Abstract
We report on a combination of magnetic solid-phase extraction and spectrophotometric determination of bromate. Cetyltrimethylammonium ion was adsorbed on the surface of phenyl-functionalized silica-coated Fe3O4 nanoparticles (Ph-SiO2@Fe3O4), and these materials served as the sorbent. The effects of surfactant and amount of sorbent, the composition of the desorption solution, the extraction time and temperature were optimized. Under optimized conditions, an enrichment factor of 12 was achieved, and the relative standard deviation is 2.9 % (for n = 5). The calibration plot covers the 1–50 ng mL−1 range with reasonable linearity (r 2 > 0.998); and the limit of detection is 0.5 ng mL−1. The method is not interfered by ionic compounds commonly found in environmental water samples. It was successfully applied to the determination of bromate in spiked water samples.

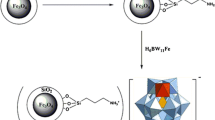
Extraction of bromate ions using surfactant-coated phenyl functionalized Fe3O4 magnetic nanoparticles followed by spectrophotometric detection.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Gunten UV, Oliveras Y (1998) Advanced oxidation of bromide-containing waters: bromate formation mechanisms. Environ Sci Technol 32:63–70. doi:10.1021/es970477j
Eickhorst T, Seubert A (2004) Germanium dioxide as internal standard for simplified trace determination of bromate, bromide, iodate and iodide by on-line coupling ion chromatography-inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry. J Chromatogr A 1050:103–109. doi:10.1016/j.chroma.2004.04.084
Reddy-Noone K, Jain A, Verma KK (2007) Liquid-phase microextraction–gas chromatography–mass spectrometry for the determination of bromate, iodate, bromide and iodide in high-chloride matrix. J Chromatogr A 1148:145–151. doi:10.1016/j.chroma.2007.03.027
Xu C, Shi J, Zhou W, Gao B, Yue Q, Wang X (2012) Bromate removal from aqueous solutions by nano crystalline akaganeite (β-FeOOH)-coated quartz sand (CACQS). Chem Eng J 187:63–68. doi:10.1016/j.cej.2012.01.087
US EPA method 300.1 (1997) The determination of inorganic anions in water by ion chromatography
Alonso-Mateos A, Almendral-Parra MJ, Fuentes-Prieto MS (2008) Sequential and simultaneous determination of bromate and chlorite (DBPs) by flow techniques: kinetic differentiation. Talanta 76:892–898. doi:10.1016/j.talanta.2008.04.059
Joyce RJ, Dhillon HS (1994) Trace level determination of bromate in ozonated drinking water using ion chromatography. J Chromatogr A 671:165–171. doi:10.1016/0021-9673(94)80235-1
Walters BD, Gordon G (1997) An ion chromatographic method for measuring <5 μg/L bromate ion in drinking water. Anal Chem 60:4275–4277. doi:10.1021/ac9703008
Echigo S, Minear RA, Yamada H, Jackson PE (2001) Comparison of three post-column reaction methods for the analysis of bromate and nitrite in drinking water. J Chromatogr A 920:205–211. doi:10.1016/S0021-9673(01)00533-7
Evenhuis CJ, Buchberger W, Hilder EF, Flook KJ, Pohl CA, Nesterenko PN, Haddad PR (2008) Separation of inorganic anions on a high capacity porous polymeric monolithic column and application to direct determination of anions in seawater. J Sep Sci 31:2598–2604. doi:10.1002/jssc.200800205
Cai Q, Guo ZX, Yu C, Zhang W, Yang Z (2003) Bromate assay in water by inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry combined with solid-phase extraction cartridges. Anal Bioanal Chem 377:740–748. doi:10.1007/s00216-003-2151-3
Snyder SA, Vanderford BJ, Rexing DJ (2005) Trace analysis of bromate, chlorate, iodate, and perchlorate in natural and bottled waters. Environ Sci Technol 39:4586–4593. doi:10.1021/es047935q
Zakaria P, Bloomfield C, Shellie RA, Haddad PR, Dicinoski GW (2011) Determination of bromate in sea water using multi-dimensional matrix-elimination ion chromatography. J Chromatogr A 1218:9080–9085. doi:10.1016/j.chroma.2011.10.029
Wang B, Cheng L, Dong S (2001) Construction of a heteropolyanion-modified electrode by a two-step sol–gel method and its electrocatalytic applications. J Electroanal Chem 516:17–22. doi:10.1016/S0022-0728(01)00677-5
Uraisin K, Takayanagi T, Nacapricha D, Motomizu S (2006) Novel oxidation reaction of prochlorperazine with bromate in the presence of synergistic activators and its application to trace determination by flow injection/spectrophotometric method. Anal Chim Acta 580:68–74. doi:10.1016/j.aca.2006.07.045
Esteves da Silva JCG, Dias JRM, Magalaes JMCS (2001) Factorial analysis of a chemiluminescence system for bromate detection in water. Anal Chim Acta 450:175–184. doi:10.1016/S0003-2670(01)01376-9
Oliveira SM, Segundo MA, Rangel AOSS, Lima JLFC, Cerda V (2011) Spectrophotometric determination of bromate in water using multisyringe flow injection analysis. Anal Lett 44:284–297. doi:10.1080/00032719.2010.500771
Weinberg HS, Yamada H, Joyce RJ (1998) New, sensitive and selective method for determining sub-microgram/l levels of bromate in drinking water. J Chromatogr A 804:137–142. doi:10.1016/S0021-9673(98)00152-6
Robinson PJ, Dunnill P, Lilly MD (1973) The properties of magnetic supports in relation to immobilized enzyme reactors. Biotechnol Bioeng 15:603–606. doi:10.1002/bit.260150318
Saraji M, Khaje N (2013) Phenyl-functionalized silica-coated magnetic nanoparticles for the extraction of chlorobenzenes, and their determination by GC-electron capture detection. J Sep Sci 36:1090–1096. doi:10.1002/jssc.201200863
Takafuji M, Ide S, Ihara H, Xu Z (2004) Preparation of poly(1-vinylimidazole)-grafted magnetic nanoparticles and their application for removal of metal ions. Chem Mater 16:1977–1983. doi:10.1021/cm030334y
Mashhadizadeh MH, Karami Z (2011) Solid phase extraction of trace amounts of Ag, Cd, Cu, and Zn in environmental samples using magnetic nanoparticles coated by 3-(trimethoxysilyl)-1-propantiol and modified with 2-amino-5-mercapto-1,3,4-thiadiazole and their determination by ICP-OES. J Hazard Mater 190:1023–1029. doi:10.1016/j.jhazmat.2011.04.051
Karatapanis AE, Fiamegos Y, Stalikas CD (2011) Silica-modified magnetic nanoparticles functionalized with cetylpyridinium bromide for the preconcentration of metals after complexation with 8-hydroxyquinoline. Talanta 84:834–839. doi:10.1016/j.talanta.2011.02.013
Faraji M, Yamini Y, Rezaee M (2010) Extraction of trace amounts of mercury with sodium dodecyle sulphate-coated magnetite nanoparticles and its determination by flow injection inductively coupled plasma-optical emission spectrometry. Talanta 81:831–836. doi:10.1016/j.talanta.2010.01.023
Merino F, Rubio S, Perez-Bendito D (2004) Evaluation and optimization of an on-line admicelle-based extraction-liquid chromatography approach for the analysis of ionic organic compounds. Anal Chem 76:3878–3886. doi:10.1021/ac049736v
Shariati S, Faraji M, Yamini Y, Rajabi AA (2011) Fe3O4 magnetic nanoparticles modified with sodium dodecyl sulfate for removal of safranin O dye from aqueous solutions. Desalination 270:160–165. doi:10.1016/j.desal.2010.11.040
Bagheri H, Zandi O, Aghakhani A (2011) Extraction of fluoxetine from aquatic and urine samples using sodium dodecyl sulfate-coated iron oxide magnetic nanoparticles followed by spectrofluorimetric determination. Anal Chim Acta 692:80–84. doi:10.1016/j.aca.2011.02.060
Zhao X, Cai Y, Wu F, Pan Y, Liao H, Xu B (2011) Determination of perfluorinated compounds in environmental water samples by high-performance liquid chromatography-electrospray tandem mass spectrometry using surfactant-coated Fe3O4 magnetic nanoparticles as adsorbents. Microchem J 98:207–214. doi:10.1016/j.microc.2011.01.011
Zhao X, Shi Y, Wang T, Cai Y, Jiang G (2008) Preparation of silica-magnetite nanoparticle mixed hemimicelle sorbents for extraction of several typical phenolic compounds from environmental water samples. J Chromatogr A 1188:140–147. doi:10.1016/j.chroma.2008.02.069
Romele L, Achilli M (1998) Spectrophotometric determination of low levels of bromate in drinking water after reaction with fuchsin. Analyst 123:291–294. doi:10.1039/A706130G
Saraji M, Hajialiakbari Bidgoli AA, Farajmand B (2011) Hollow fiber-based liquid–liquid–liquid microextraction followed by flow injection analysis using column-less HPLC for the determination of phenazopyridine in plasma and urine. J Sep Sci 34:1708–1715. doi:10.1002/jssc.201000929
Achilli M, Romele L (1999) Ion chromatographic determination of bromate in drinking water by post-column reaction with fuchsin. J Chromatogr A 847:271–277. doi:10.1016/S0021-9673(99)00190-9
Neves AIP, Albert-Garcia JR, Calatayud JM (2007) Chemiluminometric determination of the pesticide 3-indolyl acetic acid by a flow injection analysis assembly. Talanta 71:318–323. doi:10.1016/j.talanta.2006.04.003
ASTM standard D6581: Standard test method for bromate, bromide, chlorate, and chlorite in drinking water by chemically suppressed ion chromatography. doi:10.1520/D6581
Takayanagi T, Ishida M, Mbuna J, Driouich R, Motomizu S (2006) Determination of bromate ion in drinking water by capillary zone electrophoresis with direct photometric detection. J Chromatogr A 1128:298–302. doi:10.1016/j.chroma.2006.06.056
Acknowledgments
The authors wish to thank research council of Isfahan University of Technology (IUT) and Center of Excellence in Sensor and Green Chemistry for financial support of this project.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Saraji, M., Khaje, N. & Ghani, M. Cetyltrimethylammonium-coated magnetic nanoparticles for the extraction of bromate, followed by its spectrophotometric determination. Microchim Acta 181, 925–933 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-014-1188-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-014-1188-7