Abstract
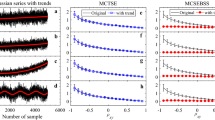
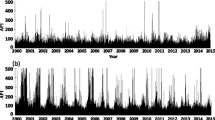
In terms of the chaos theory, the phase-space-reconstruction method has been employed to describe the multi-dimensional phase space for the time series of air pollution index (API) during the past 10 years in Lanzhou, northwest China. The mutual information and Cao method were used to determine the reconstruction parameters, and the characteristic quantities including the Lyapunov exponent and the correlation dimension were calculated respectively. As a result, the correlation dimensions were fractioned, and the maximum Lyapunov exponent (λ 1) > 0. It shows that these presented the obvious chaotic characteristics that resulted from the evolution of non-linear chaotic dynamic system in the time series of air pollution index over the past 10 years. In the meanwhile, three or even four main dynamic variables were discussed here that could effectively interpret the changes of air pollution index time series and their causes. Some reasonable preventive countermeasures were thus put forward. These findings might provide a scientific basis for probing further into the regional complexity and evolution of the time series of air pollution index.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
An XQ, Zuo HC, Chen LJ (2007) Atmospheric environmental capacity of SO2 in winter over Lanzhou in China: a case study. Adv Atmos Sci 24:688–699
Anh V, Duc H, Azzi M (1997) Modeling anthropogenic trends in air quality data. J Air Waste Manage Assoc 47:66–71
Ardalani-Farsa M, Zolfaghari S (2010) Chaotic time series prediction with residual analysis method using hybrid Elman–NARX neural networks. Neurocomputing 73:2540–2553
Cao LY (1997) Practical method for determining the minimum embedding dimension of a scalar time series. Phys D 110:43–50
Chen JL, Islam S, Biswas P (1998) Nonlinear dynamics of hourly ozone concentrations: nonparametric short term prediction. Atmos Environ 32:1839–1848
Chen L, Omaye ST, Yang W (2001) A comparison of two statistical models for analyzing the association between PM10 and hospital admissions for chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Toxicol Mech Method 11:233–246
Chu PC, Chen YC, Lu SH (2008a) Atmospheric effects on winter SO2 pollution in Lanzhou, China. Atmos Res 89:365–373
Chu PC, Chen YC, Lu SH, Li ZC, Lu YQ (2008b) Particulate air pollution in Lanzhou China. Environ Int 34:698–713
Dong ZL, He HG, Yu T, Li HY (2009) Correlation analysis on influencing factors of the atmospheric environmental quality in Lanzhou City. J Arid Land Resour Environ 23(12):49–53 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Fraser AM, Swinney HL (1986) Independent coordinates for strange attractors from mutual information. Phys Rev A 33:1134–1140
Frazier C, Kockelman KM (2004) Chaos theory & transportation systems: an instructive example. Transp Res Rec 1897:9–17
Gomez-Sanchis J, Martin-Guerrero J, Soria-Olivas E, Vila-Frances J, Carrasco J, del Valle-Tascon S (2006) Neural networks for analysing the relevance of input variables in the prediction of tropospheric ozone concentration. Atmos Environ 40:6173–6180
Grassberger P, Procaccia I (1983a) Measuring the strangeness of strange attractor. Phys D 9:189–208
Grassberger P, Procaccia I (1983b) Estimation of the Kolmogorov entropy from a chaotic signal. Phys Rev A 28:2591–2593
Harvey AC (1989) Forecasting, structural time series models and the Kalman filter. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge
Ho DS, Juang LC, Liao YY, Wang CC, Lee CK, Hsu TC, Yang YS (2004) The temporal variations of PM10 concentration in Taipei: Fractal Approach. Aerosol Air Qual Res 4:37–54
Horowitz J, Barakat S (1979) Statistical analysis of the maximum concentration of an air pollutant: effects of autocorrelation and non-stationarity. Atmos Environ 13:811–818
Hu YQ, Zhang Q (1999) Atmospheric pollution mechanism and prevention countermeasure of the Lanzhou. China Environ Sci 19(2):119–122 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Ibarra-Berastegi G, Elias A, Barona A, Saenz J, Ezcurra A, Argadona JD (2008) From diagnosis to prognosis for forecasting air pollution using neural networks: air pollution monitoring in Bilbao. Environ Modell Softw 23:622–637
Jazwinski AH (1970) Stochastic processes and filtering theory. Academic Press, New York
Jiang JH, Peng XD (2002) Numerical study on air pollution concentration over Lanzhou in winter under complex terrain. Plateau Meteorol 21(1):1–7 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Jiang JH, Chen YC, Peng XD, Hu F, Li L (2001) Contributions of industrial and residential sources to atmospheric SO2 concentration in winter over Lanzhou. Plateau Meteorol 20(Suppl):15–21 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Kin HS, Eykholt R, Salas JD (1999) Nonlinear dynamics, delay time, and embedding window. Phys D 127:48–60
Kocak K, Saylan L, Sen O (2000) Nonlinear time series prediction of O3 concentration in Istanbul. Atmos Environ 34:1267–1271
Kugiumtzis D (1996) State space reconstruction parameters in the analysis of chaotic time series: the role of the time window length. Phys D 95:13–28
Kukkonen J, Partanen L, Karppinen A, Ruuskanen J, Junninen H, Kolehmainen M, Niska H, Dorling S, Chatterton T, Foxall R, Cawley G (2003) Extensive evaluation of neural network models for the prediction of NO2 and PM10 concentrations, compared with a deterministic modelling system and measurements in central Helsinki. Atmos Environ 37:4539–4550
Kumar U, Prakash A, Jain VK (2008) Characterization of chaos in air pollutants: a Volterra–Wiener–Korenberg series and numerical Titration approach. Atmos Environ 42:1537–1551
Kurt A, Gulbagci B, Karaca F (2008) An online air pollution forecasting system using neural networks. Environ Int 34:592–598
Lee CK (2002) Multifractal characteristics in air pollutant concentration time series. Water Air Soil Pollut 135:389–409
Lee CK, Lin SH (2008) Chaos in air pollutant concentration (APC) time series. Aerosol Air Qual Res 8(4):381–391
Lee CK, Ho DS, Yu CC, Wang CC (2003) Fractal analysis of temporal variation of air pollutant concentration by box counting. Environ Modell Softw 18:243–251
Lee IF, Biswas P, Islam S (1994) Estimation of the dominant degrees of freedom for air pollutant concentration data: applications to ozone measurements. Atmos Environ 28:1707–1714
Li J, Tang H (1998) Model for predicting the acidity of precipitation in China. China Environ Sci 18(1):8–11 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Li IF, Biswas P, Islam S (1994) Estimation of the dominant degrees of freedom for air pollutant concentration data: applications to ozone measurements. Atmos Environ 28:1707–1714
Liang SX, Wu H, Li ZC, Zheng J, Dong ZM (2010) Fuzzy mathematics-based comprehensive evaluation of dynamics of atmospheric environmental quality. J Arid Land Resour Environ 24(6):77–81 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Liu LC, Fan Y, Wu G, Wei YM (2007) Using LMDI method to analyze the change of China’s industrial CO2 emissions from final fuel use: an empirical analysis. Energy Policy 35:5892–5900
Lorenz EN (1963) Detemministic nonperiodic flow. J Atmos Sci 20:130–141
Lorenz EN (1993) The essence of chaos. UCL Press, Los Angeles
Ma JH, Liu LX (2007) Testing for nonlinearity in time series of monthly rainfall in Yunnan Province. J Syst Eng 22(6):561–567 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Martinerie JM, Albano AM, Mees AI, Rapp PE (1992) Mutual information, strange attractors, and the optimal estimation of dimension. Phys Rev A 45:7058–7064
Millán H, Ghanbarian-Alavijeh B, García-Fornaris I (2010) Nonlinear dynamics of mean daily temperature and dewpoint time series at Babolsar, Iran, 1961–2005. Atmos Res 98:89–101
OECD (2007) OECD Annual Report 2007: Environmental Performance Review of China. The Public Affairs Division, Public Affairs and Communications Directorate, Paris
Ott E, Sauer T, Yorke JA (1994) Coping with Chaos. Wiley, New York
Packard NH, Crutchfield JP, Farmers JD, Shaw RS (1980) Geometry from a time series. Phys Rev Lett 45:712–716
Poon C, Barahona M (2001) Titration of chaos with added noise. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 98:7107–7112
Raga GB, Le Moyne L (1996) On the nature of air pollution dynamics in Mexico City—I, nonlinear analysis. Atmos Environ 30:3987–3993
Rosenstein MT, Collins JJ, De Luca CJ (1993) A practical method for calculating largest Lyapunov exponents from small data sets. Phys D 65:117–134
Saarikoski S, Sillanpää M, Sofiev M, Timonen H, Saarnio K, Teinilä K, Karppinen A, Kukkonen J, Hillamo R (2007) Chemical composition of aerosols during a major biomass burning episode over northern Europe in spring 2006: experimental and modelling assessments. Atmos Environ 41:3577–3589
Sannasiraj SA, Zhang H, Vladan Babovic, Chan ES (2004) Enhancing tidal prediction accuracy in a deterministic model using chaos theory. Adv Water Resour 27:761–772
Schlink U, Stephen D, Emil P, Giuseppe N, Gavin C, Heikki J, Alison G, Rob F, Krystof E (2003) A rigorous inter-comparison of ground-level ozone predictions. Atmos Environ 37:3237–3253
Schlink U, Herbarth O, Richter M, Dorling S, Nunnari G, Cawley G, Pelikan E (2006) Statistical models to assess the health effects and to forecast ground-level ozone. Environ Modell Softw 21:547–558
Shang KZ, Da CY, Fu YZ, Wang SG, Yang DB (2001) The stable energy in Lanzhou city and the relations between air pollution and it. Plateau Meteorol 20(1):76–81 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Shi K, Liu CQ, Ai NS, Zhang XH (2008) Using three methods to investigate time-scaling properties in air pollution indexes time series. Nonlinear Anal Real World Appl 9:693–707
Sivakumar B (2000) Chaos theory in hydrology: important issues interpretations. J Hydrol 227:1–20
Sivakumar B (2004) Chaos theory in geophysics: past, present and future. Chaos Solitons Fract 19:441–462
Sivakumar B, Wallender WW, Horwath WR, Mitchell JP (2007) Nonlinear deterministic analysis of air pollution dynamics. Adv Complex Syst 10:581–597
Slini T, Kaprara A, Karatzas K, Moussiopoulos N (2006) PM10 forecasting for Thessaloniki, Greece. Environ Modell Softw 21:559–565
Song HJ, Miao CY, Shen ZQ, Roel W, Maja DH, Franck C (2010) Design of fuzzy cognitive maps using neural networks for predicting chaotic time series. Neural Netw 23:1264–1275
Sun YB, Piyamarn S, Vladan B, Chan ES (2009) Efficient data assimilation method based on chaos theory and Kalman filter with an application in Singapore Regional Model. J Hydro Environ Res 3:85–95
Ta WQ, Wang T, Xiao HL, Zhu XY, Xiao Z (2004) Gaseous and particulate air pollution in the Lanzhou Valley, China. Sci Total Environ 320:163–176
Takens F (1981) Detecting strange attractors in fluid turbulence. Lect Notes Math 898:366–381
Tao JH, Huang YX, Lu DR (2007) Influence of sand-dust activities in Hexi Corridor on PM10 concentration in Lanzhou and its assessment. J Desert Res 27(4):272–276 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Tao ZN, Geoffrey H, Kieran D (2010) An economic analysis of Midwestern US criteria pollutant emissions trends from 1970 to 2000. Ecol Econ 691:666–1674
Tian QX, Zhou LZ, Wang R, Tian ZM (2001) The pollution law of the metal and nonmetal elements in the aerosol in Lanzhou. Environ Monitor China 17(7):18–22 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Tunç GI, Türüt-Aşik S, Akbostancı E (2009) A decomposition analysis of CO2 emissions from energy use: Turkish case. Energy Policy 37:4689–4699
Wang JM (1992) Turbulence characteristics in an urban atmosphere of complex terrain. Atmos Environ 26:2717–2724
Wang XK, Lu WZ (2006) Seasonal variation of air pollution index: Hong Kong case study. Chemosphere 63:1261–1272
Wang SG, Yang M, Qi B, Xin CL, Yang MF (1999) Influence of sand-dust storms occurring over the Gansu Hexi district on the air pollution in Lanzhou city. J Desert Res 19(4):354–358 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Wang SG, Jiang DB, Yang DB, Shang KZ, Qi B (2000) A study on characteristics of change of maximum mixing depths in Lanzhou. Plateau Meteorol 19(3):363–370 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Wang SG, Yuan W, Shang KZ (2006) The impacts of different kinds of dust events on PM10 pollution in northern China. Atmos Environ 40:7975–7982
Wang SG, Feng XY, Zeng XQ, Ma YX, Shang KZ (2009) A study on variations of concentrations of particulate matter with different sizes in Lanzhou, China. Atmos Environ 43:2823–2828
Windsor HL, Toumi R (2001) Scaling and persistence of UK pollution. Atmos Environ 35:4545–4556
Wolf A, Swift JB, Swinny HL et al (1985) Determining Lyapunov exponents from a time serises. Phys D 16:285–317
Xia DS, Yang LP, Ma JY, Yu Y, Wang G, Chen FH (2007) Magnetic characteristics of dustfall in urban area of north China and its environmental significance. Sci China Ser D Earth Sci 50:1724–1732
Xie XJ, Li J, Wang ZF (2010) Numerical simulation of diurnal variations of the air pollutants in winter of Lanzhou city. Clim Environ Res 15(5):695–703 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Xu H, Zhai J, Liu ZQ, Zhang JQ (2003) Effect of energy structure on atmospheric environment of Lanzhou. Urban Environ Urban Ecol 16(1):73–75 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Zhang Q (2003) A study of the interaction between pollutants concentration and the climatic and environmental factors of Lanzhou. J Lanzhou Univ (Nat Sci) 39(1):99–106 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Zhang W, Hu B, Chen CH, Du P, Zhang L, Feng GH (2004) Scattering properties of atmospheric aerosols over Lanzhou city and applications using an integrating nephelometer. Adv Atmos Sci 21:848–856
Zhang N, Li LP, Wang SG, Wang D, Wang Z (2008) The composition characteristics of main inorganic ions in atmospheric aerosol of the urban and atmospheric background in Lanzhou city in winter. Environ Chem 27(4):494–498 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Zhu JL, Liu ZG (2003) Long-range persistence of acid deposition. Atmos Environ 37:2605–2613
Acknowledgments
The authors are grateful to Professor Yong Li of Institute of Mountain Hazards and Environment, Chinese Academy of Sciences and two anonymous reviewers for their insightful comments and valuable advice. This study is financially supported by the Program for New Century Excellent Talents in University of China (Grant No. NCET-08-0379).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yu, B., Huang, C., Liu, Z. et al. A chaotic analysis on air pollution index change over past 10 years in Lanzhou, northwest China. Stoch Environ Res Risk Assess 25, 643–653 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00477-011-0471-y
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00477-011-0471-y