Abstract
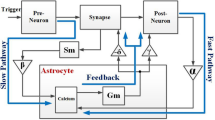
Based on recent findings, astrocytes, a subtype of glial cells, dynamically regulate the synaptic transmission of neuronal networks. In this research, a biologically inspired neuronal network model is constructed by connecting two Morris-Lecar neuron models. In this minimal network model, neuron–astrocyte interactions are considered in a functional-based procedure. Utilizing the developed model and according to the theoretical analysis carried out in the article, it is confirmed that, the astrocyte increases the threshold value of synchronization and provides appropriate feedback control in regulating the neural activities. Therefore, the healthy astrocyte has the potential to desynchronize the synchrony between two coupled neurons. Next, we investigate malfunction of the astrocyte in the regulatory feedback loop. Mathematically, we verify that pathologic astrocyte is no longer able to increase the synchronization threshold and therefore, it cannot compensate excessive increase in the excitation level. The main reason behind this is the fact that healthy astrocyte can optimally increase the input current of the individual neurons, while the so-called pathological astrocyte is unable to modify correctly the amount of this current. Consequently, disruptions of the signaling function of astrocyte initiate the hypersynchronous firing of neurons. In other words, reduction in neuron–astrocyte cross-talk will lead to synchronized firing of neurons. Therefore, our results propose that the astrocyte could have a key role in stabilizing neural activity.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ackert JM, Wu SH, Lee JC, Abrams J, Hu EH, Perlman I, Bloomfield SA (2006) Light-induced changes in spike synchronization between coupled ON direction selective ganglion cells in the mammalian retina. J Neurosci 26: 4206–4215
Amiri M, Bahrami F, Janahmadi M (2010) Functional modeling of astrocytes in epilepsy: a feedback system perspective. Neural Comput Appl. doi:10.1007/s00521-010-0479-0
Araque A, Parpura V, Sanzgiri RP, Haydon PG (1999) Tripartite synapses: glia, the unacknowledged partner. Trend Neurosci 22: 208–215
Benda J, Longtin A, Maler L (2006) A synchronization-desynchronization code for natural communication signals. Neuron 52: 347–358
Bowser DN, Khakh BS (2004) ATP excites interneurons and astrocytes to increase synaptic inhibition in neuronal networks. J Neurosci 24: 8606–8620
Chakravarthy N, Sabesan S, Iasemidis LD, Tsakalis K (2007) Modeling and controlling synchronization in a neuron level population model. Int J Neural Syst 17: 123–138
De Keyser J, Mostert JP, Koch MW (2008) Dysfunctional astrocytes as key players in the pathogenesis of central nervous system disorders. J Neurol Sci 267: 3–16
Ermentrout B, Wechselberger M (2009) Canards, clusters, and synchronization in a weakly coupled interneuron model. SIAM J Appl Dyn Syst 8: 253–278
Fellin T, Carmignoto G (2004) Neurone-to-astrocyte signaling in the brain represents a distinct multifunctional unit. J Physiol 559: 3–15
Fellin T, Pascual O, Haydon PG (2006) Astrocytes coordinate synaptic networks: balanced excitation and inhibition. J Physiol 21: 208–215
Garbo AD (2009) Dynamics of a minimal neural model consisting of an astrocyte, a neuron, and an interneuron. J Biol Phys 35: 361–382
Garbo AD, Barbi M, Chillemi S, Alloisio S, Nobile M (2007) Calcium signaling in astrocytes and modulation of neural activity. BioSystems 89: 74–83
Halassa MM, Fellin T, Haydon PG (2009) Tripartite synapses: Roles for astrocytic purines in the control of synaptic physiology and behavior. Neuropharmacology 57: 343–346
Hauptmann C, Popovych O, Tass PA (2005) Effectively desynchronizing deep brain stimulation based on coordinated delayed feedback stimulation via several sites: a computational study. Biol Cybernetic 93: 463–470
Haydon PG, Araque A (2002) Astrocytes as modulators of synaptic transmission. In: Volterra A, Magistretti PJ, Haydon PG (eds) The tripartite synapse: glia in synaptic transmission. Oxford University Press, New York, pp 185–198
Hertz L, Zielke HR (2004) Astrocytic control of glutamatergic activity: astrocytes as stars of the show. Trends in Neuroscience 27: 735–743
Hung J, Colicos MA (2008) Astrocytic Ca 2+ waves guide CNS growth cones to remote regions of neuronal activity. PLoS ONE 3: e3692
Koizumi S, Fujishita K, Tsuda M, Shigemoto-Mogami Y, Inoue K (2003) Dynamic inhibition of excitatory synaptic transmission by astrocyte-derived ATP in hyppocampal cultures. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 100: 11023–11028
Labourian IS, Rodrigues HM (2003) Synchronization of coupled equations of Hodgkin–Huxley type. Dynamic of continuous, discrete and impulsive systems. Ser A Math Anal 10: 463–476
Luo M, Wu Y, Peng J (2009) Washout filter aided mean field feedback desynchronization in an ensemble of globally coupled neural oscillators. Biol Cybernetic 101: 241–246
Mancilla JG, Lewis TJ, Pinto DJ, Rinzel J, Connors BW (2007) Synchronization of electrically coupled pairs of inhibitory interneurons in neocortex. J Neurosci 27: 2058–2073
Morris C, Lecar H (1981) Voltage oscillations in the barnacle giant muscle fiber. Biophys J 35: 193–213
Nadkarni S, Jung P (2004) Dressed neurons: modeling neural-glial interactions. Phys Biol 1: 35–41
Nadkarni S, Jung P (2007) Modeling synaptic transmission of the tripartite synapse. Phys Biol 4: 1–9
Nadkarni S, Jung P, Levine H (2008) Astrocytes optimize the synaptic transmission of information. PLoS Comput Biol 4: e1000088
Nedergaard M, Ransom B, Goldman SA (2003) New roles for astrocytes: Redefining the functional architecture of the brain. Trends Neurosci 26: 523–530
Newman EA (2003) New roles for astrocytes: regulation of synaptic transmission. Trends Neurosci 26: 536–542
Perea G, Araque A (2005) Properties of synaptically evoked astrocyte calcium signal reveal synaptic information processing by astrocytes. J Neurosci 25: 2192–2203
Pereira A Jr, Furlan FA (2009) On the role of synchrony for neuron–astrocyte interactions and perceptual conscious processing. J Biol Phys 35: 465–480
Pinsky PF, Rinzel J (1995) Synchrony measures for biological neural networks. Biol Cybernetic 73: 129–137
Popovych OV, Hauptmann C, Tass PA (2006) Control of neuronal synchrony by nonlinear delayed feedback. Biol Cybernetic 95: 69–85
Postnov DE, Koreshkov RN, Brazhe NA, Brazhe AR, Sosnovtseva OV (2009) Dynamical patterns of calcium signaling in a functional model of neuron-astrocyte networks. J Biol Phys 35: 425–445
Postnov DE, Ryazanov LS, Sosnovtseva OV (2007) Functional modeling of neural-glial interaction. BioSystems 89: 84–91
Rinzel J, Ermentrout GB (1989) Analysis of neural excitability and oscillations. In: Koch CH, Segev I (eds) Methods in neuronal modelling from synapses to networks. MIT Press, Cambridge, pp 135–169
Rodrigues HM (1996) Abstract methods for synchronization and applications. Appl Anal 62: 263–296
Seifert G, Carmignoto G, Steinhäuser C (2010) Astrocyte dysfunction in epilepsy. Brian Res Rev 63: 212–221
Silchenko AN, Tass PA (2008) Computational modeling of paroxysmal depolarization shifts in neurons induced by the glutamate release from astrocytes. Biol Cybernetic 98: 61–74
Steur E, Tyukin I, Nijmeijer H (2009) Semi-passivity and synchronization of diffusively coupled neuronal oscillators. Physica D 238: 2119–2128
Suffczynski P, Kalitzin S, Lopesda Silva FH (2004) Dynamics of non-convulsive epileptic phenomena modeled by a bistable neuronal network. Neuroscience 126(2): 467–484
Tass PA, Hauptmann C (2007) Therapeutic modulation of synaptic connectivity with desynchronizing brain stimulation International. J Psychophysiol 64: 53–61
Terman D, Rubin JE, Yew AC, Wilson CJ (2002) Activity patterns in a model for the subthalamopallidal network of the basal ganglia. J Neurosci 22: 2963–2976
Velazquez JLP (2003) Mathematics and the gap junctions: In-phase synchronization of identical neurons. Int J Neurosci 113: 1095–1101
Volman V, Ben-Jacob E, Levine H (2007) The astrocyte as a gatekeeper of synaptic information transfer. Neural Comput 19: 303–326
Voltarra A, Steinhäuser C (2004) Glial modulation of synaptic transmission in the hippocampus. GLIA 47: 249–257
Wang J, Lu Mi, Li H (2008) Synchronization of coupled equations of Morris–Lecar model. Commun Nonlinear Sci Numer Simul 13: 1169–1179
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Amiri, M., Montaseri, G. & Bahrami, F. On the role of astrocytes in synchronization of two coupled neurons: a mathematical perspective. Biol Cybern 105, 153–166 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00422-011-0455-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00422-011-0455-5