Abstract
The authors describe a photometric method for the determination of free cholesterol based on the oxidation of cholesterol by the catalytic action of the enzyme cholesterol oxidase. The hydrogen peroxide formed is used to oxidize the chromogenic compound 3,3′,5,5′-tetramethylbenzidine (TMB) by exploiting the peroxidase-like activity of carbon nanotube-supported Prussian blue (PB). This enzyme mimic was synthesized from a mixture of ferric chloride and hexacyanoferrate(III) in the presence of intrinsically reducing multi-walled carbon nanotubes. The composite can trigger the formation of a blue-green dye from TMB in the presence of H2O2. The findings were exploited to design a photometric (652 nm) assay that has a linear response in the 4 to 100 μM cholesterol concentration range and a 3 μM detection limit. The practicability of the method was verified by the successful analysis of free cholesterol in human blood samples.

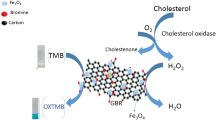
Schematic of a carbon nanotube-supported Prussian blue (PB/MWCNT) hybrid used as a promising peroxidase mimic. It has the advantages of low cost, simple synthesis, high activity, and good stability. PB/MWCNTs along with cholesterol oxidase (ChOx) are used in a colorimetric assay for the determination of free cholesterol.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Saric M, Kronzon I (2011) Cholesterol embolization syndrome. Curr Opin Cardiol 26:472–479
Wisitsoraat A, Sritongkham P, Karuwan C, Phokharatkul D, Maturos T, Tuantranont A (2010) Fast cholesterol detection using flow injection microfluidic device with functionalized carbon nanotubes based electrochemical sensor. Biosens Bioelectron 26:1514–1520
Hayat A, Haider W, Raza Y, Marty JL (2015) Colorimetric cholesterol sensor based on peroxidase-like activity of zinc oxide nanoparticles incorporated carbon nanotubes. Talanta 143:157–161
Bui TT, Park SY (2016) A carbon dot-hemoglobin complex-based biosensor for cholesterol detection. Green Chem 18:4245–4253
Tong YJ, Li HD, Guan HM, Zhao JM, Majeed S, Anjum S, Liang F, Xu GB (2013) Electrochemical cholesterol sensor based on carbon nanotube@molecularly imprinted polymer modified ceramic carbon electrode. Biosens Bioelectron 47:553–558
Cai XJ, Gao X, Wang LS, Wu Q, Lin XF (2013) A layer-by-layer assembled and carbon nanotubes/gold nanoparticles-based bienzyme biosensor for cholesterol detection. Sensor Actuat B-Chem 181:575–583
Hanefeld U, Cao LQ, Magner E (2013) Enzyme immobilisation: fundamentals and application. Chem Soc Rev 42:6211–6212
Gao LZ, Zhuang J, Nie L, Zhang JB, Zhang Y, Gu N, Wang TH, Feng J, Yang DL, Perrett S, Yan X (2007) Intrinsic peroxidase-like activity of ferromagnetic nanoparticles. Nat Nanotechnol 2:577–583
Yan J, Huang YF, Zhang CH, Fang ZZ, Bai WH, Yan MM, Zhu C, Chen AL (2017) Aptamer based photometric assay for the antibiotic sulfadimethoxine based on the inhibition and reactivation of the peroxidase-like activity of gold nanoparticles. Microchim Acta 184:59–63
Pan N, Li-Ying W, Wu LL, Peng CF, Xie ZJ (2017) Colorimetric determination of cysteine by exploiting its inhibitory action on the peroxidase-like activity of au@Pt core-shell nanohybrids. Microchim Acta 184:65–72
Niu XH, He YF, Pan JM, Li X, Qiu FX, Yan YS, Shi LB, Zhao HL, Lan MB (2016) Uncapped nanobranch-based CuS clews used as an efficient peroxidase mimic enable the visual detection of hydrogen peroxide and glucose with fast response. Anal Chim Acta 947:42–49
Ding CP, Yan YH, Xiang DS, Zhang CL, Xian YZ (2016) Magnetic Fe3S4 nanoparticles with peroxidase-like activity, and their use in a photometric enzymatic glucose assay. Microchim Acta 183:625–631
Espinosa JC, Navalon S, Primo A, Moral M, Sanz JF, Alvaro M, Garcia H (2015) Graphenes as efficient metal-free fenton catalysts. Chem Eur J 21:11966–11971
Chen J, Chen Q, Chen JY, Qiu HD (2016) Magnetic carbon nitride nanocomposites as enhanced peroxidase mimetics for use in colorimetric bioassays, and their application to the determination of H2O2 and glucose. Microchim Acta 183:3191–3199
Wei H, Wang EK (2013) Nanomaterials with enzyme-like characteristics (nanoenzymes): next-generation artificial enzymes. Chem Soc Rev 42:6060–6093
Nasir M, Nawaz MH, Latif U, Yaqub M, Hayat A, Rahim A (2017) An overview on enzyme-mimicking nanomaterials for use in electrochemical and optical assays. Microchim Acta 184:323–342
Zhao Y, Qiang H, Chen ZB (2017) Colorimetric determination of hg(II) based on a visually detectable signal amplification induced by a cu@au-hg trimetallic amalgam with peroxidase-like activity. Microchim Acta 184:107–115
Ferlay S, Mallah T, Ouahes R, Veillet P, Verdaguer M (1995) A room-temperature organometallic magnet based on Prussian blue. Nature 378:701–703
DeLongchamp DM, Hammond PT (2004) High-contrast electrochromism and controllable dissolution of assembled Prussian blue/polymer nanocomposites. Adv Funct Mater 14:224–232
Kong B, Selomulya C, Zheng GF, Zhao DY (2015) New faces of porous Prussian blue: interfacial assembly of integrated hetero-structures for sensing applications. Chem Soc Rev 44:7997–8018
Čunderlová V, Hlaváček A, Horňáková V, Peterek M, Němeček D, Hampl A, Eyer L, Skládal P (2015) Catalytic nanocrystalline coordination polymers as an efficient peroxidase mimic for labeling and optical immunoassays. Microchim Acta 183:651–658
Karyakin AA, Karyakina EE (1999) Prussian blue-based ‘artificial peroxidase’ as a transducer for hydrogen peroxide detection: application to biosensors. Sensor. Actuat. B-Chem. 57:268–273
Liu Y, Chu ZY, Jin WQ (2009) A sensitivity-controlled hydrogen peroxide sensor based on self-assembled Prussian blue modified electrode. Electrochem Commun 11:484–487
Wang T, Fu YC, Chai LY, Chao L, Bu LJ, Meng Y, Chen C, Ma M, Xie QJ, Yao SZ (2014) Filling carbon nanotubes with Prussian blue nanoparticles of high peroxidase-like catalytic activity for colorimetric chemoand biosensing. Chem Eur J 20:2623–2630
Dujardin E, Ebbesen TW, Krishnan A, Treacy MMJ (1998) Purification of single-shell nanotubes. Adv Mater 10:611–613
Taguchi M, Yagi I, Nakagawa M, Iyoda T, Einaga Y (2006) Photocontrolled magnetization of CdS-modified Prussian blue nanoparticles. J Am Chem Soc 128:10978–10982
Nie P, Shen LF, Luo HF, Ding B, Xu GY, Wang J, Zhang XG (2014) Prussian blue analogues: a new class of anode materials for lithium ion batteries. J Mater Chem A 2:5852–5857
Zhang WM, Ma D, Du JX (2014) Prussian blue nanoparticles as peroxidase mimetics for sensitive colorimetric detection of hydrogen peroxide and glucose. Talanta 120:362–367
Ding N, Yan N, Ren CL, Chen XG (2010) Colorimetric determination of melamine in dairy products by Fe3O4 magnetic nanoparticles-H2O2-ABTS detection system. Anal Chem 82:5897–5899
Cheng HJ, Zhang L, He J, Guo WJ, Zhou ZY, Zhang XJ, Nie SM, H. Wei (2016) Integrated nanozymes with nanoscale proximity for in vivo neurochemical monitoring in living brains. Anal Chem 88:5489–5497
Shi WJ, Fan H, Ai SY, Zhu LS (2015) Honeycomb-like nitrogen-doped porous carbon supporting Pt nanoparticles as enzyme mimic for colorimetric detection of cholesterol. Sensor. Actuat. B-Chem. 221:1515–1522
Nirala NR, Pandey S, Bansal A, Singh VK, Mukherjee B, Saxena PS, Srivastava A (2015) Different shades of cholesterol: gold nanoparticles supported on MoS2 nanoribbons for enhanced colorimetric sensing of free cholesterol. Biosens Bioelectron 74:207–213
Nirala NR, Abraham S, Kumar V, Bansal A, Srivastava A, Saxena PS (2015) Colorimetric detection of cholesterol based on highly efficient peroxidase mimetic activity of graphene quantum dots. Sensor. Actuat. B-Chem. 218:42–50
Tyagi M, Chandran A, Joshi T, Prakash J, Agrawal VV, Biradar AM (2014) Self assembled monolayer based liquid crystal biosensor for free cholesterol detection. Appl Phys Lett 104:154104
Lee YJ, Park JY (2010) Nonenzymatic free-cholesterol detection via a modified highly sensitive macroporous gold electrode with platinum nanoparticles. Biosens Bioelectron 26:1353–1358
Acknowledgements
This work was financially supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Nos. 21605061 and 31601549), the Natural Science Foundation of Jiangsu Province (No. BK20160489), the Natural Science Fund for Colleges and Universities in Jiangsu Province (No. 16KJB150009), the Postdoctoral Fund of China (No. 2016 M600365), the Postdoctoral Fund of Jiangsu Province (No. 1601015B), the Open Fund from the Shanghai Key Laboratory of Functional Materials Chemistry (No. SKLFMC201601), the Start-Up Research Fund of Jiangsu University (No. 15JDG143), and the Open Funding Project of the State Key Laboratory of Bioreactor Engineering.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
The author(s) declare that they have no competing interests.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(DOCX 1477 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
He, Y., Niu, X., Shi, L. et al. Photometric determination of free cholesterol via cholesterol oxidase and carbon nanotube supported Prussian blue as a peroxidase mimic. Microchim Acta 184, 2181–2189 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-017-2235-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-017-2235-y