10 knockout mice. Nutrition 22:275–282
Angelino D, Gennari L, Blasa M, Selvaggini R, Urbani S, Esposto S, Servili M, Ninfali P (2011) Chemical and cellular antioxidant activity of phytochemicals purified from olive mill waste waters. J Agric Food Chem 59:2011–2018
Martín MA, Ramos S, Granado-Serrano AB, Rodríguez-Ramiro I, Trujillo M, Bravo L, Goya L (2010) Hydroxytyrosol induces antioxidant/detoxificant enzymes and Nrf2 translocation via extracellular regulated kinases and phosphatidylinositol-3-kinase/protein kinase B pathways in HepG2 cells. Mol Nutr Food Res 54:956–966
Ilavarasi K, Kiruthiga PV, Pandian SK, Devi KP (2011) Hydroxytyrosol, the phenolic compound of olive oil protects human PBMC against oxidative stress and DNA damage mediated by 2,3,7,8-TCDD. Chemosphere 84:888–893
Oussalah A, Danese S, Peyrin-Biroulet L (2010) Efficacy of TNF antagonists beyond one year in adult and pediatric inflammatory bowel diseases: a systematic review. Curr Drug Targets 11:156–175
Lindsay JO, Sandison A, Cohen P, Brennan FM, Hodgson HJF (2004) IL-10 gene therapy is therapeutic for dextran sodium sulfate-induced murine colitis. Dig Dis Sci 49:1327–1334
Martín AR, Villegas I, Sánchez-Hidalgo M, de la Lastra CA (2006) The effects of resveratrol, a phytoalexin derived from red wines, on chronic inflammation induced in an experimentally induced colitis model. Br J Pharmacol 147:873–885
Itzkowitz SH (2006) Molecular biology of dysplasia and cancer in inflammatory bowel disease. Gastroenterol Clin North Am 35:553–571
Gravaghi C, La Perle KM, Ogrodwski P, Kang JX, Quimby F, Lipkin M, Lamprecht SA (2010) Cox-2 expression, PGE(2) and cytokines production are inhibited by endogenously synthesized n−3 PUFAs in inflamed colon of fat-1 mice. J Nutr Biochem. doi:10.1016/j.jnutbio.2010.03.003
Hassan A, Ibrahim A, Mbodji K, Coëffier M, Ziegler F, Bounoure F, Chardigny JM, Skiba M, Savoye G, Déchelotte P, Marion-Letellier R (2010) An α-linolenic acid-rich formula reduces oxidative stress and inflammation by regulating NF-κB in rats with TNBS-induced colitis. J Nutr 140:1714–1721
Maiuri MC, De Stefano D, Di Meglio P, Irace C, Savarese M, Sacchi R, Cinelli MP (2005) Carnuccio R Hydroxytyrosol, a phenolic compound from virgin olive oil, prevents macrophage activation. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol 371:457–465
Zhang X, Cao J, Zhong L (2009) Hydroxytyrosol inhibits pro-inflammatory cytokines, iNOS, and COX-2 expression in human monocytic cells. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol 379:581–586
Camacho-Barquero L, Villegas I, Sánchez-Calvo JM, Talero E, Sánchez-Fidalgo S, Motilva V, Alarcón de la Lastra C (2007) Curcumin, a Curcuma longa constituent, acts on MAPK p38 pathway modulating COX-2 and iNOS expression in chronic experimental colitis. Int Immunopharmacol 7:333–342
Docena G, Rovedatti L, Kruidenier L, Fanning A, Leakey NA, Knowles CH, Lee K, Shanahan F, Nally K, McLean PG, Di Sabatino A, MacDonald TT (2010) Down-regulation of p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase activation and proinflammatory cytokine production by mitogen-activated protein kinase inhibitors in inflammatory bowel disease. Clin Exp Immunol 162:108–115
Kyriakis JM, Avruch J (2001) Mammalian mitogen-activated protein kinase signal transduction pathways activated by stress and inflammation. Physiol Rev 81:807–869
Kim JM, Jung HY, Lee JY, Youn J, Lee CH, Kim KH (2005) Mitogen-activated protein kinase and activator protein-1 dependent signals are essential for Bacteroides fragilis enterotoxin-induced enteritis. Eur J Immunol 35:2648–2657
Kim YA, Lim SY, Rhee SH, Park KY, Kim CH, Choi BT, Lee SJ, Park YM, Choi YH (2006) Resveratrol inhibits inducible nitric oxide synthase and cyclooxygenase-2 expression in beta-amyloid-treated C6 glioma cells. Int J Mol Med 17:1069–1075
Corona G, Deiana M, Incani A, Vauzour D, Dessì MA, Spencer JP (2007) Inhibition of p38/CREB phosphorylation and COX-2 expression by olive oil polyphenols underlies their anti-proliferative effects. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 362:606–611
Acknowledgments
The research was supported in part by grants from Ministerio de Ciencia y tecnología (AGL 2008-02475) and Junta de Andalucía (Spain). The authors are grateful to Teresa Lopez-Soto (Department of English Language, University of Seville) for revision of grammar and linguistic style.
Conflict of interest
The authors have declared no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
L. Sánchez de Ibargüen has to be considerate equal as the first author.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sánchez-Fidalgo, S., Sánchez de Ibargüen, L., Cárdeno, A. et al. Influence of extra virgin olive oil diet enriched with hydroxytyrosol in a chronic DSS colitis model. Eur J Nutr 51, 497–506 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00394-011-0235-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00394-011-0235-y