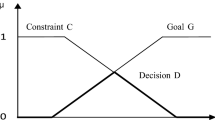
Abstract
In this study, an inexact two-stage stochastic programming model is developed, which can provide an effective linkage between conflicting economic benefits and the associated penalties attributed to the violation of the predefined policies. The developed model was applied to irrigation water allocation optimization system in Minqin County, Gansu province, China. Three different water demands (high, middle, and low) were considered. Fuzzy parameters in the inexact two-stage stochastic programming model were introduced to account for fuzzy events that exist in the irrigation water allocation optimizing system. As the result, the optimal water allocation plans, both from surface water and groundwater, were obtained at different flow levels and different α-cut levels of Minqin County. The final results were expert to make great contributions in helping local managers to make decisions on allocating irrigation water more effectively under uncertainty.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahmed S, Tawarmalani M, Sahinidis NV (2004) A finite branch-and bound algorithm for two-stage stochastic integer programs. Math Progr Ser A 100:355–377
Cao MF, Huang GH, Sun Y et al (2010) Dual inexact fuzzy chance-constraint programming for planning waste management systems. Stoch Environ Res Risk Assess 24:1163–1174
Deng XP, Shan L, Zhang HP et al (2006) Improving agricultural water use efficiency in arid and semiarid areas of China. Agric Water Manag 24(1–3):23–40
Edirisinghe NCP, Ziemba WT (1994) Bounds for two-stage stochastic programs with fixed resources. Math Oper Res 19:292–313
Guo P, Huang GH (2009) Two-stage fuzzy chance-constrained programming: application to water resources management under dual uncertainties. Stoch Environ Res Risk Assess 23:349–359
Guo HC, Liu L, Huang GH et al (2001) A system dynamics approach for regional environmental planning and management: a study for the Lake Erhai Basin. J Environ Manage 61(1):93–111
Guo P, Huang GH, Zhu H, He L (2009) Interval-parameter two-stage stochastic semi-infinite programming application to water resources management under uncertainty. Water Resour Manage 23:1001–1023
Guo P, Huang GH, Zhu H et al (2010) A two-stage programming approach for water resources management under randomness and fuzziness. Environ Model Softw 25:1573–1581
He L, Huang GH, Zeng GM et al (2008) Wavelet-based multi-resolution analysis technique for data cleaning and its application to water quality management system. Expert Syst Appl 35(3):1301–1310
Huang GH, Louck DP (2000) An inexact two-stage stochastic programming model for water resources management under uncertainty. Civil Eng Environ Syst 17:95–118
Li YP, Huang GH (2007) Inexact multistage stochastic quadratic programming method for planning water resources systems under uncertainty. Environ Eng Sci 24(10):1361–1377
Li YP, Huang GH (2008) Interval-parameter two-stage stochastic nonlinear programming for water resources management under uncertainty. Water Resour Manage 22:681–698
Li YP, Huang GH, Nie SL (2006) An interval-parameter multi-stage stochastic programming model for water resources management under uncertainty. Adv Water Resour 29:776–789
Li YP, Huang GH, Xiao HN et al (2007a) An inexact two-stage quadratic program for water resources planning. J Environ Inform 10(2):99–105
Li YP, Huang GH, NIE SL (2007b) Mixed interval–fuzzy two-stage integer programming and its application to flood-diversion planning. Eng Optim 39(2):163–183
Li YP, Huang GH, Chen X (2009) Multistage scenario-based interval-stochastic programming for planning water resources allocation. Stoch Environ Res Risk Assess 23:781–792
Li W, Li YP, Li CH et al (2010) An inexact two-stage water management model for planning agricultural irrigation under uncertainty. Agric Water Manag 97:1905–1914
Loukas A, Mylopoulos N, Vasiliades L (2007) A modeling system for the evaluation of water resources management strategies in Thessaly, Greece. Water Resour Manag 21(10):1673–1702
Lu HW, Huang GH, Zeng GM et al (2008) An inexact two-stage fuzzy-stochastic programming model for water resources management. Water Resour Manag 22:991–1016
Lu HW, Huang GH, He L (2009a) Inexact rough-interval two-stage stochastic programming for conjunctive water allocation problems. J Environ Manage 91:261–269
Lu HW, Huang GH, He L (2009b) A semi-infinite analysis-based inexact two-stage stochastic fuzzy linear programming approach for water resources management. Eng Optim 41(1):73–85
Lu HW, Huang GH, He L (2009c) An inexact programming method for agricultural irrigation system under parameter uncertainty. Stoch Environ Res Risk Assess 23:759–768
Luo B, Maqsood I, Yin YY et al (2003) Adaption to climate change through water trading under uncertainty—an inexact two-stage nonlinear programming approach. J Environ Inform 3(2):58–68
Luo B, JB L, Huang GH et al (2006) A simulation-based interval two-stage stochastic model for agricultural nonpoint source pollution control through land retirement. Sci Total Environ 361:38–56
Maqsood I, Huang GH (2003) A two-stage interval-stochastic programming model for waste management under uncertainty. J Air Waste Manag Assoc 53:540–552
Olsen OR, Dickson SE, Baetz BW (2006) Decision support system for rural water supply in the Nilgiris district of South India. J Environ Inform 7(1):1–13
Ruszczynski A (1993) Parallel decomposition of multi-stage-stochastic programming problems. Math Program 58:201–228
Seifi A, Hipel KW (2001) Interior-point method for reservoir operation with stochastic inflows. J Water Resour Plan Manag 127(1):48–57
Sen S, Higle JL (1999) An introduction tutorial on stochastic linear programming models. Interfaces 29:33–61
Acknowledgments
This research was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 91125017, 41271536, 71071154), National High Technology Research and Development Program of China (863 Program) (No. 2011AA100502), the Government Public Research Funds for Projects of Ministry of Agriculture (No. 201203077) and Ministry of Water Resources (No. 201001060, and 201001061).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Appendix
Appendix
- t:
-
Water resources type, t = 1 is surface water, t = 2 is groundwater
- n:
-
Irrigation area
- h:
-
Flow levels, h = 1 is low level, h = 2 is middle level, h = 3 is high level
- W ± tn :
-
Water application target (water resources type t) for irrigation area n, (104 m3) (decision variable of the first stage)
- C ± tn :
-
The cost for irrigation area n per unit of water application target (water resources type t) (RMB ¥/104 m3)
- S ± tnh :
-
The shortage of water by which the water allocation target (W ± tn ) is not met under inflow q ± tnh (104 m3) (decision variable of the second stage)
- L ± tn :
-
The reduction of net benefit (penalty) for irrigation area n when per unit of water(surface water and groundwater) not delivered (RMB ¥/104 m3)
- p tnh :
-
The probabilities of inflow q ± tnh
- Q ± tn :
-
The available water supply (water resources type t) for irrigation area n at initial stages (104 m3)
- q ± tnh :
-
The water from other resources (water resources type t) for irrigation area n under inflow probabilities p tnh (104m3)
- \( \mathop {C_{tn} }\limits^{\sim } \) :
-
The cost for irrigation area n per unit of Water application target (water resources type t) (RMB ¥/104 m3) (fuzzy number)
- \( \mathop {L_{tn} }\limits^{\sim } \) :
-
The reduction of net benefit (penalty) for irrigation area n when per unit of water (surface water and groundwater) not delivered (RMB ¥/104 m3) (fuzzy number)
- \( \mathop {Q_{tn} }\limits^{\sim } \) :
-
The available water supply (water resources type t) for irrigation area n at initial stages (104 m3) (fuzzy number)
- \( \mathop {q_{tnh} }\limits^{\sim } \) :
-
The available water supply (water resources type t) for irrigation area nr under inflow probabilities p tn h (104 m3) (fuzzy number)
- α:
-
The fuzzy degree of membership level
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, M., Guo, P., Fang, S.Q. et al. An inexact fuzzy parameter two-stage stochastic programming model for irrigation water allocation under uncertainty. Stoch Environ Res Risk Assess 27, 1441–1452 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00477-012-0681-y
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00477-012-0681-y