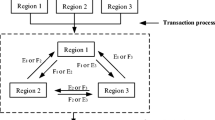
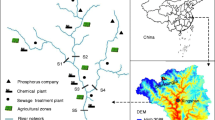
Abstract
This paper presents the development and the first application of an inexact quadratic programming (IQP) approach for sustainable water supply under multiple uncertainties. The developed IQP improves conventional nonlinear programming by tackling multiple uncertainties within an individual parameter; IQP is also superior to existing inexact methods due to its reflection of economies of scale and reduction of computational requirements. An interactive solution algorithm with high computational efficiency was also proposed. The application of IQP to long-term planning of a multi-source multi-sector water supply system demonstrated its applicability. The close reflection of system complexities, such as multiple uncertainties, scale economies and dynamic parameters, could enhance the robustness of the optimization process as well as the acceptability of obtained results. Corresponding to varied system conditions and decision priorities, the interval solutions from IQP could help generate a series of long-term water supply strategies under a number of economic, environmental, ecological, and water-security targets.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abrishamchi A, Marino MA, Afshar A (1991) Reservoir planning for irrigation district. J Water Resour Plann Manag 117:74–85
Aladenola OO, Adeboye OB (2010) Assessing the potential for rainwater harvesting. Water Resour Manage 24:2129–2137
ASCE Task Committee on Sustainability Criteria (1998) Sustainability criteria for water resource systems. Water Resources Planning and Management Division—ASCE, Reston
Beck MB (1987) Water quality modeling: a review of the analysis of uncertainty. Water Resour Res 23(8):1393–1442
Brookshire DS, Whittington D (1993) Water resources issues in the developing countries. Water Resour Res 29:1883–1888
Cai YP, Huang GH, Lin QG, Nie XH, Tan Q (2009) An optimization-model-based interactive decision support system for regional energy management systems planning under uncertainty. Expet Syst Appl 36(2):3470–3482
Cai YP, Huang GH, Tan Q, Chen B (2010) Identification of optimal strategies for improving eco-resilience to floods in ecologically vulnerable regions of a wetland. Ecol Model 222(2):360–369
CDDC, Centre for Digital Discourse and Culture (2004) Choices and challenges project: sharing the earth’s water supply. Virginia Tech, Blacksburg
Chang NB (2005) Sustainable water resources management under uncertainty. Stoch Environ Res Risk Assess 19:97–98
Chen MJ, Huang GH (2001) A derivative algorithm for inexact quadratic program—application to environmental decision-making under uncertainty. Eur J Oper Res 128:570–586
Clark RM, Dorsey P (1982) A model of costs for treating drinking water. J Am Water Works Assoc 74(12):618–627
Clark RM, Sivaganesan M, Selvakumar A, Sethi V (2002) Cost models for water supply distribution systems. J Water Resour Plann Manag 128(5):312–321
Eker I, Kara T (2003) Operation and control of a water supply system. ISA Trans 42(3):461–473
Escudero LF (2000) WARSYP: a robust modeling approach for water resources system planning under uncertainty. Ann Oper Res 95:313–339
Fry A (2005) Water facts and trends world business council for sustainable development, Switzerland
Gao S, Chen B, Yang ZF, Huang GH (2010) Network environ analysis of spatial arrangement for reserves in Wuyishan nature reserve, China. J Environ Inform 15(2):74–86
Han Y, Xu SG, Xu XZ (2008) Modeling multisource multiuser water resources allocation. Water Resour Manag 22:911–923
He YT, Li WH, Li GC (2004) Ecological water requirement of forests in Loess Plateau. Environ Sci (Chinese) 25(3):35–39
Hoekstra AY (2006) The global dimension of water governance: nine reasons for global arrangements in order to cope with local problems. Value of Water Research Report, UNESCO-IHE Institute for Water Education, Delft
Huang GH (1996) IPWM: an interval parameter water quality management model. Eng Optim 26:79–103
Huang GH, Cohen SJ, Yin YY, Bass B (1996) Incorporation of inexact dynamic optimization with fuzzy relation analysis for integrated climate change impact study. J Environ Manag 48(1):45–68
Huang GH, Linton JD, Yeomans JS, Yoogalingam R (2005) Policy planning under uncertainty: efficient starting populations for simulation-optimization methods applied to municipal solid waste management. J Environ Manag 77:22–34
Inuiguchi M, Ichihashi H, Tanaka H (1990) Fuzzy programming: a survey of recent developments. In: Slowinski R, Teghem J (eds) Stochastic versus fuzzy approaches to multiobjective mathematical programming under uncertainty. Kluwer Academic Publishers, Dordrecht, pp 45–70
Jairaj PG, Vedula S (2000) Multireservoir system optimization using fuzzy mathematical programming. Water Resour Mange 14:457–472
Julien B (1994) Water quality management with imprecise information. Eur J Oper Res 76:15–27
Karmakar S, Mujumdar PP (2007) A two-phase grey fuzzy optimization approach for water quality management of a river system. Adv Water Resour 30:1218–1235
Kashaigili JJ, Mccartney M, Mahoo HF (2007) Estimation of environmental flows in the Great Ruaha River Catchment, Tanzania. Phys Chem Earth 32:1007–1014
King JM, Tharme RE, De Villiers MS (2002) Environmental flow assessments for rivers: manual for the building block methodology. Water Research Commission Technology Transfer Report, Water Research Commission, Pretoria
Lee YW, Bogardi I, Kim JH (2000) Decision of water supply line under uncertainty. Water Resour Res 34:3371–3379
Loucks DP, Stakhiv EZ, Martin LR (2000) Sustainable water resources management. J Water Resour Plann Manag 126(2):43–47
Lund JR, Israel M (1995) Optimization of transfers in urban water supply planning. J Water Resour Plann Manag 121(1):41–48
Maqsood I, Huang GH, Huang YF, Chen B (2005) ITOM: an interval-parameter two-stage optimization model for stochastic planning of water resources systems. Stoch Environ Res Risk Assess 19(2):125–133
Min QW, Geng YH (2005) Estimation and analysis of ecological water requirement in the Jinghe watershed. Resour Sci (Chinese) 27(4):14–17
Mousavi H, Ramamurthy AS (2000) Optimal design of multi-reservoir systems for water supply. Adv Water Resour 23:613–624
Rosenberg DE, Lund JR (2009) Modeling integrated decision for a municipal water system with recourse and uncertainties: Amman, Jordan. Water Resour Manag 23:85–115
Sutardi, Cheng TCE, Goulter I (1991) Water resources planning under budgetary uncertainty: the case in Indonesia. Int J Prod Econ 25:201–217
Sutardi, Bector CR, Goulter I (1995) Multiobjective water resources investment planning under budgetary uncertainty and fuzzy environment. Eur J Oper Res 82(3):556–591
Tan Q, Huang GH, Cai Y (2010a) Radial-interval linear programming for environmental management under varied protection levels. J Air Waste Manag Assoc 60(9):1078–1093
Tan Q, Huang GH, Wu CZ, Cai YP (2010b) IF-EM: an interval-parameter fuzzy linear programming model for environment-oriented evacuation management under uncertainty. J Adv Transport. doi:10.1002/atr.137
Tennant DL (1976) Instream flow regimens for fish, wildlife, recreation and related environmental resources. Fisheries 1(4):6–10
Tu XY, Wu TS, Wang S (2009) Research on eco-environmental water requirement for main rivers in Haihe Basin. J Arid Land Resour Environ (Chinese) 23(5):65–71
Wang ZX (2005) Using the modified Tennant method worked on water demand of ecological environment for middle and Small River in high and cold area. J Heilongjiang Hydraulic Engg Coll (Chinese) 32(4):100–103
Yan XP, Ma XF, Huang GH, Wu CZ (2010) An inexact transportation planning model for supporting vehicle emissions management. J Environ Inform 15(2):87–98
Yang W, Yang Z (2010) An interactive fuzzy satisfying approach for sustainable water management in the Yellow River Delta, China. Water Resour Manag 24:1273–1284
Yang FM, Zhong FY (1994) Feedback effect of Zoige alpine’s environment to the nutrition composition of marsh vegetation. J Sichuan Grassl (Chinese) 2:23–26
Yang ZF, Cui BS, Liu JL (2005) Estimation methods of eco-environmental water requirements: case study. Sci China Ser D 48(8):1280–1292
Zuo QT (2002) Study on vegetation ecological use for water resources in arid and semiarid region. J Soil Water Conserv (Chinese) 16(3):114–118
Acknowledgments
This research was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (51009004), the Major State Program of Water Pollution Control (2009ZX07104-004), and the Natural Sciences and Engineering Research Council of Canada (NSERC). The authors would like to extend special thanks to the editor and the anonymous reviewers for their constructive comments and suggestions in improving the quality of this paper.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cai, Y.P., Huang, G.H., Wang, X. et al. An inexact programming approach for supporting ecologically sustainable water supply with the consideration of uncertain water demand by ecosystems. Stoch Environ Res Risk Assess 25, 721–735 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00477-011-0477-5
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00477-011-0477-5