Abstract
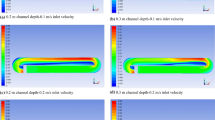
The open raceway ponds are nowadays the most used large-scale reactors for microalgae culture. To avoid the stacking of microalgae, the paddle wheels are the most widely used to circulate and mix the culture medium. In this paper, a numerical simulation using computational fluid dynamics (CFD) was used to investigate the hydrodynamic characteristics of open raceway ponds with different types of paddle wheels (the traditional paddle wheels and the novel paddle wheels with specially inclined angle of the blades). The particle image velocimetry (PIV) was used to validate the reliability of the CFD model. The CFD simulation results showed that the novel raceway pond with 15° inclined angle of the blades had the best mixing efficiency under the same power consumption. Lastly, the results of microalgae culture experiments showed that the growth rates of Chlorella pyrenoidosa in the novel raceway pond with 15° inclined angle of the blades were higher than those in the traditional reactor. The results of the culture experiments and CFD simulations were identical with each other. Therefore, a novel paddle wheel with 15° inclined angle of the blades was obtained for better microalgae cultivation.











Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- L :
-
Length of open raceway ponds, m
- W :
-
Width of open raceway ponds, m
- H :
-
Height of open raceway ponds, m
- a :
-
Inclination angle to agitation axis for paddle wheel blades, °
- TKE:
-
Turbulent kinetic energy, J kg−1
- U :
-
Average velocity, m s−1
- U z :
-
Average velocity magnitude along the light direction, m s−1
- U x :
-
Average velocity magnitude along the horizontal direction, m s−1
- D z :
-
The volume percentage of dead zone, %
- h 0 :
-
Depth of deionized water, mm
- H :
-
Depth of water, m
- V tip :
-
Impeller tip velocity, m s−1
References
Pulz O, Gross W (2004) Valuable products from biotechnology of microalgae. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 65:635–648
Huang JJ, Xia J, Jiang W, Li Y, Li J (2015) Biodiesel production from microalgae oil catalyzed by a recombinant lipase. Bioresour Technol 180:47–53
Brune DE, Lundquist TJ, Benemann JR (2012) Microalgal biomass for greenhouse gas reductions: potential for replacement of fossil fuels and animal feeds. J Environ Eng 135:1136–1144
Borowitzka MA, Moheimani NR (2013) Algae for biofuels and energy. Springer, Netherlands
Mendoza JL, Granados MR, Godos ID, Acién FG, Molina E, Banks C, Heaven S (2013) Fluid-dynamic characterization of real-scale raceway reactors for microalgae production. Biomass Bioenergy 54:267–275
Fox RO (2006) CFD models for analysis and design of chemical reactors. Adv Chem Eng 31:231–305
Xia JY, Wang SJ, Zhang SL (2008) Computational investigation of fluid dynamics in a recently developed centrifugal impeller bioreactor. Biochem Eng J 38:406–413
Perner-Nochta I, Posten C (2007) Simulation of light intensity variation in photobioreactors. J Biotechnol 131:276–285
Perner I, Posten C, Broneske J (2003) CFD Optimization of a plate photobioreactor used for cultivation of microalgae. Eng Life Sci 3:287–291
Sato T, Yamada D, Hirabayashi S (2010) Development of virtual photobioreactor for microalgae culture considering turbulent flow and flashing light effect. Energy Convers Manag 51:1196–1201
Sato T, Usuib S, Tsuchiya Y (2006) Invention of outdoor closed type photobioreactor for microalgae. Energy Convers Manag 47:791–799
Su Z, Kang R, Shi S (2010) Study on the destabilization mixing in the flat plate photobioreactor by means of CFD. Biomass Bioenergy 34:1879–1884
Yu G, Li Y, Shen G (2009) A novel method using CFD to optimize the inner structure parameters of flat photobioreactors. J Appl Phycol 21:719–727
Pruvost J, Pottier L, Legrand J (2006) Numerical investigation of hydrodynamic and mixing conditions in a torus photobioreactor. Chem Eng Sci 61:4476–4489
Wu LB, Li Z, Song YZ (2010) Hydrodynamic conditions in designed spiral photobioreactors. Bioresour Technol 101:298–303
Wu LB, Li Z, Song YZ (2009) Numerical investigation of flow characteristics and irradiance history in a novel photobioreactor. Afr J Biotechnol 8:4672–4679
Wang HF, Liu ZH, Guo FS, Zhang CG (2004) Estimation of turbulent kinetic energy dissipation rate In channel flow by PIV. J Chem Ind Eng 55:1067–1071
Jakubowski M, Wyczalkowski W, Poreda A (2015) Flow in a symmetrically filled whirlpool: CFD modelling and experimental study based on particle image velocimetry (PIV). J Food Eng 145:64–72
Sultana T, Morrison G, Taylor R, Rosengarten G (2015) Numerical and experimental study of a solar micro concentrating collector. Sol Energy 112:20–29
Amokrane A, Charton S, Lamadie S, Paisant JF, Puel F (2014) Single-phase flow in a pulsed column: particle image velocimetry validation of a CFD based model. Chem Eng Sci 114:40–50
Stogiannis IA, Passos AD, Mouza AA, Paras SV, Pěnkavová V, Tihon J (2014) Flow investigation in a microchannel with a flow disturbing rib. Chem Eng Sci 119:65–76
Pruvost J, Pottier L, Legrand J (2006) Numerical investigation of hydrodynamic and mixing conditions in a torus photobioreactor. Chem Eng Sci 61:4476–4489
Lin C, Li YG, Wang WL, Shen GM, Chen JP, Wu HX, Huang JK (2009) Numerical and experimental investigation of a novel flat-photobioreactor with multistage-separator. J Chem Eng Chin Univ 23:263–269
Chiaramonti D, Prussi M, Casini D, Tredici MR, Rodolfi L, Bassi N, Zittelli GC, Bondioli P (2013) Review of energy balance in raceway ponds for microalgae cultivation: re-thinking a traditional system is possible. Appl Energy 102:101–111
Ketheesan B, Nirmalakhandan N (2011) Development of a new airlift-driven raceway reactor for algal cultivation. Appl Energy 88:3370–3376
Hreiz R, Sialve B, Morchain J (2014) Experimental and numerical investigation of hydrodynamics in raceway reactors used for algaculture. Chem Eng J 250:230–239
Chung K, Barigou M, Simmons M (2007) Reconstruction of 3-D flow field inside miniature stirred vessels using a 2-D PIV technique. Chem Eng Res Des 85:560–567
Sheng J, Meng H, Fox R (2000) A large eddy PIV method for turbulence dissipation rate estimation. Chem Eng Sci 55:4423–4434
Zhu F, Huang J, Chen J, Li Y (2012) CFD simulation and optimization of an open raceway photo-bioreactor. Chem Ind Eng Prog 31:1184–1192
Meng C, Huang J, Ye C (2015) Comparing the performances of circular ponds with different impellers by CFD simulation and microalgae culture experiments. Bioprocess Biosyst Eng 38:1347–1363
Ge C, Wang J, Gu X, Feng L (2014) Application of PIV and CFD in impeller design and optimization. Chem Pharma Eng 35:29–33
Su ZF, Kang RJ, Shi SY, Cong W, Cai ZL (2010) Study on the destabilization mixing in the flat plate photobioreactor by means of CFD. Biomass Bioenergy 34:1879–1884
Huang J, Li Y, Wan M, Yan Y, Feng F, Qu X, Wang J, Shen G, Li W, Fan J (2014) Novel flat-plate photobioreactors for microalgae cultivation with special mixers to promote mixing along the light gradient. Bioresour Technol 159:8–16
Xu L, Liu R, Wang F, Liu CZ (2012) Development of a draft-tube airlift bioreactor for Botryococcus braunii with an optimized inner structure using computational fluid dynamics. Bioresour Technol 119:300–305
Sompech K, Chisti Y, Srinophakun T (2012) Design of raceway ponds for producing microalgae. Rev Environ Sci Bio 3:387–397
Han F, Huang J, Li Y, Wang W, Fan J, Shen G (2012) Enhancement of microalgal biomass and lipid productivities by a model of photoautotrophic culture with heterophic cells as seed. Bioresour Technol 118:431–437
Hou SD, Zhang Z, Wang YC, Shi LT (2000) Numerical simulation of turbulent flow in stirred tank agitated by axial impeller. J Chem Ind Eng 51:70–76
David C, Matteo P, David C, Mario R, Tredici Liliana R, Niccolo B, Graziella CZ, Paolo B (2013) Review of energy balance in raceway ponds for microalgae cultivation: re-thinking a traditional system is possible. Appl Energ 102:101–111
Acknowledgments
This research was funded by National Basic Research Program China (973 Program: 2011CB200903).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
F. Zeng and J. Huang contributed equally to this study and share first authorship.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zeng, F., Huang, J., Meng, C. et al. Investigation on novel raceway pond with inclined paddle wheels through simulation and microalgae culture experiments. Bioprocess Biosyst Eng 39, 169–180 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00449-015-1501-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00449-015-1501-9