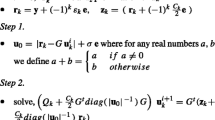Abstract
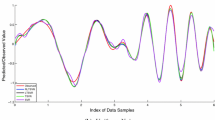
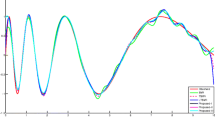
This study proposes a new regressor—ε-twin support vector regression (ε-TSVR) based on TSVR. ε-TSVR determines a pair of ε-insensitive proximal functions by solving two related SVM-type problems. Different form only empirical risk minimization is implemented in TSVR, the structural risk minimization principle is implemented by introducing the regularization term in primal problems of our ε-TSVR, yielding the dual problems to be stable positive definite quadratic programming problems, so can improve the performance of regression. In addition, the successive overrelaxation technique is used to solve the optimization problems to speed up the training procedure. Experimental results for both artificial and real datasets show that, compared with the popular ε-SVR, LS-SVR and TSVR, our ε-TSVR has remarkable improvement of generalization performance with short training time.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Cortes C, Vapnik VN (1995) Support vector networks. Mach Learn 20:273–297
Vapnik VN (1998) Statistical learning theory. Wiley, New York
Burges C (1998) A tutorial on support vector machines for pattern recognition. Data Min Knowl Discov 2:121–167
Deng NY, Tian YJ, Zhang CH (2012) Support vector machines: theory, algorithms, and extensions. CRC Press, Boca Raton
Noble WS (2004) Support vector machine applications in computational biology. In: Schöelkopf B, Tsuda K, Vert J-P (eds) Kernel methods in computational biology. MIT Press, Cambridge, pp 71–92
Lee S, Verri A (2002) Pattern recognition with support vector machines. In: First international workshop, Springer, Niagara Falls, Canada
Ince H, Trafalis TB (2002) Support vector machine for regression and applications to financial forecasting. In: International joint conference on neural networks, Como, Italy, IEEE-INNS-ENNS
Suykens JAK, Lukas L, van Dooren P, De Moor B, Vandewalle J (1999) Least squares support vector machine classifiers: a large scale algorithm. In: Proceedings of European conference of circuit theory design, pp 839–842
Mangasarian OL, Wild EW (2006) Multisurface proximal support vector classification via generalize deigenvalues. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell 28(1):69–74
Jayadeva, Khemchandani R, Chandra S (2007) Twin support vector machines for pattern classification. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell 29(5):905–910
Kumar MA, Gopal M (2008) Application of smoothing technique on twin support vector machines. Pattern Recognit Lett 29(13):1842–1848
Shao YH, Deng NY (2012) A novel margin based twin support vector machine with unity norm hyperplanes. Neural Comput Appl. doi:10.1007/s00521-012-0894-5
Kumar MA, Gopal M (2009) Least squares twin support vector machines for pattern classification. Expert Syst Appl 36(4):7535–7543
Ghorai S, Mukherjee A, Dutta PK (2009) Nonparallel plane proximal classifier. Signal Process 89(4):510–522
Shao YH, Zhang CH, Wang XB, Deng NY (2011) Improvements on twin support vector machines. IEEE Trans Neural Netw 22(6):962–968
Shao YH, Deng NY (2012) A coordinate descent margin based-twin support vector machine for classification. Neural Netw 25:114–121
Peng X (2011) TPMSVM: a novel twin parametric-margin support vector machine for pattern recognition. Pattern Recognit 44(10–11):2678–2692
Suykens JAK, Vandewalle J (1999) Least squares support vector machine classifiers. Neural Process Lett 9(3):293–300
Peng X (2010) TSVR: an efficient twin support vector machine for regression. Neural Netw 23(3):365–372
Zhong P, Xu Y, Zhao Y (2011) Training twin support vector regression via linear programming. Neural Comput Appl. doi:10.1007/s 00521-011-0526-6
Chen X, Yang J, Liang J, Ye Q (2011) Smooth twin support vector regression. Neural Comput Appl. doi:10.1007/s00521-010-0454-9
Peng X (2010) Primal twin support vector regression and its sparse approximation. Neurocomputing 73(16–18):2846–2858
Peng X (2012) Efficient twin parametric insensitive support vector regression model. Neurocomputing 79:26–38
Chen X, Yang J, Liang J (2011) A flexible support vector machine for regression. Neural Comput Appl. doi:10.1007/s00521-011-0623-5
Schölkopf B, Smola A (2002) Learning with kernels. MIT Press, Cambridge
Bi J, Bennett KP (2003) A geometric approach to support vector regression. Neurocomputing 55:79–108
Smola A, Schölkopf B (2004) A tutorial on support vector regression. Stat Comput 14:199–222
Golub GH, Van Loan CF (1996) Matrix computations, 3rd edn. The John Hopkins University Press, Baltimore
Fung G, Mangasarian OL (2001) Proximal support vector machine classifiers. In: Proceedings of seventh international conference on knowledge and data discovery, San Francisco, pp 77–86
Mangasarian OL, Musicant DR (1999) Successive overrelaxation for support vector machines. IEEE Trans Neural Netw 10(5):1032–1037
http://www.mathworks.com (2007)
Pelckmans K, Suykens JAK, Van Gestel T, De Brabanter D, Lukas L, Hamers B, De Moor B, Vandewalle J (2003) LS-SVMlab: a Matlab/C toolbox for least squares support vector machines. Available at http://www.esat.kuleuven.ac.be/sista/lssvmlab
Weisberg S (1985) Applied linear regression seconded. Wiley, New York
Staudte RG, Sheather SJ (1990) Robust estimationand testing: Wiley series in probability and mathematical statistics. Wiley, New York
Lee CC, Chung PC, Tsai JR, Chang CI (1999) Robust radial basis function neural networks. IEEE Trans Syst Man Cybern B Cybern 29(6):674–685
Eubank RL (1999) Nonparametric regression and spline smoothing statistics: textbooks and monographs, vol 157, seconded. Marcel Dekker, New York
Blake CL, Merz CJ (1998) UCI repository for machine learning databases. Department of Information and Computer Sciences, University of California, Irvine, http://www.ics.uci.edu/mlearn/MLRepository.html
Jiao L, Bo L, Wang L (2007) Fast sparse approximation for least squares support vector machine. IEEE Trans Neural Netw 18:1–13
Wen W, Hao Z, Yang X (2008) A heuristic weight-setting strategy and iteratively updating algorithm for weighted least-squares support vector regression. Neurocomputing 71:3096–3103
Acknowledgments
We thank the anonymous reviewers for their valuable suggestions. This work is supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 10971223, No. 11071252, No. 11161045 and No. 61101231) and the Zhejiang Provincial Natural Science Foundation of China (No. Y1100237, No. Y1100629).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shao, YH., Zhang, CH., Yang, ZM. et al. An ε-twin support vector machine for regression. Neural Comput & Applic 23, 175–185 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00521-012-0924-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00521-012-0924-3