Abstract
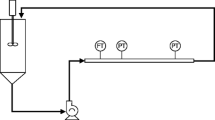
In this paper, The drag reduction characteristics of surfactant solutions have been experimentally studied, as well as, the shear viscosities of turbulent drag-reducing surfactant solution have been measured as a function of concentration, shear rate and temperature by using AG-G2 (TA Instruments, New Castle, USA) rheometer. In comparison the rheological property with the macroscopic behavior of the solutions in turbulent channel flow, a deeper insight into the mechanisms of drag-reducing surfactant solution has been obtained. For no shear induced structure of surfactant solutions they just show features shear thinning, but the drag reduction is very significant phenomenon. Surfactant solution of the shear induced structure is not a surfactant fluid drag reduction of the necessary elements.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Virk P.S.: Drag reduction fundamentals. ACHE J. 21(4), 625–657 (1975)
Zakin J.L., LU B., Bewersdorff H.W.: Surfactant drag reduction. Rev. Chem. Eng. 14, 253–320 (1998)
Toms, B.A.: Some observations on the flow of linear polymer solutions straight tubes at large Reynolds numbers. In: Proceedings of 1st congress on rheology, North Holland, Amsterdam, pp. 135–141 (1948)
Zakin, J.L., Myska, J., Lin, Z.: Similarities and differences in drag reduction behavior of high polymer and surfactant solutions. In: Proceeding of International Symposium on Seawater Drag Reduction, pp. 277–280 (1998a)
Myska J., Chara Z.: The effect of a zwitterionic and cationic surfactant in turbulent flows. Exp. fluids 30, 229–236 (2001)
Hetsroni G., Mosyak A., Talmon Y., Bernheim-Groswasser A.: The effect of a cationic surfactant on turbulent flow patterns. J. Heat Transf. 125, 947–950 (2003)
Gasljevic K., Aguilar G., Matthys E.F.: An improved diameter scaling correlation for turbulent flow of drag-reducing polymer solutions. J. Non-Newtonian Fluid Mech. 84, 131–148 (1999)
Suzuki H., Fuller G.G., Nakayama T., Usui H.: Development characteristics of drag-reducing surfactant solution flow in a duct. Rheol. Acta 43, 232–239 (2004)
Aguilar G., Gasljevic K., Matthys E.F.: Asymptotes of maximum friction and heat transfer reductions for drag-redcing surfactant solutions. Int. J. Heat Transf. 44, 2835–2843 (2001)
Li F.-C., Kawaguichi Y.: Investigation on the characteristics of turbulence transport for momentum and heat in a drag-reducing surfactant solution flow. Phys. fluids 16(9), 3281–3295 (2004)
A.Kadoma I., Ylitalo, C., Van Egmond, J.: Structural transitions in wormlike micelles. Rheol. Acta 36(1), 1–12 (1997)
Hofmann S., Stern P., Myska J.: Rheological behavior and birefringence investigations on drag-reducing surfactant solutions of tallow-(tris-hydroxyethyl)-ammonium acetate/sodiumsalicylate mixtures. Rheol. Acta 33, 419–430 (1994)
Indrtono Y.S., Usui H., Suzuki H. et al.: Temperature and diameter effect on hydrodynamic characteristic of surfactant drag-reducing flows. Korea-Aust. Rheol. J. 17(4), 157–164 (2005)
Michael M.D., Schmidt G. et al.: The influence of a drag-reducing surfactant on a turbulent velocity field. J. Fluid Mech. 388, 1–20 (1999)
Bewersdorff H.W., Ohlendorf D.: The behaviour of drag-reducing cationic surfactant solutions. Colloid Polym. Sci. 266, 941–953 (1988)
Hu Y.T., Matthys E.F.: Characterization of micellar structure dynamics for a drag-reducing surfactant solution under shear: normal stress studies and flow geometry effects. Rheol. Acta 34, 450–460 (1995)
Hu Y.T., Matthys E.F.: Effect of metal ions and compounds on the rheological properties of the drag-reducing cationic surfactant solution exhibiting shear-induced structure formation. J. Colloid Interf. Sci. 186, 352–359 (1997)
Lu B., Zheng Y., Davis H.T., Scriven L.E., Talmon Y., Zakin J.L.: Effect of variations in counterion to surfactant ratio on rheology and microstructures of drag reducing cationic surfactant systems. Rheol. Acta 37, 528–548 (1988)
Zhang Y., Schmidt J., Talmon Y., Zakin J.L.: Co-solvent effects on drag reduction, rheological properties and micelle microstructures of cationic surfactants. J. Colloid Interf. Sci. 286, 696–709 (2005)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, H., Wang, D. & Chen, H. Experimental study on the effects of shear induced structure in a drag-reducing surfactant solution flow. Arch Appl Mech 79, 773–778 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00419-008-0251-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00419-008-0251-4