Abstract
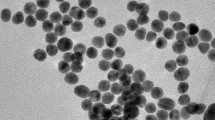
A rapid binding test has been developed for the detection of bacteria using polymer-modified magnetic nanoparticles. Polydopamine (PDA) can effectively act as a sorbent even in water solution, and a PDA coating on magnetic nanoparticles (MNPs) was therefore prepared to bind Escherichia coli (E. coli). Albeit non-selective, PDA-modified magnetic nanoparticles (MNPs@PDA) show nearly 100% efficiency in binding E. coli. If E. coli, grown in tryptic soy broth medium, is analyzed by capillary electrophoresis (CE) using phosphate buffer as the background electrolyte, two peaks are found, while a single peak is found with carbonate buffer containing 0.05% of poly(ethylene glycol). Self-polymerization of dopamine on E. coli at pH 9.5 is also feasible. The detection of E. coli is demonstrated by adding quantum dots (QDs) to form a QDs-PDA-E. coli aggregate for better CE analysis.

Development of Polymer-Modified Magnetic Nanoparticles and Quantum Dots for Escherichia coli Binding Test







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Feng P, Weagant S, Grant M (2002) Enumeration of Escherichia coli and the Coliform Bacteria. Bacteriological Analytical Manual (8th ed.). FDA/Center for Food Safety & Applied Nutrition. Sept 2002. Retrieved 2007-01-25. http://www.cfsan.fda.gov/~ebam/bam-4.html
Kung’u JK, Boor KJ, Ame SM, Ali NS, Jackson AE, Stoltzfus RJ (2009) Bacterial populations in complementary foods and drinking-water in households with children aged 10–15 months in Zanzibar, Tanzania. J Health Popul Nutr 27:41–52. PMCID: PMC2761806
Nigam S, Barick KC, Bahadur D (2011) Development of citrate-stabilized Fe3O4 nanoparticles: conjugation and release of doxorubicin for therapeutic applications. J Magn Magn Mater 323:237–243. doi:10.1016/j.jmmm.2010.09.009
Yang K, Su WW (2011) Facile synthesis of metal-chelating magnetic nanoparticles by exploiting organophosphorus coupling. Anal Biochem 408:175–177. doi:10.1016/j.ab.2010.09.014
Forge D, Laurent S, Gossuin Y, Roch A, Vander EL, Muller RN (2011) An original route to stabilize and functionalize magnetite nanoparticles for theranosis applications. J Magn Magn Mater 323:410–415. doi:10.1016/j.jmmm.2010.09.031
Sima VH, Patris S, Aydogmus Z, Sarakbi A, Sandulescu R, Kauffmann JM (2011) Tyrosinase immobilized magnetic nanobeads for the amperometric assay of enzyme inhibitors: application to the skin whitening agents. Talanta 83:980–987. doi:10.1016/j.talanta.2010.11.005
Hnaiein M, Hassen WM, Abdelghani A, Fournier WC, Coste JBF, Leonard D, Jaffrezic RN (2008) A conductometric immunosensor based on functionalized magnetic nanoparticles for E. coli detection. Electrochem Commun 10:1152–1154. doi:10.1016/j.elecom.2008.04.009
Wan Y, Zhang D, Wang Y, Qi P, Hou B (2011) Direct immobilisation of antibodies on a bioinspired architecture as a sensing platform. Biosens Bioelectron 26:2595–2600. doi:10.1016/j.bios.2010.11.013
Ou J, Wang J, Zhou J, Liu S, Yu Y, Pang X, Yang S (2010) Construction and study on corrosion protective property of polydopamine-based 3-layer organic coatings on aluminum substrate. Prog Org Coat 68:244–247. doi:10.1016/j.porgcoat.2010.01.004
McCloskey BD, Park HB, Ju H, Rowe BW, Miller DJ, Chun BJ, Kin K, Freeman BD (2010) Influence of polydopamine deposition conditions on pure water flux and foulant adhesion resistance of reverse osmosis, ultrafiltration, and microfiltration membranes. Polymer 51:3472–3485. doi:10.1016/j.polymer.2010.05.008
Ouyang R, Lei J, Ju H (2010) Artificial receptor-functionalized nanoshell: facile preparation, fast separation and specific protein recognition. Nanotechnology 21:185502. Epub 2010 April 14. PMID:20388981
Iqbal Z, Alsudir S, Miah M, Lai EPC (2011) Rapid CE-UV binding tests of environmentally hazardous compounds with polymer-modified magnetic nanoparticles. Electrophoresis 32:1–7. doi:10.1002/elps.201100106
Chen P, Li RK, Xu XH, Rao PF (2002) Rapid separation and determination of enterotoxigenic E. coli by capillary zone electrophoresis. Chin J Chromatogr 20:39–41. doi:1000 8713(2002) 05 0439 03
Igor VK, Mirjana RP, Edward D, Carmel GR, Andreas K, Annelise EB (2003) Detection of Escherichia coli O157:H7 bacteria by a combination of immunofluorescent staining and capillary electrophoresis. Electrophoresis 24:655–661. doi:10.1002/elps.200390077
Law WS, Li SFY, Kricka LJ (2009) Microchip Methods in Diagnostics Series. In: Bilitewski U (ed) Methods in Molecular Biology. Chapter 12, pp169-179, Humana Press, USA. Pub. Date: Apr-01-2008. doi: 10.1007/978-1-59745-372-1_12
Mukhopadhyay B, Martins MB, Karamanska R, Russell DA, Field RA (2009) Bacterial detection using carbohydrate-functionalised CdS quantum dots: a model study exploiting E. coli recognition of mannosides. Tetrahedron Lett 50:886–889. doi:10.1016/j.tetlet.2008.12.029
Carrillo CC, Simonet BM, Valcárcel M (2011) Colistin-functionalised CdSe/ZnS quantum dots as fluorescent probe for the rapid detection of Escherichia coli. Biosens Bioelectron 26:4368–4374. doi:10.1016/j.bios.2011.04.050
Wen HZ, Chun HL, Xiu CG, Fa RC, Huang HY, Xiao RW (2010) Mussel-inspired molecularly imprinted polymer coating superparamagnetic nanoparticles for protein recognition. J Mater Chem 20:880–883. doi:10.1039/b916619j
Roy H (2009) Tuning the properties of the bacterial membrane with aminoacylated phosphatidylglycerol. IUBMB Life 61:940–953. PMCID: PMC2757517
Liu A, Zhao L, Bai H, Zhao H, Xing X, Shi G (2009) Polypyrrole actuator with a bioadhesive surface for accumulating bacteria from physiological media. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 1:951–955
Sureshkumar M, Lee CK (2011) Polydopamine coated magnetic-chitin (MCT) particles as a new matrix for enzyme immobilization. Carbohydr Polym 84:775–780. doi:10.1016/j.carbpol.2010.03.036
Acknowledgments
The authors thank Laura Novitsky for technical assistance. This work was supported by Natural Sciences and Engineering Research Council of Canada (NSERC) fund 315574 to EPCL, and Bangladesh Agricultural University study leave to ZI.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Esm 1
(DOC 494 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Iqbal, Z., Lai, E.P.C. & Avis, T.J. Development of polymer-modified magnetic nanoparticles and quantum dots for Escherichia coli binding test. Microchim Acta 176, 193–200 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-011-0712-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-011-0712-2