Abstract
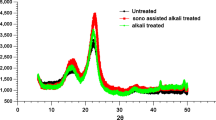
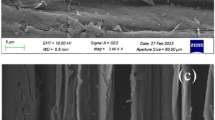
In this study, we carried out sodium hydroxide and sonication pretreatments of rapeseed straw (Brassica napus) to obtain monosugar suitable for production of biofuels. To optimize the pretreatment conditions, we applied a statistical response-surface methodology. The optimal pretreatment conditions using sodium hydroxide under sonication irradiation were determined to be 75.0 °C, 7.0 % sodium hydroxide, and 6.8 h. For these conditions, we predicted 97.3 % enzymatic digestibility. In repeated experiments to validate the predicted value, 98.9 ± 0.3 % enzymatic digestibility was obtained, which was well within the range of the predicted model. Moreover, sonication irradiation was found to have a good effect on pretreatment in the lower temperature range and at all concentrations of sodium hydroxide. According to scanning electron microscopy images, the surface area and pore size of the pretreated rapeseed straw were modified by the sodium hydroxide pretreatment under sonication irradiation.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alvira P, Tomas-Pejo E, Balesteros M, Negto MJ (2010) Pretreatment technologies for an efficient bioethanol production process based on enzymatic hydrolysis: a review. Bioresour Technol 101:4851–4861
Jeong GT, Park DH (2010) Production of sugars and levulinic acid from marine biomass Gelidium amansii. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 161:41–52
Fang LT, Gharpuray MM, Lee YH (1987) Cellulose hydrolysis biotechnology monographs. Springer, Berlin 55
Yunus R, Salleh SF, Abdullah N, Biak DRA (2010) Effect of ultrasonic pre-treatment on low temperature acid hydrolysis of oil palm empty fruit bunch. Bioresour Technol 101:9792–9796
Mosier N, Wyman C, Dale B, Elander R, Lee YY, Holtzapple M, Ladisch M (2005) Features of promising technologies for pretreatment of lignocellulosic biomass. Bioresour Technol 96:673–686
Balat M (2011) Production of bioethanol from lignocellulosic materials via the biochemical pathway: a review. Energy Conversat Manag 52:858–875
Silverstein RA, Chen Y, Sharma-Shivappa RR, Boyette MD, Osborne J (2007) A comparison of chemical pretreatment methods for improving saccharification of cotton stalks. Bioresour Technol 98:3000–3011
Tarkov H, Feist WC (1969) A mechanism for improving the digestibility of lignocellulosic materials with dilute alkali and liquid ammonia. Adv Chem Ser 95(1):197–218
Kang KE, Jeong GT, Park DH (2012) Pretreatment of rapeseed straw by sodium hydroxide. Bioprocess Biosyst Eng 35:705–713
Díaz MJ, Cara C, Ruiz E, Romero I, Moya M, Castro E (2010) Hydrothermal pre-treatment of rapeseed straw. Bioresour Technol 101(7):2428–2435
Lu X, Zhang Y, Angelidaki I (2009) Optimization of H2SO4-catalyzed hydrothermal pretreatment of rapeseed straw for bioconversion to ethanol: focusing on pretreatment at high solids content. Bioresour Technol 100(12):3048–3053
Castro E, Díaz MJ, Cara C, Ruiz E, Romero I, Moya M (2011) Dilute acid pretreatment of rapeseed straw for fermentable sugar generation. Bioresour Technol 102(2):1270–1276
Kang KE, Jeong GT, Sunwoo C, Park DH (2012) Pretreatment of rapeseed straw by soaking in aqueous ammonia. Bioprocess Biosyst Eng 35:77–84
Millet MA, Baker AJ, Scatter LD (1976) Physical and chemical pretreatment for enhancing cellulose. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 29:462–468
Akhtar MS, Saleem M, Akhtar MW (2001) Saccharification of lignocellulosic materials by the cellulases of Bacillus subtilis. Int J Agr Biol 3:199–202
Li Y, Ruan R, Chen PL, Liu Z, Pan X, Lin X (2004) Enzymatic hydrolysis of corn stover pretreated by combined dilute alkaline treatment and homogenization. Trans ASAE 47:821–825
García A, Alriols MG, Llano-Ponte R, Labidi J (2011) Ultrasound-assisted fractionation of the lignocellulosic material. Bioresour Technol 102(10):6326–6330
Nikolic′ S, Mojovic′a L, Rakin M, Pejin D, Pejin J (2010) Ultrasound-assisted production of bioethanol by simultaneous saccharification and fermentation of corn meal. Food Chem 122:216–222
Vilkhu K, Mawson R, Simons L, Bates D (2008) Applications and opportunities for ultrasound assisted extraction in the food industry—a review. Innov Food Sci Emerg 9:161–169
Shaw LE, Lee D (2009) Sonication of pulp and paper effluent. Ultrason Sonochem 16:321–324
Sun RC, Tomkinson J (2002) Comparative study of lignins isolated by alkali and ultrasound-assisted alkali extractions from wheat straw. Ultrason Sonochem 9:85–93
Sun RC, Tomkinson J, Ye J (2003) Physico-chemical and structural characterization of residual lignins isolated with TAED activated peroxide from ultrasound irradiated and alkali pre-treated wheat straw. Polym Degrad Stabil 79:241–251
Romdhane M, Gourdon C (2002) Investigation in solid-liquid extraction: influence of ultrasound. Chem Eng J 87:11–19
Koberg M, Cohen M, Ben-Amotz A, Gedanken A (2011) Bio-diesel production directly from the microalgae biomass of Nannochloropsis by microwave and ultrasound radiation. Bioresour Technol 102:4265–4269
Patist A, Bates D (2008) Ultrasonic innovations in the food industry: from the laboratory to commercial production. Innov Food Sci Emerg 9(2):147–154
Ebringerová A, Hromádková Z (2002) Effect of ultrasound on the extractability of corn bran hemicelluloses. Ultrason Sonochem 9:225–229
Liu CF, Sun RC, Quin MH, Zhang AP, Ren JL, Xu F, Ye J, Wu SB (2007) Chemical modification of ultrasound-pretreated sugarcane bagasse with maleic anhydride. Ind Crops Prod 26:212–219
Toma M, Vinatoru M, Paniwnyk L, Mason TJ (2007) Investigation of the effects of ultrasound on vegetal tissues during solvent extraction. Ultrason Sonochem 8:137–142
Jeong GT, Park DH (2009) Optimization of biodiesel production from castor oil using response surface methodology. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 156:431–441
Selig M, Weiss N, Ji Y (2008) Enzymatic saccharification of lignocellulosic biomass in laboratory analytical procedure. National Renewable Energy Laboratory, Golden
Acknowledgments
This research was supported by Basic Science Research Program through the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) funded by the Ministry of Education, Science and Technology (2012R1A1A2006718).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
G.-T. Jeong and D.-H. Park have equally contributed as corresponding author to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kang, K.E., Jeong, GT. & Park, DH. Rapeseed-straw enzymatic digestibility enhancement by sodium hydroxide treatment under ultrasound irradiation. Bioprocess Biosyst Eng 36, 1019–1029 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00449-012-0854-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00449-012-0854-6