Abstract
Background
Subretinal implants intend to replace photoreceptor function in patients suffering from degenerative retinal disease by topically applying electrical stimuli from the subretinal space. This study intended to prove the feasibility of a newly developed transchoroidal surgery and, furthermore, of a subretinal electrode array, which closely resembles envisioned human implants to electrically stimulate the visual system in rabbits.
Methods
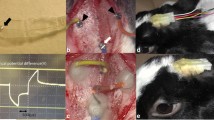
Five rabbits (ten eyes) were implanted with a 4×2-electrode array via a transchoroidal access to the subretinal space. The electrodes were connected to an arbitrary stimulus generator to apply voltage pulses. Retinae were accessed by light microscopy after stimulation with various intensities.
Results
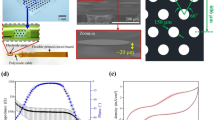
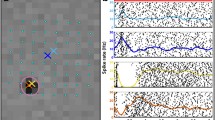
The stimulating foil could be introduced into the subretinal space in all eyes. In seven of ten eyes electrically evoked cortical potentials following subretinal electrical stimulation could be elicited. Threshold voltages ranged from less than 0.1 to 2.38 V with a corresponding threshold charge of approximately 1.0 nC per electrode or 10 µC/cm2. Histology revealed localized retinal damage over some of the electrodes succeeding stimulation strengths of 2 V and consistent damage over all electrodes succeeding voltages of 3 V.
Conclusions
The study demonstrates the feasibility of the transchoroidal surgical access to place subretinal implants in rabbit eyes and provides proof of successful cortical activation following subretinal electrical stimulation by an electrode array envisioned for human implantations.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Baratta R, Ichie M, Hwang SK, Solomonow M (1989) Orderly stimulation of skeletal muscle motor units with tripolar nerve cuff electrode. IEEE Trans Biomed Eng 36:836–843
Brindley GS (1955) The site of electrical excitation of the human eye. J Physiol127:189–200
Brindley GS (1973) Sensory effects of electrical stimulation of the visual and para-visual cortex in man. In: Jung R (ed) Handbook of sensory physiology, vol 3. pp 583–594
Brindley GS, Lewin WS (1968) The sensations produced by electrical stimulation of the visual cortex. J Physiol Lond 196:479–493
Chow AY, Chow VY (1997) Subretinal electrical stimulation of the rabbit retina. Neurosci Lett 225:13–16
Crapper DR, Noell WK (1963) Retinal excitation and inhibition from direct electrical stimulation. J Neurophysiol 26:924–947
Dawson WW, Radtke ND (1977) The electrical stimulation of the retina by indwelling electrodes. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 16:249–252
Dobelle WH (2000) Artificial vision for the blind by connecting a television camera to the visual cortex. ASAIO J 46:3–9
Dobelle WH, Mladejovsky MG, Evans JR, Roberts TS, Girvin JP (1976) “Braille” reading by a blind volunteer by visual cortex stimulation. Nature 259:111–112
Dobelle WH, Mladejovsky MG, Girvin JP (1974) Artificial vision for the blind: electrical stimulation of visual cortex offers hope for a functional prosthesis. Science 183:440–444
Dobelle WH, Turkel J, Henderson DC, Evans JR (1979) Mapping the representation of the visual field by electrical stimulation of human visual cortex. Am J Ophthalmol 88:727–735
Drasdo N, Aldebasi YH, Chiti Z, Mortlock KE, Morgan JE, North RV (2001) The SCone PhNR and Pattern ERG in Primary Open Angle Glaucoma. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 42:1266–1272
Eckhorn R, Stett A, Schanze T, Gekeler F, Schwahn H, Zrenner E, Wilms M, Eger M, Hesse L (2001) Physiological functional evaluation of retinal implants in animal models. Ophthalmologe 98:369–375 [in German]
Gekeler F, Schwahn HN, Stett A, Kohler K, Zrenner E (2001) Subretinal microphotodiodes to replace photoreceptor-function: a review of the current state. In: Doly M, Droy M-T, Christen Y (eds) Vision, sensations et environment, Irvinn, Paris, pp 77–95
Hesse L, Schanze T, Wilms M, Eger M (2000) Implantation of retina stimulation electrodes and recording of electrical stimulation responses in the visual cortex of the cat. Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol 238:840–845
Humayun MS, de Juan EJ (1998) Artificial vision. Eye 12:605–607
Humayun MS, de Juan EJ, Dagnelie G, Greenberg RJ, Propst RH, Phillips DH (1996) Visual perception elicited by electrical stimulation of retina in blind humans. Arch Ophthalmol 114:40–46
Humayun MS, de Juan EJ, Weiland JD, Dagnelie G, Katona S, Greenberg R, Suzuki S (1999) Pattern electrical stimulation of the human retina. Vision Res 39:2569–2576
Humayun MS, Prince M, de Juan EJ, Barron Y, Moskowitz M, Klock IB, Milam AH (1999) Morphometric analysis of the extramacular retina from postmortem eyes with retinitis pigmentosa. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 40:143–148
Humayun MS, Propst RH, de Juan EJ, McCormick K, Hickingbotham D (1994) Bipolar surface electrical stimulation of the vertebrate retina. Arch Ophthalmol 112:110–116
Humayun MS, Weiland JD, de Juan EJ (1999) Electrical stimulation of the human retina. In: Hollyfield JG, Anderson RE, LaVail MM (eds) Retinal degenerative diseases and experimental therapy. Kluwer Academic /Plenum Publishers, New York, p 479
Kohler K, Hartmann JA, Werts D, Zrenner E (2001) Histological studies of retinal degeneration and biocompatibility of subretinal implants. Ophthalmologe 98:364–368
Milam AH, Li ZY, Fariss RN (1998) Histopathology of the human retina in retinitis pigmentosa. Prog Retin Eye Res 17:175–205
Normann RA, Maynard EM, Guillory KS, Warren DJ (1996) Cortical implants for the blind. IEEE Spectrum 33:54–59
Normann RA, Maynard EM, Rousche PJ, Warren DJ (1999) A neural interface for a cortical vision prosthesis. Vision Res 39:2577–2587
Pardue MT, Stubbs EB Jr, Perlman JI, Narfstrom K, Chow AY, Peachey NS (2001) Immunohistochemical studies of the retina following long-term implantation with subretinal microphotodiode arrays. Exp Eye Res 73:333–343
Peyman G, Chow AY, Liang C, Chow VY, Perlman JI, Peachey NS (1998) Subretinal semiconductor microphotodiode array. Ophthalmic Surg Lasers 29:234–241
Rizzo JF, Loewenstein J, Wyatt JL (1999) Development of an epiretinal electronic visual prosthesis: the Harvard Medical School–Massachusetts Institute of Technology Research Program. In: Hollyfield JG, Anderson RE, LaVail MM (eds) Retinal degenerative diseases and experimental therapy. Kluwer Academic /Plenum Publishers, New York, p 463
Ronner SF, Foote WE, Feldon SE (1980) Activation of single cells in cat visual cortex by electrical stimulation of the cortical surface. Exp Neurol 70:47–64
Santos A, Humayun MS, de Juan EJ, Greenburg RJ, Marsh MJ, Klock IB, Milam AH (1997) Preservation of the inner retina in retinitis pigmentosa. A morphometric analysis. Arch Ophthalmol 115:511–515
Schmidt EM, Bak M, Hambrecht FT, Kufta CV, O’Rourke DK, Vallabhanath P (1996) Feasibility of a visual prosthesis for the blind based on intracortical microstimulation of the visual cortex. Brain 119:507–522
Schwahn HN, Gekeler F, Kohler K, Kobuch K, Sachs HG, Schulmeyer F, Jakob W, Gabel VP, Zrenner E (2001) Studies on the feasibility of a subretinal visual prosthesis: data from Yucatan micropig and rabbit. Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol 239:961–967
Schwahn HN, Gekeler F, Kohler K, Zrenner E (2001) Stimulation des visuellen Systems durch subretinale Elektrostimulation: Tierexperimentelle Daten zur Machbarkeit einer subretinalen Netzhautprothese. Nova Acta Leopoldina NF 84:209–221
Stett A, Barth W, Weiss S, Haemmerle H, Zrenner E (2000) Electrical multisite stimulation of the isolated chicken retina. Vision Res 40:1785–1795
Stieglitz T, Blau C, Beutel H, Keller R, Meyer JU (1997) Conception and development of flexible stimulator structures within a retinal implant system] Konzeption und Entwicklung von flexiblen Stimulatorstrukturen innerhalb eines Retina Implantat Systems. Biomed Tech Berl 42 (Suppl):458–459 [in German]
Veraart C, Raftopoulos C, Mortimer JT, Delbeke J, Pins D, Michaux G, Vanlierde A, Parrini S, Wanet-Defalque MC (1998) Visual sensations produced by optic nerve stimulation using an implanted self-sizing spiral cuff electrode. Brain Res 813:181–186
Volker M, Gekeler F, Shinoda K, Sachs H, Gmeiner H, Kohler K, Inhoffen W, Bartz-Schmidt KU, Zrenner E (2002) Implantation of Microphotodiode Arrays (MPDA) in cats: OCT and fluorescein angiography. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci (abstract)
Walter P, Heimann K (2000) Evoked cortical potentials after electrical stimulation of the inner retina in rabbits. Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol 238:315–318
Walter P, Szurman P, Vobig M, Berk H, Ludtke-Handjery HC, Richter H, Mittermayer C, Heimann K, Sellhaus B (1999) Successful long-term implantation of electrically inactive epiretinal microelectrode arrays in rabbits. Retina 19:546–552
Yagi T, Ito Y, Kanda H, Tanaka S, Watanabe M, Uchikawa Y (1994) Hybrid retinal implant: fusion of engineering and neuroscience. IEEE 4:382–385
Yamamoto S, Yamamoto T, Hayashi M, Takeuchi S (2001) Morphological and functional analyses of diabetic macular edema by optical coherence tomography and multifocal electroretinograms. Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol 239:96–101
Zrenner E The spectral properties of the human visual Ssystem as revealed by visually evoked cortical potentials/VECP) and psychophysical investigations. In: Braitenberg V, Barlow HB, Bullock H, Florey E, Grüsser OJ, Peters A (eds) Neurophysiological aspects of color vision in primates. Springer, Berlin Heidelberg New York, pp 112–172
Zrenner E (2002) Will retinal implants restore vision? Science 295:1022–1025
Zrenner E, Gekeler F, Gabel VP, Graf HG, Graf M, Guenther E, Haemmerle H, Hoefflinger B, Kobuch K, Kohler K, Nisch W, Sachs H, Schlosshauer B, Schubert M, Schwahn H, Stelzle M, Stett A, Troeger B, Weiss S (2001) Subretinal microphotodiode array as replacement for degenerated photoreceptors?. Ophthalmologe 98:357–363
Zrenner E, Miliczek K-D, Gabel V-P, Graf HG, Guenther E, Haemmerle H, Hoefflinger B, Kohler K, Nisch W, Schubert M, Stett A, Weiss S (1997) The development of subretinal microphotodiodes for replacement of degenerated photoreceptors [see comments]. Ophthalmic Res 29:269–280
Zrenner E, Stett A, Weiss S, Aramant RB, Guenther E, Kohler K, Miliczek K-D, Seiler MJ, Haemmerle H (1999) Can subretinal microphotodiodes successfully replace degenerated photoreceptors? Vision Res 39:2555–2567
Zrenner E, Weiss S, Stett A, Brunner B, Gabel V-P, Graf M, Graf HG, Haemmerle H, Hoefflinger B, Kobuch K, Miliczek K-D, Nisch W, Sachs H, Stelzle M (1999) Are subretinal microphotodiodes suitable as a replacement for degenerated photoreceptor? In: Hollyfield JG, Anderson RE, LaVail MM (eds) Retinal degenerative diseases and experimental therapy. Kluwer Academic /Plenum Publishers, New York, pp 497–506
Acknowledgements
Support for this study was provided by the German Federal Ministry of Education and Research (BMBF; grant no. 01KP0008). We gratefully acknowledge the help of our project partners in this work (Institute for Microelectronics, Stuttgart; Institute for Physical Electronics, Stuttgart; Natural and Medical Sciences Institute, Reutlingen; Fraunhofer-Institute for Biomedical Techniques, St. Ingbert; all Germany). E. Eckert was extremely helpful in surgery and animal care. The Ewald+Karin Hochbaum-Stiftung generously supported our work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gekeler, F., Kobuch, K., Schwahn, H.N. et al. Subretinal electrical stimulation of the rabbit retina with acutely implanted electrode arrays. Graefe's Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol 242, 587–596 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00417-004-0862-6
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00417-004-0862-6