Abstract
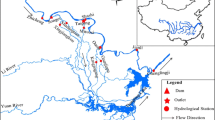
The refill operation of Three Gorges Reservoir (TGR) in the end of flood season significantly alters the water level regimes in Poyang Lake by reducing Yangtze River flow discharge. This study aims to investigate the impact of TGR refill operation on water level probability distribution of the Poyang Lake. The multiple linear regression model was established to estimate the water level with catchment inflow and Yangtze River flow as explanatory variables. A probability distribution of water level was derived and the refill operation effects were quantified by comparing the water level distribution at Xingzi station in the Poyang Lake before and after TGR. It is revealed that Yangtze River flow, rather than the catchment inflow is the dominant factor affecting the water level of Poyang Lake during TGR refill operation period. Results also show that the water level distribution estimated by the derived distribution method can be accepted as a theoretical distribution and has a comparable accuracy as the directly fitted distribution method before TGR. The derived method can be adapted to the environment change, thus is well suited for estimating the water level distribution after TGR. It is observed that Xingzi water levels with different design frequencies have been reduced due to the TGR refill operation. The water level reductions induced by TGR refill operation are 1.28, 0.87, and 0.50 m corresponding with design frequencies of 50, 90 and 99 %, respectively. The results from this work would improve the understanding of the TGR effects on the downstream river–lake system and provide scientific evidences for formulating better scheme for water resources management in this region.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Altinbilek D (2002) The role of dams in development. Int J Water Resour Dev 45(1):9–24
Cunnane C (1989) Statistical distribution for flood frequency analysis. WMO Operational Hydrology Report 33
Dai ZJ, Du JZ, Chu A, Li JF, Chen JY, Zhang XL (2010) Groundwater discharge to the Changjiang River, China, during the drought season of 2006: effects of the extreme drought and the impoundment of the Three Gorges Dam. Hydrogeol J 18:359–369
Dai X, Wan RR, Yang GS (2015) Non-stationary water-level fluctuation in China’s Poyang Lake and its interactions with Yangtze River. J Geogr Sci 25(3):274–288
De Michele C, Salvadori G (2002) On the derived flood frequency distribution: analytical formulation and the influence of antecedent soil moisture condition. J Hydrol 262:245–258
Diaz-Granados MA, Valdes JB, Bras RL (1984) A physically based flood frequency distribution. Water Resour Res 20(7):995–1002
Eagleson PS (1972) Dynamics of flood frequency. Water Resour Res 8(4):878–898
Eagleson PS (1978a) Climate, soil, and vegetation 5: a derived distribution of storm surface runoff. Water Resour Res 14(5):741–748
Eagleson PS (1978b) Climate, soil, and vegetation 7: a derived distribution of annual water yield. Water Resour Res 14(5):765–776
Feng L, Hu CM, Chen XL, Cai XB, Tian LQ, Gan WX (2012) Assessment of inundation changes of Poyang Lake using MODIS observations between 2000 and 2010. Remote Sens Environ 121:80–92
Feng L, Hu CM, Chen XL, Zhao X (2013) Dramatic inundation changes of China’s two largest freshwater lakes linked to the Three Gorges Dam. Environ Sci Technol 47:9628–9634
Gao B, Yang D, Yang H (2013) Impact of the Three Gorges Dam on flow regime in the middle and lower Yangtze River. Quatern Int 304:43–50
Gottschalk L, Weingartner R (1998) Distribution of peak flow derived from a distribution of rainfall volume and runoff coefficient, and a unit hydrograph. J Hydrol 208:148–162
Guo JL, Guo SL, Li TY (2011) Daily runoff simulation in Poyang Lake Intervening Basin based on remote sensing data. Procedia Environmental Sciences 10:2740–2747
Guo H, Hu Q, Zhang Q, Feng S (2012) Effects of the Three Gorges Dam on Yangtze River flow and river interaction with Poyang Lake, China: 2003–2008. J Hydrol 416:19–27
Hervé Y, Claire H, Lai XJ et al (2011) Nine years of water resources monitoring over the middle reaches of the Yangtze River, with ENVISAT, MODIS, Beijing-1 time series, Altimetric data and field measurements. Lakes Reserv Res Manag 16(3):231–247
Hong XJ, Guo SL, Xiong LH, Liu ZJ (2014a) Spatial and temporal analysis of drought using entropy-based standardized precipitation index: a case study in Poyang Lake basin. Theor Appl Climatol, China. doi:10.1029/2008WR006897
Hong XJ, Guo SL, Zhou YL, Xiong LH (2014b) Uncertainties in assessing hydrological drought using streamflow drought index for the upper Yangtze River basin. Stoch Environ Res Risk Assess. doi:10.1007/s00477-014-0949-5
Hosking JR (1990) L-Moments: analysis and estimation of distributions using linear combinations of order statistics. J R Stat Soc Ser B 52(1):105–124
Hu Q, Feng S, Guo H, Chen G, Jiang T (2007) Interactions of the Yangtze River flow and hydrologic processes of the Poyang Lake, China. J Hydrol 347:90–100
Jiang C, Xiong LH, Xu C-Y, Guo SL (2015) Bivariate frequency analysis of nonstationary low-flow series based on the time-varying copula. Hydrol Process 29(6):1521–1534
Lai X, Huang Q, Zhang Y, Jiang J (2014a) Impact of lake inflow and the Yangtze River flow alterations on water levels in Poyang Lake, China. Lake Reserv Manag 30(4):321–330
Lai X, Jiang J, Yang G, Lu XX (2014b) Should the three Gorges Dam be blamed for the extremely low water levels in the middle-lower Yangtze River? Hydrol Process 28(1):150–160
Lai X, Liang Q, Jiang J, Huang Q (2014c) Impoundment effects of the Three-Gorges-Dam on flow regimes in two China’s largest freshwater lakes. Water Resour Manag 28(14):5111–5124
Lai X, Shankman D, Huber C, Yesou H, Huang Q, Jiang J (2014d) Sand mining and increasing Poyang Lake’s discharge ability: a reassessment of causes for lake decline in China. J Hydrol 519:1698–1706
Li J (2009) Scientists line up against dam that would alter protected wetlands. Science 326:508–509
Li TY, Guo SL, Chen L, Guo JL (2013) Bivariate flood frequency analysis with historical information based on copula. J Hydrol Eng. doi:10.1061/(ASCE)HE.1943-5584.0000684
Li Y, Guo SL, Guo JL, Wang Y, Li TY, Chen J (2014) Deriving the optimal refill rule for multi-purpose reservoir considering flood control risk. J Hydro-Environ Res 8(3):248–259
Li X, Zhang Q, Xu C-Y, Ye X (2015a) The changing patterns of floods in Poyang Lake, China: characteristics and explanations. Nat Hazards 76(1):651–666
Li YL, Zhang Q, Werner AD, Yao J (2015b) Investigating a complex lake-catchment river system using artificial neural networks: Poyang Lake (China). Hydrol Res. doi:10.2166/nh.2015.150
Liu Y, Wu G, Zhao X (2013) Recent declines in China’s largest freshwater lake: trend or regime shift? Environ Res Lett 8:014010
MWR (Ministry of Water Resources) of the People’s Republic of China (2009) Optimal OPERATION RULES FOR THE Three Gorges Reservoir. Beijing (in Chinese)
Myoung JU, Hyeseon Y, Chang SJ, Jun HH (2011) Factor analysis and multiple regression between topography and precipitation on Jeju Island, Korea. J Hydrol 410:189–203
Rahman MM, Arya DS, Goel NK, Dhamy AP (2010) Design flow and stage computations in the Teesta River, Bangladesh, using frequency analysis and MIKE 11 modeling. J Hydrol Eng 16(2):176–186
Shankman D, Keim BD, Song J (2006) Flood frequency in China’s Poyang Lake region: trends and teleconnections. Int J Climatol 26(9):1255–1266
Sivapalan M, Bloschl G, Merz R, Gutknecht D (2005) Linking flood frequency to long-term water balance: incorporating effects of seasonality. Water Resour Res 41:W06012. doi:10.1029/2004WR003439
Sun FD, Zhao YY, Gong P, Ma RH, Dai YJ (2014a) Monitoring dynamic changes of global land cover types: fluctuations of major lakes in China every 8 days during 2000-2010. Chin Sci Bull 59(2):171–189
Sun S, Chen H, Ju W, Yu M, Hua W, Yin Y (2014b) On the attribution of the changing hydrological cycle in Poyang Lake Basin, China. J Hydrol 514:214–225
Tao H, Fraedrich K, Menz C, Zhai J (2014) Trends in extreme temperature indices in the Poyang Lake Basin, China. Stoch Environ Res Risk Assess 28(6):1543–1553
Tsai CN, Adrian DD, Singh VP (2001) Finite Fourier probability distribution and applications. J Hydrol Eng 6(6):460–471
Vogel RM, Wilson I (1996) Probability distribution of annual maximum, mean, and minimum streamflows in the United Sates. J Hydrol Eng 1(2):69–76
Wang JD, Sheng YW, Gleason CJ, Wada Y (2013) Downstream Yangtze River levels impacted by Three Gorges Dam. Environ Res Lett 8(4):044012. doi:10.1088/1748-9326/8/4/044012
Wang JD, Sheng YW, Tong TSD (2014) Monitoring decadal lake dynamics across the Yangtze Basin downstream of Three Gorges Dam. Remote Sens Environ 152:251–269
Xiong LH, Yu KX, Zhang H, Zhang L (2013) Annual runoff change in the headstream of Yangtze River and its relation to precipitation and air temperature. Hydro Res 44(5):850–874
Xiong LH, Yu KX, Gottschalk L (2014) Estimation of the distribution of annual runoff from climatic variables using copulas. Water Resour Res. doi:10.1029/2008WR006897
Xu K, Milliman JD (2009) Seasonal variation of sediment discharge from the Yangtze River before and after impoundment of the Three Gorges Dam. Geomorphology 104:278–283
Yang T, Xu C-Y, Shao QX, Chen X (2010) Regional flood frequency and spatial patterns analysis in the Pearl River Delta region using L-moments approach. Stoch Environ Res Risk Assess 24(2):165–182
Ye X, Zhang Q, Bai L, Hu Q (2011) A modeling study of catchment discharge to Poyang Lake under future climate in China. Quatern Int 244(2):221–229
Ye X, Zhang Q, Liu J, Li X, Xu C-Y (2013) Distinguishing the relative impacts of climate change and human activities on variation of streamflow in the Poyang Lake catchment, China. J Hydrol 494:83–95
Ye X, Li X, Liu J, Xu C-Y, Zhang Q (2014a) Variation of reference evapotranspiration and its contributing climatic factors in the Poyang Lake catchment, China. Hydrol Process 28(25):6151–6162
Ye X, Li Y, Li X, Zhang Q (2014b) Factors influencing water level changes in China’s largest freshwater lake, Poyang Lake, in the past 50 years. Water Int 39(7):983–999
Yu KX, Xiong LH, Gottschalk L (2014) Derivation of low flow distribution functions using copulas. J Hydrol 508:273–288
Yuan Y, Zeng G, Liang J et al (2015) Variation of water level in Dongting Lake over a 50-year period: implications for the impacts of anthropogenic and climatic factors. J Hydrol 525:450–456
Zhang L, Singh VP (2006) Bivariate flood frequency analysis using the copula method. J Hydrol Eng 11(2):150–164
Zhang Q, Li L, Wang Y-G, Werner AD, Xin P, Jiang T, Barry DA (2012) Has the Three-Gorges Dam made the Poyang Lake wetlands wetter and drier? Geophys Res Lett 39:L20402
Zhang Q, Xiao MZ, Li J, Singh VP, Wang Z (2014a) Topography-based spatial patterns of precipitation extremes in the Poyang Lake basin, China: changing properties and causes. J Hydrol 512:229–239
Zhang Q, Ye XC, Werner AD, Li YL, Yao J, Li XH, Xu C-Y (2014b) An investigation of enhanced recessions in Poyang Lake: comparison of Yangtze River and local catchment impacts. J Hydrol 517:425–434
Zhang Q, Xiao MZ, Singh VP, Wang Y (2015a) Spatiotemporal variations of temperature and precipitation extremes in the Poyang Lake basin. Theor Appl Climatol, China. doi:10.1029/2008WR006897
Zhang R, Zhang SH, Xu W, Wang H (2015b) Flow regime of the three outlets on the south bank of Jingjiang River, China: an impact assessment of the Three Gorges Reservoir for 2003–2010. Stoch Environ Res Risk Assess. doi:10.1007/s00477-015-1121-6
Zhang ZX, Chen X, Xu C-Y, Hong Y, Hardy J, Sun ZH (2015c) Examining the influence of river-lake interaction on the drought and water resources in the Poyang Lake basin. J Hydrol 522:510–521
Acknowledgments
This study is financially supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (NSFC 51539009, 51579183, 51190094). The authors would like to thank the editor and anonymous reviewers whose comments and suggestions helping to improve the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, Z., Guo, S., Guo, J. et al. The impact of Three Gorges Reservoir refill operation on water levels in Poyang Lake, China. Stoch Environ Res Risk Assess 31, 879–891 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00477-016-1209-7
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00477-016-1209-7