Abstract.
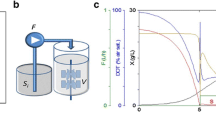
A series of continuous-culture runs were conducted on a T7-expression-based two-plasmid system for heat induction of recombinant streptokinase. Different dilution rates were used and it was observed that a high dilution rate of 0.3 h–1, both before and after induction, helped in increasing the product concentration to a fairly high level of 421 plasmin units per ml. Accumulation of active streptokinase, which is toxic to the cells, in the periplasm also resulted in the loss of cell viability. Thus, a slow washout was observed after induction and in just 2.5 h all the growing cells were those which had lost the ability to produce streptokinase. Increasing the selection pressure by using high dosage of antibiotic concentration (5×) in the feed helped in reducing the instability of the culture.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Electronic Publication
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yazdani, .S., Mukherjee, .K. Continuous-culture studies on the stability and expression of recombinant streptokinase in Escherichia coli . Bioprocess Biosyst Eng 24, 341–346 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1007/s004490100221
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s004490100221