Abstract
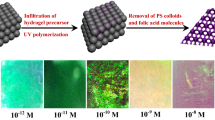
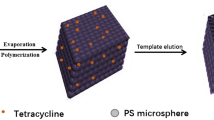
A molecularly imprinted photonic hydrogel (MIPH) is described for the optical determination of L-histidine (L-His). The inverse opal structure of MIPH was obtained by placing silica particles (230 nm) in molecularly imprinted polymer on a glass slide. After being fully etched by hydrofluoric acid, this inverse opal structure brings about a high specific surface and plentiful binding sites for L-His. If L-His is absorbed by the modified MIPH, its average effective refraction coefficient is increased. This causes the Bragg diffraction peak to be red-shifted by about 34 nm as the concentration of L-His increases from 0 to 100 nM. Much smaller diffraction peak shifts are obtained for other amino acids. The detection limit of this method is 10 pM. The response time towards L-His is as short as 60 s. In addition, the sensor can be recovered by treatment with 0.1 M acetic acid/methanol. It was applied to the determination of L-His in drinks sample.

After absorbing L-histidine, the average effective refractive index of this molecularly imprinted photonic hydrogel (MIPH) is increased, and the Bragg diffraction peak is shifted. The shift of the diffraction peak can be used for the detection of L-His








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Nan CG, Ping WX, Ping DJ, Qing CH (1999) A study on electrochemistry of histidine and its metabolites based on the diazo coupling reaction. Talanta 49(2):319–330
Rawat KA, Kailasa SK (2014) Visual detection of arginine, histidine and lysine using quercetin-functionalized gold nanoparticles. Microchim Acta 181(15–16):1917–1929
Yu M, Chu W, Wu Z (2010) XAFS study of the configuration of l-histidine with Mn 2+, co 2+, Ni 2+, cu 2+, Zn 2+ at pH 6.0. Nucl Inst Methods Phys Res A 619(1):408–410
Sasmal M, Maiti TK, Bhattacharyya TK (2015) Ultra-low level detection of L-histidine using solution-processed ZnO nanorod on flexible substrate. IEEE Trans Nanobiosci 14(6):634–640
Meng J, Zhang W, Cao C-X, Fan L-Y, Wu J, Wang Q-L (2010) Moving affinity boundary electrophoresis and its selective isolation of histidine in urine. Analyst 135(7):1592–1599
Wadud S, Or-Rashid MM, Onodera R (2002) Method for determination of histidine in tissues by isocratic high-performance liquid chromatography and its application to the measurement of histidinol dehydrogenase activity in six cattle organs. J Chromatogr B 767(2):369–374
Zheng X, Yao T, Zhu Y, Shi S (2015) Cu(2+) modulated silver nanoclusters as an on-off-on fluorescence probe for the selective detection of L-histidine. Biosens Bioelectron 66:103–108
Shamsipur M, Molaabasi F, Shanehsaz M, Moosavi-Movahedi AA (2015) Novel blue-emitting gold nanoclusters confined in human hemoglobin, and their use as fluorescent probes for copper(II) and histidine. Microchim Acta 182(5–6):1131–1141
Zhu X, Zhao T, Nie Z, Miao Z, Liu Y, Yao S (2016) Nitrogen-doped carbon nanoparticle modulated turn-on fluorescent probes for histidine detection and its imaging in living cells. Nanoscale 8(4):2205–2211
Li L-D, Chen Z-B, Zhao H-T, Guo L (2011) Electrochemical real-time detection of l-histidine via self-cleavage of DNAzymes. Biosens Bioelectron 26(5):2781–2785
Chen Z, Nai J, Ma H, Li Z (2014) Nickel hydroxide nanocrystals-modified glassy carbon electrodes for sensitive l-histidine detection. Electrochim Acta 116:258–262
Natsume T, Nakayama H, Cs J, Isobe T, Takio K, Mikoshiba K (2000) Combination of biomolecular interaction analysis and mass spectrometric amino acid sequencing. Anal Chem 72(17):4193–4198
Yablonovitch E (1987) Inhibited spontaneous emission in solid-state physics and electronics. Phys Rev Lett 58(20):2059–2062
John S (1987) Strong localization of photons in certain disordered dielectric superlattices. Phys Rev Lett 58(23):2486–2489
Fenzl C, Hirsch T, Wolfbeis OS (2014) Photonic crystals for chemical sensing and biosensing. Angew Chem Int Ed 53(13):3318–3335
Lee K, Asher SA (2000) Photonic crystal chemical sensors: pH and ionic strength. J Am Chem Soc 122(39):9534–9537
Wang J, Cao Y, Feng Y, Yin F, Gao J (2007) Multiresponsive inverse-opal hydrogels. Adv Mater 19(22):3865–3871
Ye B, Zhao Y, Cheng Y, Li T, Xie Z, Zhao X, Gu Z (2012) Colorimetric photonic hydrogel aptasensor for the screening of heavy metal ions. Nanoscale 4(19):5998–6003
Xue F, Meng Z, Wang F, Wang Q, Xue M, Xu Z (2014) A 2-D photonic crystal hydrogel for selective sensing of glucose. J Mater Chem 2(25):9559–9565
Hu X, Li G, Li M, Huang J, Li Y, Gao Y, Zhang Y (2008) Ultrasensitive specific stimulant assay based on molecularly imprinted photonic hydrogels. Adv Funct Mater 18(4):575–583
Wang C, Lim CY, Choi E, Park Y, Park J (2016) Highly sensitive user friendly thrombin detection using emission light guidance from quantum dots-aptamer beacons in 3-dimensional photonic crystal. Sensors Actuators B Chem 223:372–378
Wulff G (2002) Enzyme-like catalysis by molecularly imprinted polymers. Chem Rev 102(1):1–27
Wackerlig J, Lieberzeit PA (2015) Molecularly imprinted polymer nanoparticles in chemical sensing – synthesis, characterisation and application. Sensors Actuators B Chem 207:144–157
Cheong WJ, Yang SH, Ali F (2013) Molecular imprinted polymers for separation science: a review of reviews. J Sep Sci 36(3):609–628
Schirhagl R (2014) Bioapplications for molecularly imprinted polymers. Anal Chem 86(1):250–261
Wang H, Yi J, Velado D, Yu Y, Zhou S (2015) Immobilization of carbon dots in molecularly imprinted microgels for optical sensing of glucose at physiological pH. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 7(29):15735–15745
Kamra T, Zhou T, Montelius L, Schnadt J, Ye L (2015) Implementation of molecularly imprinted polymer beads for surface enhanced Raman detection. Anal Chem 87(10):5056–5061
Wei C, Zhou H, Zhou J (2011) Ultrasensitively sensing acephate using molecular imprinting techniques on a surface plasmon resonance sensor. Talanta 83(5):1422–1427
Li N, Qi L, Shen Y, Qiao J, Chen Y (2014) Novel oligo(ethylene glycol)-based molecularly imprinted magnetic nanoparticles for thermally modulated capture and release of lysozyme. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 6(19):17289–17295
Chen L, Xu S, Li J (2011) Recent advances in molecular imprinting technology: current status, challenges and highlighted applications. Chem Soc Rev 40(5):2922–2942
Lofgreen JE, Ozin GA (2014) Controlling morphology and porosity to improve performance of molecularly imprinted sol–gel silica. Chem Soc Rev 43(3):911–933
Guo C, Zhou C, Sai N, Ning B, Liu M, Chen H, Gao Z (2012) Detection of bisphenol a using an opal photonic crystal sensor. Sensors Actuators B Chem 166-167:17–23
Hu X, An Q, Li G, Tao S, Liu J (2006) Imprinted photonic polymers for chiral recognition. Angew Chem Int Ed 45(48):8145–8148
Meng L, Meng P, Zhang Q, Wang Y (2013) Fast screening of ketamine in biological samples based on molecularly imprinted photonic hydrogels. Anal Chim Acta 771:86–94
Jiang P, Hwang KS, Mittleman DM, Bertone JF, Colvin VL (1999) Template-directed preparation of macroporous polymers with oriented and crystalline arrays of voids. J Am Chem Soc 121(50):11630–11637
Acknowledgements
This study was financially supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (21874037, 21675045, and 21505038) and the International Scientific and Technological Cooperation Projects of China (2012DFR40480).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors. In this experiment, we did not collect any samples of human and animals.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, Q., Shi, W., Cheng, M. et al. Molecularly imprinted photonic hydrogel sensor for optical detection of L-histidine. Microchim Acta 185, 557 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-018-3080-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-018-3080-3