Abstract
Background
The development of islet cultures is desirable for successful clinical islet transplantation. Fetal bovine serum (FBS) has been used as a supplement in islet culture medium, but it may be an unsuitable supplement due recent animal health problems. We have evaluated the use of the silk protein, sericin, derived from Bombyx mori as a replacement for FBS in islet culture medium.
Methods
Twenty rat islets were cultured in medium containing either sericin or FBS, or no supplement, for 14 days, during which time viable islets were counted in order to evaluate islet survival. Insulin secretion was measured in vitro by static incubation on days 3 and 7. In vivo function of cultured islets was tested by syngeneic transplantation. The islets were evaluated histologically and immunohistochemically after culture and transplantation.
Results
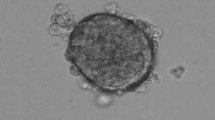
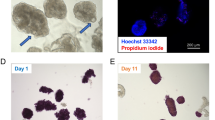
Ninety-five percent of islets were viable after culture for 14 days in culture medium supplemented with either FBS or sericin, while no islets survived beyond 7 days in culture without supplement. No significant differences in stimulated insulin secretion were noted between two groups of islets grown on supplemented media. Following transplantation, islets cultured in FBS or sericin rapidly reversed hyperglycemia and maintained normal glycemic control. Histologically, islets cultured with sericin displayed a well-preserved structure and strong insulin staining before and after transplantation.
Conclusion
Serum-free medium containing sericin appears to be useful for islet culture.




Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- FBS:
-
Fetal bovine serum
- HBSS:
-
Hank’s balanced salt solution
References
Ricordi C. Islet transplantation: a brave new world. Diabetes. 2003;52:1595–603.
Ryan EA, Lakey JR, Paty BW, Imes S, Korbutt GS, Kneteman NM, et al. Continued insulin reserve provides long-term glycemic control. Diabetes. 2002;51:2148–57.
Brown P, Rohwer RG, Dunstan BC, MacAuley C, Gajdusek DC, Drohan WN. The distribution of infectivity in blood components and plasma derivatives in experimental models of transmissible spongiform encephalopathy. Transfusion. 1998;38:810–6.
Hunter N, Foster J, Chong A, McCutcheon S, Parnham D, Eaton S, et al. Transmission of prion diseases by blood transfusion. J Gen Virol. 2002;83:2897–905.
Voegeli R, Meier J, Blust R. Sericin silk protein: unique structure and properties. Cosmet Toilet. 1993;108:101–8.
Gamo T, Inokuchi T, Laufer H. Polypeptides of fibroin and sericin secreted from the different sections of the silk gland in Bombyx mori. Insect Biochem. 1977;7:285–95.
Kato N, Sato S, Yamanaka A, Yamada H, Fuwa N, Nomura M. Silk protein, sericin, inhibits lipid peroxidation and tyrosinase activity. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem. 1998;62(1):145–7.
Terada S, Nishimura T, Sasaki M, Yamada H, Miki M. Sericin, a protein derived from silkworms, accelerates the proliferation of several mammalian cell lines including a hybridoma. Cytotechnology. 2002;40:3–12.
Furuya H, Kimura T, Murakami M, Katayama K, Hirose K, Yamaguchi A. Revascularization and function of pancreatic islet isografts in diabetic rats following transplantation. Cell Transplant. 2003;12:537–44.
Tze WJ, Wong FC, Tingle AJ. The use of hypaque-ficoll in the isolation of pancreatic islets in rats. Transplantation. 1976;22(2):201–5.
Korsgren O, Andersson A, Sandler S. Pretreatment of fetal porcine pancreas in culture with nicotinamide accelerates reversal of diabetes after transplantation to nude mice. Surgery. 1993;113(2):205–14.
Murakami M, Satou H, Kimura T, Kobayashi T, Yamaguchi A, Nakagawara G, et al. Effects of micro-encapsulation on morphology and endocrine function of cryopreserved neonatal porcine islet-like cell clusters. Transplantation. 2000;70(8):1143–8.
Rush BT, Fraga DW, Kotb MY, Sabek OM, Lo A, Gaber LW, et al. Preservation of human pancreatic islet in vivo function after 6-month culture in serum-free media. Transplantation. 2004;77(8):1147–54.
Clayton HA, Goward YM, Prevost P, Swift M, Kimber D, Contractor HH, et al. In vitro islet culture: development of a serum-free medium. Transplant Proc. 2000;30(2):379.
Clark SA, Chick WL. Islet cell culture in defined serum-free medium. Endocrinology. 1990;126(4):1895–903.
Nakano M, Matsumoto I, Sawada T, Ansite J, Oberbroeckling J, Zhang HJ, et al. Caspase-3 inhibitor prevents apoptosis of human islets immediately after isolation and improves islet graft function. Pancreas. 2004;29(2):104–9.
Fournier A. Quantitative data on Bombyx mori L. silkworm: a review. Biochimie. 1979;61:283–320.
Nilsen JH. Growth and function of the pancreatic β-cells in vitro: effects of glucose, hormones and serum factors on mouse, rat and human pancreatic islets in organ culture. Acta Endocrinol. 1985;266:1–39.
Sasaki M, Kato N, Watanabe H, Yamada H. Silk protein, sericin, suppresses colon carcinogenesis induced by 1,2-dimethylhydrazine in mice. Oncol Rep. 2000;7:1049–52.
Acknowledgments
We wish to thank Mr. Masahiro Sasaki from the Technology Department of Seiren Co. for providing both sericin and advice, Dr. Yoshiaki Imamura of the Department Pathology at the University of Fukui and Dr. Takashi Maki of Transplant Center at Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center for advice.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
About this article
Cite this article
Morikawa, M., Kimura, T., Murakami, M. et al. Rat islet culture in serum-free medium containing silk protein sericin. J Hepatobiliary Pancreat Surg 16, 223–228 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00534-009-0049-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00534-009-0049-y