Abstract
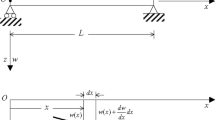
Various experimental and theoretical researches have been shown the size-dependence behavior of the effective Young modulus (EYM) in the micron and sub-micron scales. One of the most accurate methods is the electrostatic pull-in instability (EPI) method that is based on the bending of the classical beam under the electrostatic force. In this paper, the modified couple stress theory (MCST) is employed to calculate the EYM of silicon nanocantilevers. The MCST compensates the inability of the classical continuum mechanic to predicting the size-dependent behavior of the nano-scale structures. Next, as a case study the EYM of silicon nanocantilevers have been calculated and results compared with classical EPI. The governing equation is solved by the Galerkin method and obtained results show significant size-dependent behavior in the EYM. From the other hand, a new value for the material length scale parameter is introduced based on the dimension of the crystal or grain size of the material.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Agrawal R, Peng B, Gdoutos EE, Espinosa HD (2008) Elasticity size effects in ZnO nanowires—a combined experimental-computational approach. Nano Lett 8(11):3668–3674
Baghani M (2012) Analytical study on size-dependent static pull-in voltage of microcantilevers using the modified couple stress theory. Int J Eng Sci 54:99–105
Barati MR, Zenkour AM (2018) Post-buckling analysis of imperfect multi-phase nanocrystalline nanobeams considering nanograins and nanopores surface effects. Compos Struct 184:497–505
Begley MR, Hutchinson JW (1998) The mechanics of size-dependent indentation. J Mech Phys Solids 46(10):2049–2068
Chong A, Lam DC (1999) Strain gradient plasticity effect in indentation hardness of polymers. J Mater Res 14(10):4103–4110
Cuenot S, Frétigny C, Demoustier-Champagne S, Nysten B (2004) Surface tension effect on the mechanical properties of nanomaterials measured by atomic force microscopy. Phys Rev B 69(16):165410
Ding JN, Meng YG, Wen SZ (2001) Specimen size effect on mechanical properties of polysilicon microcantilever beams measured by deflection using a nanoindenter. Mater Sci Eng B 83(1):42–47
Du H, Zhou G, Zhao Y, Chen G, Chau FS (2017) Magnetic field sensor based on coupled photonic crystal nanobeam cavities. Appl Phys Lett 110(6):061110
Eremeyev VA (2016) On the effective properties of elastic materials and structures at the micro-and nano-scale considering various models of surface elasticity. In: Materials with internal structure. Springer International Publishing, pp 29–41
Fan T, Yang L (2017) Effective Young’s modulus of nanoporous materials with cuboid unit cells. Acta Mech 228(1):21–29
Fleck NA, Muller GM, Ashby MF, Hutchinson JW (1994) Strain gradient plasticity: theory and experiment. Acta Metallurgica et Materialia 42(2):475–487
Gomez J, Basaran C (2007) Determination of strain gradient plasticity length scale for microelectronics solder alloys. J Electron Packag 129(2):120–128
Gordon MJ, Baron T, Dhalluin F, Gentile P, Ferret P (2009) Size effects in mechanical deformation and fracture of cantilevered silicon nanowires. Nano Lett 9(2):525–529
Gouadec G, Colomban P (2007) Raman Spectroscopy of nanomaterials: how spectra relate to disorder, particle size and mechanical properties. Prog Cryst Growth Charact Mater 53(1):1–56
Guo JG, Zhao YP (2007) The size-dependent bending elastic properties of nanobeams with surface effects. Nanotechnology 18(29):295701
Houben L, Luysberg M, Carius R (2003) Microtwinning in microcrystalline silicon and its effect on grain-size measurements. Phys Rev B 67(4):045312
Itou S (1981) The effect of couple-stresses on the stress concentration around a moving crack. Int J Math Math Sci 4(1):165–180
Kim JS, Park SH, Park JH, Lee JS (2006) Molecular dynamics simulation of elastic properties of silicon nanocantilevers. Nanoscale Microscale Thermophys Eng 10(1):55–65
Kizuka T, Takatani Y, Asaka K, Yoshizaki R (2005) Measurements of the atomistic mechanics of single crystalline silicon wires of nanometer width. Phys Rev B 72(3):035333
Koiter WT (1964) Couple stresses in the theory of elasticity, I and II. Nederl Akad Wetensch Proc Ser B 67:17–29
Li X, Ono T, Wang Y, Esashi M (2003) Ultrathin single-crystalline-silicon cantilever resonators: fabrication technology and significant specimen size effect on Young’s modulus. Appl Phys Lett 83(15):3081–3083
Li M, Tang HX, Roukes ML (2007) Ultra-sensitive NEMS-based cantilevers for sensing, scanned probe and very high-frequency applications. Nat Nanotechnol 2(2):114–120
Maani Miandoab E, Nejat Pishkenari H, Yousefi-Koma A, Tajaddodianfar F, Ouakad H (2017) Size effect impact on the mechanical behavior of an electrically actuated polysilicon nanobeam based NEMS resonator. J Appl Comput Mech 3(2):135–143
Miller RE, Shenoy VB (2000) Size-dependent elastic properties of nanosized structural elements. Nanotechnology 11(3):139
Mindlin RD, Tiersten HF (1962) Effects of couple-stresses in linear elasticity. Arch Ration Mech Anal 11(1):415–448
Nilsson SG, Borrise X, Montelius L (2004) Size effect on Young’s modulus of thin chromium cantilevers. Appl Phys Lett 85:3555
Nix WD, Gao H (1998) Indentation size effects in crystalline materials: a law for strain gradient plasticity. J Mech Phys Solids 46(3):411–425
Osterberg PM (1995) electrostatically actuated micromechanical test structure for material property measurement. Ph.D. Dissertation, Massachusetts Institute of Technology
Osterberg PM, Senturia SD (1997) M-TEST: a test chip for MEMS material property measurement using electrostatically actuated test structures. Microelectromech Syst J 6(2):107–118
Park SH, Kim JS, Park JH, Lee JS, Choi YK, Kwon OM (2005) Molecular dynamics study on size-dependent elastic properties of silicon nanocantilevers. Thin Solid Films 492(1):285–289
Poelma RH, Sadeghian H, Noijen SPM, Zaal JJM, Zhang GQ (2011) A numerical experimental approach for characterizing the elastic properties of thin films: application of nanocantilevers. J Micromech Microeng 21(6):065003
Rahaeifard M, Kahrobaiyan MH, Asghari M, Ahmadian MT (2011) Static pull-in analysis of microcantilevers based on the modified couple stress theory. Sens Actuators A 171(2):370–374
Rahmani O, Niaei AM, Hosseini SAH, Shojaei M (2017) In-plane vibration of FG micro/nano-mass sensor based on nonlocal theory under various thermal loading via differential transformation method. Superlattices Microstruct 101:23–39
Rezazadeh G, Fathalilou M, Shabani R (2009) Static and dynamic stabilities of a microbeam actuated by a piezoelectric voltage. J Microsyst Technol 15:1785–1791
Rokni H, Seethaler RJ, Milani AS, Hosseini-Hashemi S, Li XF (2013) Analytical closed-form solutions for size-dependent static pull-in behavior in electrostatic micro-actuators via Fredholm integral equation. Sens Actuators A 190:32–43
Sadeghian H, Yang CK, Goosen JFL, Van Der Drift E, Bossche A, French PJ, Van Keulen F (2009) Characterizing size-dependent effective elastic modulus of silicon nanocantilevers using electrostatic pull-in instability. Appl Phys Lett 94(22):221903
Sadeghian H, Yang CK, Goosen JF, Bossche A, Staufer U, French PJ, van Keulen F (2010a) Effects of size and defects on the elasticity of silicon nanocantilevers. J Micromech Microeng 20(6):064012
Sadeghian H, Goosen JF, Bossche A, Thijsse BJ, van Keulen F (2010b) Surface reconstruction and elastic behavior of silicon nanobeams: the impact of applied deformation. Thin Solid Films 518(12):3273–3275
Sadeghian H, Goosen H, Bossche A, Thijsse B, van Keulen F (2011) On the size-dependent elasticity of silicon nanocantilevers: impact of defects. J Phys D Appl Phys 44(7):072001
Sedighi HM, Ouakad HM, Khooran M (2017) Instability characteristics of free-standing nanowires based on the strain gradient theory with the consideration of casimir attraction and surface effects. Metrol Meas Syst 24(3):489–507
Shilo D, Drezner H, Dorogoy A (2008) Investigation of interface properties by nanoscale elastic modulus mapping. Phys Rev Lett 100(3):035505
Stölken JS, Evans AG (1998) A microbend test method for measuring the plasticity length scale. Acta Mater 46(14):5109–5115
Yang F, Chong ACM, Lam DCC, Tong P (2002) Couple stress based strain gradient theory for elasticity. Int J Solids Struct 39(10):2731–2743
Yu H, Sun C, Zhang WW, Lei SY, Huang QA (2013) Study on size-dependent Young’s modulus of a silicon nanobeam by molecular dynamics simulation. J Nanomater 2013:319302. https://doi.org/10.1155/2013/319302
Zhang Y, Ai J, Xiang Y, He Q, Li T, Ma J (2017) Mass sensor based on split-nanobeam optomechanical oscillator. In: Selected papers of the Chinese Society for Optical Engineering conferences held October and November 2016. International Society for Optics and Photonics, p 102552U
Zhao M, Slaughter WS, Li M, Mao SX (2003) Material-length-scale-controlled nanoindentation size effects due to strain-gradient plasticity. Acta Mater 51(15):4461–4469
Zhu HX (2010) Size-dependent elastic properties of micro-and nano-honeycombs. J Mech Phys Solids 58(5):696–709
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rahimi, Z., Rezazadeh, G. & Sadeghian, H. Study on the size dependent effective Young modulus by EPI method based on modified couple stress theory. Microsyst Technol 24, 2983–2989 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00542-018-3708-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00542-018-3708-6