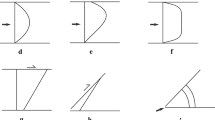Abstract
Symmetric structures in ductile shear zones range widely in shapes and geneses. Matrix rheology, its flow pattern, its competency contrast with the clast, degree of slip of the clast, shear intensity and its variation across shear zone and deformation temperature, and degree of confinement of clast in shear zones affects (independently) the degree of symmetry of objects. Kinematic vorticity number is one of the parameters that govern tail geometry across clasts. For example, symmetric and nearly straight tails develop if the clast–matrix system underwent dominantly a pure shear/compression. Prolonged deformation and concomitant recrystallization can significantly change the degree of symmetry of clasts. Angular relation between two shear zones or between a shear zone and anisotropy determines fundamentally the degree of symmetry of lozenges. Symmetry of boudinaged clasts too depends on competency contrast between the matrix and clast in some cases, and on the degrees of slip of inter-boudin surfaces and pure shear. Parasitic folds and post-tectonic veins are usually symmetric.















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abe S, Urai JL (2012) Discrete element modeling of boudinage: insights on rock rheology, matrix flow, and evolution of geometry. J Geophys Res. doi:10.1029/2011JB008555
Arslan A, Passchier CW, Koehn D (2008) Foliation boudinage. J Struct Geol 30:291–309
Augustithis SS (1979) Atlas of the textural patterns of basic and ultrabasic rocks and their genetic significance. Walter de Gruyter, Berlin, pp 17–107
Awdal A, Healy D, Alsop GI (2014) Geometrical analysis of deformation band lozenges and their scaling relationships to fault lenses. J Struct Geol 66:11–23
Barbour GP (1930) Origin of the Bedford augen-gneiss. Am J Sci 219:351–358
Bard JP (1986) Microtextures of igneous and metamorphic rocks. Reidel, Dordrecht, p 87
Barker AJ (1998) Introduction to metamorphic textures and microstructures, 2nd edn. Stanley Thornes (Publishers) Ltd., Cheltenham
Bellot J-P, Bronner G, Laverne C (2002) Transcurrent strain partitioning along a suture zone in the Maures massif (France): result of an eastern indenter tectonics in European Variscides? In: Martı́nez Catalán JR, Hatcher RD, Arenas R Jr, Dı́az Garcıa F (eds) Variscan–Appalachian dynamics: the building of the late Paleozoic basement, vol 364. Geol Soc Am Spec Pap, Boudler, pp 223–237
Bjornerud M (1989) Toward a unified conceptual framework for shear sense indicators. J Struct Geol 11:1045–1049
Bons PD, Barr TD, ten Brink CE (1997) The development of d-clasts in non-linear viscous materials: a numerical approach. Tectonophysics 270:29–41
Bons PD, Druguet E, Hamann I, Carreras J, Passchier CW (2004) Apparent boudinage in dykes. J Struct Geol 26:625–636
Bons PD, Druguet E, Castano L-M, Elburg MA (2008) Finding what is now not there anymore: recognizing missing fluid and magma volumes. Geology 36:851–854
Bose S, Marques FO (2004) Controls on the geometry of tails around rigid circular inclusions: insights from analogue modelling in simple shear. Tectonophysics 26:2145–2156
Bouchez JL, Lister GS, Nicolas A (1987) Fabric asymmetry and shear sense in movement zones. Geol Rund 72:401–419
Bucher K, Grapes R (2011) Petrogenesis of metamorphic rocks. Introduction and general aspects of metamorphism. Part I. Springer, Berlin
Cannon RT (1964) Porphyroblastic and augen gneisses in the bartica assemblage, British Guiana. Geol Mag 501:541–547
Chattopadhyay N, Ray S, Sanyal S, Sengupta P (2015) Mineralogical, textural and chemical reconstitution of granitic rock in ductile shear zone: a study from a part of the South Purulia Shear Zone, West Bengal, India. In: Mukherjee S, Mulchrone KF (eds) Ductile shear zones: from micro- to macro-scales. Wiley, Chichester, pp 141–163
Cliff RA, Meffan-Main S (2003) Evidence from Rb-Sr microsampling geochronology for the timing of Alpine deformation in the Sonnblick Dome, SE Taueren Window Australia. In: Vance D, Muller W, Villa IM (eds) Geochronology: Linking the isotropic record with petrology and textures, vol 220. Geological Society London Special, pp 159–172
Cosgrove JW (2007) The use of shear zones and related structures as kinematic indicators: a review. In: Ries AC, Butler RWH, Graham R (eds) Deformation of the continental crust: the legacy of Mike Coward, vol 272. Geol Soc, London, Spec Publ, pp 59–74
Dabrowski M, Grasemann B (2014) Domino boudinage under layer-parallel simple shear. J Struct Geol 68:58–65
Davis GH, Reynolds SJ, Kluth CF (2012) Structural geology of rocks and regions, vol 500, 3rd edn. Wiley, New York, pp 570–571
De Sitter LU (1956) Structural geology. McGraw-Hill, London, p 86
Dell’Angello LN, Tullis J (1989) Fabric development in experimentally sheared quartzites. Tectonophysics 169:1–21
Duretz T, Schmalholz SM (2015) From symmetric necking to localized asymmetric shearing: the role of mechanical layering. Geology 43:711–715
Fry N (1997) The field description of metamorphic rocks. Geological Society of London Handbook. Wiley, Chichester
Ghosh SK (1993) Structural geology: fundamentals and modern developments. Pergamon Press, Oxford 387
Goscombe BD, Passchier CW (2003) Asymmetric boudins as shear sense indicators—an assessment from field data. J Struct Geol 25:575–589
Goscombe BD, Passchier CW, Hand M (2004) Boudinage classification: end-member boudin types and modified boudin structures. J Struct Geol 26:739–763
Grasemann B, Dabrowski M (2015) Winged inclusions: pinch-and-swell objects during high-strain simple shear. J Struct Geol 70:78–94
Grasemann B, Fritz H, Vannay J-C (1999) Quantitative kinematic flow analysis from the main central thrust zone (NW-Himalaya, India): implications for a decelerating strain path and the extrusion of orogenic wedges. J Struct Geol 21:837–853
Hanmer S, Passchier CW (1991) Shear sense indicators: a review. Geol Surv Can Pap 90:1–71
Hills ES (1963) Elements of structural geology. Methuen and Co Ltd., London, p 302
Hobbs B, Ord A (2014) Structural geology: the mechanics of deforming metamorphic rocks. Principles, vol 1. Elsevier, Amsterdam, pp 1–665
Hollocher K (2014) A pictorial guide to metamorphic rocks in the field. CRC Press, New York, p 174
Hooper RJ, Hatcher RD Jr (1988) Mylonites from the Towaliga fault zone, central Georgia: products of heterogeneous non-coaxial deformation. Tectonophysics 152:1–17
Ishii K (1995) Estimation of non-coaxiality from crinoid-type pressure fringes: comparison between natural and simulated examples. J Struct Geol 17:1267–1278
Ishii K, Kanagawa K, Shigematsu N et al (2007) High ductility of K-feldspar and development of granitic banded ultramylonite in the Ryoke metamorphic belt, SW Japan. J Struct Geol 29:1083–1098
Jain AK, Singh S (2008) Tectonics of the southern Asian Plate margin along the Karakoram Shear Zone: constraints from field observations and U-Pb SHRIMP ages. Tectonophysics 451:186–205
Kanagawa K (1996) Simulated pressure fringes, vorticity, and progressive deformation. In: de Paor DG (ed) Structural geology and personal computers. Elsevier, Oxford
Kenis I, Urai JL, Sintubin M (2006) The development of bone-shaped structures in initially segmented layers during layer-parallel extension: numerical modelling and parameter sensitivity analysis. J Struct Geol 28:1183–1192
Koehn D, Aerden DGAM, Bons PD et al (2001) Computer experiments to investigate complex fibre patterns in natural antitaxial strain fringes. J Meta Geol 19:217–232
Kornprobst J (2002) Metamorphic rocks and their geodynamic significance—A petrological handbook. Kluwer Academic Publishers, Netherlands
Lacassin R (1988) Large scale foliation boudinage in gneisses. J Struct Geol 10:643–647
Law R, Stahr III DW, Ahmad T et al. (2010) Deformation temperatures and flow vorticities near the base of the greater Himalayan Crystalline Sequence, Sutlej Valley and Shimla Klippe, NW India. In Leech ML et al. (eds) Proceedings for the 25th Himalaya-Karakoram-Tibet Workshop. U.S. Geological Survey, Open-File Report 2010–1099, p 2
Le Hebel F, Gapais D, Fourcade S, Capdevila R (2002) Fluid-assisted large strains in a crustal-scale décollement (Hercynian Belt of South Brittany, France). In: De Meer S, Drury MR, De Bresser JHP, Pennock GM (eds) Deformation mechanisms, rheology and tectonics: current status and future perspectives, vol 200. Geol Soc, London, Spec Publ, pp 85–101
Leiss B, Groger HR, Ullemeyer K, Lebit H (2002) Textures and microstructures of naturally deformed amphibolites from the northern Cascades, NW USA: methodology and regional aspects. In: de Meer S, Drury MR, de Bresser JHP, Pennock GM (eds) Deformation mechanisms, rheology and tectonics: current status and future perspectives, vol 200. Geol Soc, London, Spec Publ, pp 219–238
Lister GS, Snoke AW (1984) S-C Mylonites. J Struct Geol 6:617–638
Maeder X, Passchier CW, Koehn DL (2009) Modelling of segment structures: boudins, bone-boudins, mullions and related single- and multiphase deformation features. J Struct Geol 31:817–830
Malavielle J, Lacassin R (1988) ‘Bone-shaped’ boudins in progressive shearing. J Struct Geol 10:335–345
Mandal N, Samanta SK, Chakraborty C (2000) Progressive development of mantle structures around elongate porphyroclasts: insights from numerical models. J Struct Geol 22:993–1008
Mandal N, Samanta SK, Chakraborty C (2004) Problem of folding in ductile shear zones: a theoretical and experimental investigation. J Struct Geol 26:475–489
Marques FO, Taborda R, Bose S et al (2005) Effects of confinement on matrix flow around a rigid inclusion in viscous simple shear: insights from analogue and numerical modeling. J Struct Geol 27:379–396
Mason R (1978) Petrology of the metamorphic rocks. George Allen & Unwin, London
Masuda T, Mizuno N (1995) Deflection of pure shear viscous flow around a rigid spherical body. J Struct Geol 17:1615–1629
Menegon L, Pennacchioni G, Stünitz H (2006) Nucleation and growth of myrmekite during ductile shear deformation in metagranites. J Metamorph Geol 24:553–568
Menegon L, Pennacchioni G, Spiess R (2008) Dissolution-precipitation creep of K-feldspar in mid-crustal granite mylonites. J Struct Geol 30:565–579
Misra AA, Mukherjee S (2016) Dyke-brittle shear relationships in the Western Deccan Strike Slip Zone around Mumbai (Maharashtra, India). In: Mukherjee S, Misra AA, Calvès G, Nemčok M (eds) Tectonics of the Deccan large Igneous Province. Geological Society, London, Special Publications
Mukherjee S (2011a) Mineral Fish: their morphological classification, usefulness as shear sense indicators and genesis. Int J Earth Sci 100:1303–1314
Mukherjee S (2011b) Flanking Microstructures from the Zanskar Shear Zone, NW Indian Himalaya. YES Bull 1:21–29
Mukherjee S (2012) Simple shear is not so simple! Kinematics and shear senses in Newtonian viscous simple shear zones. Geol Mag 149:819–826
Mukherjee S (2013a) Deformation microstructures in rocks. Springer, Berlin
Mukherjee S (2013b) Channel flow extrusion model to constrain dynamic viscosity and Prandtl number of the Higher Himalayan Shear Zone. Int J Earth Sci 102:1811–1835
Mukherjee S (2013c) Higher Himalaya in the Bhagirathi section (NW Himalaya, India): its structures, backthrusts and extrusion mechanism by both channel flow and critical taper mechanisms. Int J Sci 102:1851–1870
Mukherjee S (2013d) Symmetric and near-symmetric objects in ductile shear zones- examples from Higher Himalaya, Bhagirathi section, India. Geophys Res Abs 15:2585
Mukherjee S (2014) Atlas of shear zone structures in meso-scale. Springer, Cham
Mukherjee S (2015) Atlas of structural geology. Elsevier, Amsterdam
Mukherjee S, Biswas R (2014) Kinematics of horizontal simple shear zones of concentric arcs (Taylor Couette flow) with incompressible Newtonian rheology. Int J Earth Sci 103:597–602
Mukherjee S, Biswas R (2015) Biviscous horizontal simple shear zones of concentric arcs (Taylor Couette flow) with incompressible Newtonian rheology. In: Mukherjee S, Mulchrone KF (eds) Ductile shear zones: from micro- to macro-scales. Wiley, Chichester, pp 59–62
Mukherjee S, Koyi HA (2009) Flanking microstructures. Geol Mag 146:517–526
Mukherjee S, Koyi HA (2010a) Higher Himalayan Shear Zone, Sutlej section: structural geology and extrusion mechanism by various combinations of simple shear, pure shear and channel flow in shifting modes. Int J Earth Sci 99:1267–1303
Mukherjee S, Koyi HA (2010b) Higher Himalayan Shear Zone, Zanskar Indian Himalaya: microstructural studies and extrusion mechanism by a combination of simple shear and channel flow. Int J Earth Sci 99:1083–1110
Mukherjee S, Mulchrone KF (2012) Estimating the viscosity and Prandtl number of the Tso Morari crystalline gneiss dome, Indian western Himalaya. Int J Earth Sci 101:1929–1947
Mukherjee S, Mulchrone KF (2013) Viscous dissipation pattern in incompressible Newtonian simple shear zones: an analytical model. Int J Earth Sci 102:1165–1170
Mukherjee S, Koyi HA, Talbot CJ (2012) Implications of channel flow analogue models for extrusion of the Higher Himalayan Shear Zone with special reference to the out-of-sequence thrusting. Int J Earth Sci 101:253–272
Mukherjee S, Mukherjee B, Thiede R (2013) Geosciences of the Himalaya-Karakoram-Tibet Orogen. Int J Earth Sci 102:1757–1758
Mukherjee S, Carosi R, van der Beek PA et al (2015a) Tectonics of the Himalaya: an introduction. Geol Soc London Specl Publ 412:1–3
Mukherjee S, Punekar J, Mahadani T, Mukherjee R (2015b) Intrafolial folds: review and examples from the western Indian Higher Himalaya. In: Mukherjee S, Mulchrone KF (eds) Ductile shear zones: from micro- to macro-scales, 1st edn. Wiley, Chichester, pp 182–205
Mukherjee S, Misra AA, Calvès G et al. (2016) Tectonics of the Deccan Large Igneous Province: an introduction. Geological Society London Special Publications, London (in press)
Mulchrone KF, Mukherjee S (2015) Shear Senses and Viscous Dissipation of Layered Ductile Simple Shear Zones. Pure appl Geophys 172:2635–2642
Nabelek PI, Whittington AG, Hofmeister AM (2010) Strain heating as a mechanism for partial melting and ultrahigh temperature metamorphism in convergent orogens: implications of temperature dependent thermal diffusivity and rheology. J Geophys Res 115:B12417
Nicolas A (1987) Principles of rocks deformation. D. Reidel Publishing Company, Dordrecht, p 88
Ord A, Hobbs B (2013) Localized folding in general deformations. Tectonophysics 583:30–45
Passchier CW (1994) Mixing in flow perturbations: a model for development of mantled porphyroclasts in mylonites. J Struct Geol 16:733–736
Passchier CW (2001) Flanking structures. J Struct Geol 23:951–962
Passchier CW (2008) Pseudo-boudins in Pegmatite, Arunta, Australia. J Struct Geol 30:273
Passchier C, Coelho S (2006) An outline of shear-sense analysis in high-grade rocks. Gond Res 10:66–76
Passchier CW, Sokoutis D (1993) Experimental modelling of mantled porphyroclasts. J Struct Geol 15:895–909
Passchier CW, Trouw RAJ (2005) Microtectonics, 2nd edn. Springer, Berlin
Passchier CW, Myers JS, Kroner A (1990) Field Geology of High-Grade Gneiss Terrains. Springer, Berlin
Philips E (2006) Micromorphology of a debris flow deposit: evidence of basal shearing, hydrofracturing, liquefaction and rotational deformation during emplacement. Quater Sci Rev 25:720–738
Ponce C (2014) Structural analyses of tectonic lozenges in anisotropic rocks: field analysis and experimental modelling. Ph.D. Thesis. Universitat Autonoma de Bercelona. pp. 1–141
Ponce C, Druguet E, Carreras J (2013) Development of shear zone-related lozenges in foliated rocks. J Struct Geol 50:176–186
Ramberg H (1952) The origin of metamorphic and metasomatic rocks. The University of Chicago Press, Chicago, pp 233–234
Ree J-H, Kim HS, Han R, Jung H (2005) Grain-size reduction of feldspars by fracturing and neocrystallization in a low-grade granitic mylonite and its rheological effect. Tectonophysics 407:227–237
Regenauer-Lieb K, Yuen DA (2003) Modeling shear zones in geological and planetary sciences: solid- and fluid-thermal–mechanical approaches. Earth Sci Rev 63:295–349
Roshoff K (1979) Deformation structures in the Tannas augen gneiss. In: Easterling KE (ed) Mechanism of deformation and fracture. Pergamon Press Ltd., Oxford, pp 159–172
Simpson C, Schmid SM (1983) An evaluation of criteria to deduce the sense of movement in sheared rocks. Geol Soc Am Bull 94:1281–1288
Simpson C, Winsch RP (1989) Evidence for deformation-induced K-feldspar replacement by myrmekite. J Metamorph Geol 7:261–275
Smith JV (1974) Feldspar minerals: chemical and textural properties. Springer, Berlin
Spry A (1969) Metamorphic textures. Pergamon Press, Oxford, pp 242–247
Spry A (1974) Metamorphic textures. Pergamon Press, Oxford, pp 240–246
ten Grotenhuis SM, Trouw RAJ, Passchier CW (2003) Evolution of mica fish in mylonitic rocks. Tectonophysics 372:1–21
Treagus S, Lan L (2000) Pure shear deformation of square objects, and applications to geological strain analysis. J Struct Geol 22:105–122
Treagus S, Lan L (2003) Simple shear of deformable square objects. J Struct Geol 25:1993–2003
Trouw RAJ, Passchier CW, Wiersma DJ (2010) Atlas of Mylonites- and related microstructures. Springer, Berlin
Turner FJ, Verhoogen J (1951) Igneous and metamorphic petrology. McGraw Hill, New York, p 61
van der Wateren FM, Kluiving SJ, Bartek LR (2000) Kinematic indicators of subglacial shearing. In: Maltman AJ, Hubbard B, Hambrey MJ (eds) Deformation of glacial materials, vol 176. Geol Soc, London, Spec Publ, pp 259–278
Vernon RH (1986) K-feldspar megacrysts in granites- phenocrysts not porphyroblasts. Earth Sci Rev 23:1–63
Vernon R (1990) K-feldspar augen in felsic gneisses and mylonites—deformed phenocrysts or porphyroblasts? Geologiska Foreningens i Stockholm Forhandlingar 112:157–167
Vernon RH (2004) A practical guide to rock microstructure. Press Syndicate of the University of Cambridge, Cambridge
Vernon RH, Clarke GL (2008) Principles of metamorphic petrology. Cambridge University Press, New York, pp 326–345
Vidal JL, Kubin L, Debat P, Soula JC (1980) Deformation and dynamic recrystallization of K-feldspar augen in orthogneiss from Montagne Noire, Occitania, Southern France. Lithos 13:247–255
White SH (2010) Mylonites: lessons from Eriboll. In: Law RD, Butler RWH, Holdsworth RE, Krabbendam M, Strachan RA (eds) Continental tectonics and mountain building: the legacy of peach and horne, vol 335. Geol Soc, London, Spec Publ, pp 505–542
Whitten EHT (1966) Structural geology of folded rocks. Rand McNally & Company, Chicago, p 306
Winter JD (2009) Principles of igneous and metamorphic petrology, 2nd edn. Prentice Hall, New Jersey, p 473
Yin A (2006) Cenozoic tectonic evolution of the Himalayan orogen as constrained by along-strike variation of structural geometry, extrusion history, and foreland sedimentation. Earth Sci Rev 76:1–131
Acknowledgments
IIT Bombay funded partially. Ripun Kumar Gogoi (IIT Bombay) prepared few diagrams. Reviewer: David Iacopini. Editors: Karel Schulmann, Christian- and Monika Dullo.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mukherjee, S. Review on symmetric structures in ductile shear zones. Int J Earth Sci (Geol Rundsch) 106, 1453–1468 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00531-016-1366-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00531-016-1366-4