Abstract
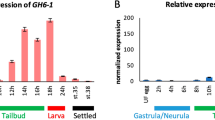
Urochordates are the only animals that produce cellulose, a polysaccharide existing primarily in the extracellular matrices of plant, algal, and bacterial cells. Here we report a Ciona intestinalis homolog of cellulose synthase, which is the core catalytic subunit of multi-enzyme complexes where cellulose biosynthesis occurs. The Ciona cellulose synthase gene, Ci-CesA, is a fusion of a cellulose synthase domain and a cellulase (cellulose-hydrolyzing enzyme) domain. Both the domains have no animal homologs in public databases. Exploiting this fusion of atypical genes, we provided evidence of a likely lateral transfer of a bacterial cellulose synthase gene into the urochordate lineage. According to fossil records, this likely lateral acquisition of the cellulose synthase gene may have occurred in the last common ancestor of extant urochordates more than 530 million years ago. Whole-mount in situ hybridization analysis revealed the expression of Ci-CesA in C. intestinalis embryos, and the expression pattern of Ci-CesA was spatiotemporally consistent with observed cellulose synthesis in vivo. We propose here that urochordates may use a laterally acquired “homologous” gene for an analogous process of cellulose synthesis.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Altschul SF, Madden TL, Schäffer AA, Zhang J, Zhang Z, Miller W, Lipman DJ (1997) Gapped BLAST and PSI-BLAST: a new generation of protein database search programs. Nucleic Acids Res 25:3389–3402
Andersson JO, Roger AJ (2002) Evolutionary analyses of the small subunit of glutamate synthase: gene order conservation, gene fusions, and prokaryote-to-eukaryote lateral gene transfers. Eukaryot Cell 1:304–310
Blanton RL, Fuller D, Iranfar N, Grimson MJ, Loomis WF (2000) The cellulose synthase gene of Dictyostelium. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 97:2391–2396
Brown JR (2003) Ancient horizontal gene transfer. Nat Rev Genet 4:121–132
Brown RM Jr (1996) The biosynthesis of cellulose. J Macromol Sci Pure Appl Chem A33:1345–1373
Bushman F (2002) Lateral DNA transfer. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press, Cold Spring Harbor, N.Y.
Cameron CB, Garey JR, Swalla BJ (2000) Evolution of the chordate body plan: new insights from phylogenetic analyses of deuterostome phyla. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 97:4469–4474
Charnock SJ, Henrissat B, Davies GJ (2001) Three-dimensional structures of UDP sugar glycosyltransferases illuminate the biosynthesis of plant polysaccharides. Plant Physiol 125:527–531
Dehal P, Satou Y, Campbell RK, Chapman J, Degnan B, De Tomaso A, Davidson B, Di Gregorio A, Gelpke M, Goodstein DM et al. (2002) The draft genome of Ciona intestinalis: insights into chordate and vertebrate origins. Science 298:2157–2167
Delmer DP (1999) Cellulose biosynthesis: exciting times for a difficult field of study. Ann Rev Plant Physiol Plant Mol Biol 50:245–276
Felsenstein J (1993) PHYLIP (Phylogeny Inference Package) version 3.5c. http://evolution.genetics.washington.edu/phylip.html
Gascuel O (1997) BIONJ: an improved version of the NJ algorithm based on a simple model of sequence data. Mol Biol Evol 14:685–695
Gianguzza M, Dolcemascolo G (1980) Morphological and cytochemical investigations on the formation of the test during the embryonic development of Ciona intestinalis. Acta Embryol Morphol Exp (ns) 1:225–239
Henrissat B, Davies G (1997) Structural and sequence-based classification of glycoside hydrolases. Curr Opin Struct Biol 7:637–644
Hirose E, Kimura S, Itoh T, Nishikawa J (1999) Tunic of pyrosomas, doliolids and salps (Thaliacea, Urochordata): morphology and cellulosic components. Biol Bull 196:113–120
Holder M, Roger AJ (2003) PUZZLEBOOT version 1.03. http://hades.biochem.dal.ca/Rogerlab/Software/software.html. Cited November 2003
Kimura S, Itoh T (1996) New cellulose synthesizing complexes (terminal complexes) involved in animal cellulose biosynthesis in the tunicate Metandrocarpa uedai. Protoplasma 194:151–163
Kimura S, Ohshima C, Hirose E, Nishikawa J, Itoh T (2001) Cellulose in the house of the appendicularian Oikopleura rufescens. Protoplasma 216:71–74
Koivula A, Ruohonen L, Wohlfahrt G, Reinikainen T, Teeri TT, Piens K, Claeyssens M, Weber M, Vasella A, Becker D et al. (2002) The active site of cellobiohydrolase Cel6 from Trichoderma reesei: the roles of aspartic acids D221 and D175. J Am Chem Soc 124:10015–10024
Koski LB, Golding GB (2001) The closest BLAST hit is often not the nearest neighbor. J Mol Evol 52:540–542
Krogh A, Larsson B, von Heijne G, Sonnhammer ELL (2001) Predicting transmembrane protein topology with a hidden Markov model: application to complete genomes. J Mol Biol 305:567–580
Kurland CG (2000) Something for everyone. EMBO Rep 1:92–95
Lacalli TC (2002) Vetulicolians—are they deuterostomes? Chordates? BioEssays 24:208–211
Lawrence JG, Ochman H (2002) Reconciling the many faces of lateral gene transfer. Trends Microbiol 10:1–4
Marks DL, Dominguez M, Wu K, Pagano RE (2001) Identification of active site residues in glucosylceramide synthase. J Biol Chem 276:26492–26498
Martin W, Rujan T, Richly E, Hansen A, Cornelsen S, Lins T, Leister D, Stoebe B, Hasegawa M, Penny D (2002) Evolutionary analysis of Arabidopsis, cyanobacterial, and chloroplast genomes reveals plastid phylogeny and thousands of cyanobacterial genes in the nucleus. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 99:12246–12251
Nobles DR, Romanovicz DK, Brown RM Jr (2001) Cellulose in cyanobacteria. Origin of vascular plant cellulose synthase? Plant Physiol 127:529–542
Rånby BG (1952) Physico-chemical investigations on animal cellulose (Tunicin). Ark Kemi 4:241–248
Read SM, Bacic T (2002) Prime time for cellulose. Science 295:59–60
Richmond PA (1991) Occurrence and functions of native cellulose. In: Haigler CH, Weimer PJ (eds) Biosynthesis and biodegradation of cellulose. Dekker, New York, pp 5–23
Richmond TA, Somerville CR (2000) The cellulose synthase superfamily. Plant Physiol 124:495–498
Rieppel O (1994) Homology, topology, and typology: the history of modern debates. In: Hall BK (eds) Homology: the hierarchical basis of comparative biology. Academic Press, London
Roberts AW, Roberts EM, Delmer DP (2002) Cellulose synthase (CesA) genes in the green alga Mesotaenium caldariorum. Eukaryot Cell 1:847–855
Romling U (2002) Molecular biology of cellulose production in bacteria. Res Microbiol 153:205–212
Satoh N (2003) The ascidian tadpole larva: comparative molecular development and genomics. Nat Rev Genet 4:285–295
Satou Y, Satoh N (1997) posterior end mark 2 (pem-2), pem-4, pem-5 and pem-6: Maternal genes with localized mRNA in the ascidian embryo. Dev Biol 192:467–481
Satou Y, Yamada L, Mochizuki Y, Takatori N, Kawashima T, Sasaki A, Hamaguchi M, Awazu S, Yagi K, Sasakura Y et al. (2002a) A cDNA resource from the basal chordate Ciona intestinalis. Genesis 33:153–154
Satou Y, Takatori N, Fujiwara S, Nishikata T, Saiga H, Kusakabe T, Shin-I T, Kohara Y, Satoh N (2002b) Ciona intestinalis cDNA projects: expressed sequence tag analyses and gene expression profiles during embryogenesis. Gene 287:83–96
Satou Y, Kawashima T, Kohara Y, Satoh N (2003) Large scale EST analyses in Ciona intestinalis: its application as northern blot analyses. Dev Genes Evol 213:314–318
Saxena IM, Brown RM Jr (2000) Cellulose synthases and related enzymes. Curr Opin Plant Biol 3:523–531
Schmidt HA, Strimmer K, Vingron M, von Haeseler A (2002) TREE-PUZZLE: maximum likelihood phylogenetic analysis using quartets and parallel computing. Bioinformatics 18:502–504
Shu DG, Chen L, Han J, Zhang XL (2001) An early Cambrian tunicate from China. Nature 411:472–473
Stasinopoulos SJ, Fisher PR, Stone BA, Stanisich VA (1999) Detection of two loci involved in (1→3)-β-glucan (curdlan) biosynthesis by Agrobacterium sp. ATCC31749, and comparative sequence analysis of the putative curdlan synthase gene. Glycobiology 9:31–41
Thompson JD, Gibson TJ, Plewniak F, Jeanmougin F, Higgins DG (1997) The CLUSTAL_X windows interface: flexible strategies for multiple sequence alignment aided by quality analysis tools. Nucleic Acids Res 25:4876–4882
Tusnády GE, Simon I (2001) The HMMTOP transmembrane topology prediction server. Bioinformatics 17:849–850
Villarreal LP, DeFilippis VR (2000) A hypothesis for DNA viruses as the origin of eukaryotic replication proteins. J Virol 74:7079–7084
Williamson RE, Burn JE, Hocart CH (2002) Towards the mechanism of cellulose synthesis. Trends Plant Sci 7:461–467
Zhang MQ (2002) Computational prediction of eukaryotic protein-coding genes. Nat Rev Genet 3:698–709
Acknowledgements
We thank A. Nakashima for discussions. We thank S. Kimura and Y. Sasakura for comments, N. Takatori for technical assistance with in situ hybridization, and C. Imaizumi for using UNIX environments. We are grateful to the Maizuru Fisheries Research Station of Kyoto University for collection of Ciona adults. K.N. and L.Y. were supported by JSPS Research Fellowships for Young Scientists. This research was also supported in part by 21COE (A14) from JSPS.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Edited by D. Tautz
Electronic Supplementary Material
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nakashima, K., Yamada, L., Satou, Y. et al. The evolutionary origin of animal cellulose synthase. Dev Genes Evol 214, 81–88 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00427-003-0379-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00427-003-0379-8