Summary
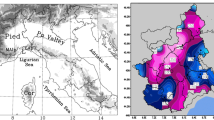
A newly developed non-hydrostatic model (MOLOCH), operating at a resolution of about 2 km, is run for a case of heavy precipitation over southeastern France. The event (8–9 September 2002) was characterized by intense convective activity leading to a severe flash flood in the region of the Gard river, south of the Massif Central. An almost stationary mesoscale convective system (MCS), developing well in advance of an approaching cold front, discharged a huge amount of rainfall over the same area, more than 600 mm in 24 hours.
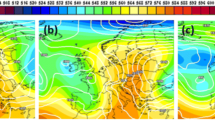
Several simulations are performed in order to test the model set-up, evaluate the sensitivity on different initial conditions, and analyse the case-study. The quantitative precipitation forecasts (QPF) appear to vary widely among the experiments, depending on the initialization time chosen (00, 06, and 12 UTC, September 8). Only the run starting at 06 UTC predicts, with a satisfactory degree of accuracy, the location where the MCS developed and its almost stationary behavior during the first stage (∼12 hours) of the event. In all the simulations, the convective system then propagated northward over the Massif Central.
In addition to experiments starting from standard ECMWF analyses, an assimilation procedure, based on Optimal Interpolation, is applied to the initial conditions. Surface observations of temperature, wind and relative humidity have been assimilated. The assimilation produces an improvement in the forecasts of surface fields and leads to a better location of the initial triggering phase.
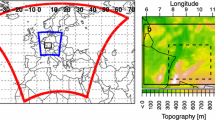
Further experiments, performed by changing the orography in the model, allow the investigation of the role of the Massif Central in triggering the mesoscale convective system and in controlling its evolution.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
S Anquetin E Yates V Ducrocq S Samouillan K Chancibault S Davolio C Accadia M Casaioli S Mariani G Ficca B Gozzini F Pasi M Pasqui A Garcia M Martorell R Romero P Chessa (2005) ArticleTitleThe 8th and 9th September 2002 flash flood event in France: an intercomparison of operational and research meteorological models Natural Hazard Earth Sys Sci 5 741–754
SJ Billet EF Toro (1997) ArticleTitleOn WAF-type schemes for multi-dimensional hyperbolic conservation laws J Comput Phys 130 1–24 Occurrence Handle10.1006/jcph.1996.5470
P Bougeault P Lacarrere (1989) ArticleTitleParameterization of the orography-induced turbulence in a mesoscale model Mon Wea Rev 117 1872–1890 Occurrence Handle10.1175/1520-0493(1989)117<1872:POOITI>2.0.CO;2
GH Bryan JC Wyngaard JM Fritsch (2003) ArticleTitleResolution requirements for the simulation of deep moist convection Mon Wea Rev 131 2394–2416 Occurrence Handle10.1175/1520-0493(2003)131<2394:RRFTSO>2.0.CO;2
A Buzzi M D’Isidoro S Davolio (2003) ArticleTitleA case study of an orographic cyclone south of the Alps during the MAP SOP Quart J R Met Soc 129 1795–1818 Occurrence Handle10.1256/qj.02.112
A Buzzi S Davolio M D’Isidoro P Malguzzi (2004) ArticleTitleThe impact of resolution and of MAP reanalysis on the simulations of heavy precipitation during MAP cases Met Zeit 13 91–97 Occurrence Handle10.1127/0941-2948/2004/0013-0091
K Chancibault S Anquetin V Ducrocq GM Saulnier (2006) ArticleTitleHydrological evaluation of high-resolution precipitation forecasts of the Gard flash-flood event (8–9 September 2002) Quar J R Met Soc 617 1091–1117 Occurrence Handle10.1256/qj.04.164
SH Chen YL Lin (2005) ArticleTitleEffects of moist Froude number and CAPE on a conditionally unstable flow over a mesoscale mountain ridge J Atmos Sci 62 331–350 Occurrence Handle10.1175/JAS-3380.1
CM Chu YL Lin (2000) ArticleTitleEffects of orography on the generation and propagation of mesoscale convective systems in a two-dimensional conditionally unstable flow J Atmos Sci 57 3817–3837 Occurrence Handle10.1175/1520-0469(2001)057<3817:EOOOTG>2.0.CO;2
S Davolio A Buzzi (2004) ArticleTitleA nudging scheme for the assimilation of precipitation data into a mesoscale model Wea Forecast 19 855–871 Occurrence Handle10.1175/1520-0434(2004)019<0855:ANSFTA>2.0.CO;2
S Davolio A Buzzi P Malguzzi (2006) ArticleTitleOrographic influence on deep convection: case study and sensitivity experiments Meteorol Z 1 215–223 Occurrence Handle10.1127/0941-2948/2006/0118
JW Deardorff (1980) ArticleTitleStratocumulus-capped mixed layer derived from a three-dimensional model Bound Layer Meteorol 18 495–527 Occurrence Handle10.1007/BF00119502
G Delrieu V Ducrocq E Gaume J Nicol O Payrastre E Yates PE Kirstetter H Andrieu PA Ayral C Bouvier JD Creutin M Livet S Anquetin M Lang L Neppel C Obled J Parent-Du Chatelet GM Saulnier A Walpersdorf W Wobrock (2005) ArticleTitleThe catastrophic flash-flood event of 8–9 September 2002 in the Gard region, France: a first case study for the Cévennes-Vivarais Mediterranean hydrometeorological observatory J Hydrometeor 6 34–52 Occurrence Handle10.1175/JHM-400.1
Drofa OV, Malguzzi P (2004) Parameterization of microphysical processes in a non hydrostatic prediction model. Proc. 14th Int. Conf. on Clouds and Precipitation (ICCP), Bologna, Italy, pp 1297–1300
V Ducrocq JP Lafore JL Redelsperger F Orain (2000) ArticleTitleInitialization of a fine-scale model for convective-system prediction: a case study Quart J R Met Soc 126 3041–3065 Occurrence Handle10.1002/qj.49712657004
V Ducrocq D Richard JP Lafore F Orain (2002) ArticleTitleStorm-scale numerical rainfall prediction for five precipitating events over France: on the importance of the initial humidity field Wea Forecast 17 1236–1256 Occurrence Handle10.1175/1520-0434(2002)017<1236:SSNRPF>2.0.CO;2
WA Gallus M Segal (2001) ArticleTitleImpact of improved initialization of mesoscale features on convective system rainfall in the 10-km Eta simulations Wea Forecast 16 680–696 Occurrence Handle10.1175/1520-0434(2001)016<0680:IOIIOM>2.0.CO;2
James RP, Bryan GH, Fritsch JM (2002) The effect of turbulence-resolving grid spacing on convective precipitation. Proc. Int. Conf. on Quantitative Precipitation Forecasting, Reading, UK, p 65
MM Miglietta A Buzzi (2004) ArticleTitleA numerical study of moist stratified flow regimes over isolated topography Quart J R Met Soc 130 1749–1770 Occurrence Handle10.1256/qj.02.225
JS Kain (2004) ArticleTitleThe Kain-Fritsch convective parameterization: an update J Appl Meteorol 43 170–181 Occurrence Handle10.1175/1520-0450(2004)043<0170:TKCPAU>2.0.CO;2
J Molinari M Dudek (1992) ArticleTitleParameterization of convective precipitation in mesoscale numerical models: a critical review Mon Wea Rev 120 326–344 Occurrence Handle10.1175/1520-0493(1992)120<0326:POCPIM>2.0.CO;2
Morcrette JJ, Clough SA, Mlawer EJ, Iacono MJ (1998) Impact of a validated radiative transfer scheme, RRTM, on the ECMWF model climate and 10-day forecasts. ECMWF Technical Memo, 252
Richard E, Asencio N, Benoit R, Buzzi A, Ferretti R, Malguzzi P, Serafin S, Zangl G, Georgis JF (2002) Intercomparison of the simulated precipitation fields of the MAP IOP 2B with different high-resolution models. Proc. 10th Conf. on Mountain Meteorology, Park City, Utah, pp 167–170
B Ritter JF Geleyn (1992) ArticleTitleA comprehensive radiation scheme for numerical weather prediction models with potential applications in climate simulations Mon Wea Rev 120 303–325 Occurrence Handle10.1175/1520-0493(1992)120<0303:ACRSFN>2.0.CO;2
Schwarb M, Frei C, Daly C, Schär C (2001) Mean annual precipitation throughout the European Alps 1971–1990. In: Hydrological atlas of Switzerland, Plate 2.6. Available from: Landeshydrologie und Geologie, 3003 Bern, Switzerland
S Sénési P Bougeault JL Chèze P Cosentino RM Thepenier (1996) ArticleTitleThe Vaison-la Romaine flash flood: mesoscale analysis and predictability issues Wea Forecast 11 417–442 Occurrence Handle10.1175/1520-0434(1996)011<0417:TVLRFF>2.0.CO;2
J Stein (2004) ArticleTitleExploration of some convective regimes over the Alpine orography Quart J R Met Soc 130 481–502 Occurrence Handle10.1256/qj.02.220
J Stein E Richard JP Lafore JP Pinty N Asencio S Cosma (2000) ArticleTitleHigh-resolution non-hydrostatic simulations of flash-flood episodes with gridnesting and ice-phase parameterization Meteorol Atmos Phys 72 203–221 Occurrence Handle10.1007/s007030050016
A Walser D Lüthi C Schär (2004) ArticleTitlePredictability of precipitation in a cloud-resolving model Mon Wea Rev 132 560–577 Occurrence Handle10.1175/1520-0493(2004)132<0560:POPIAC>2.0.CO;2
ML Weisman WC Skamarock JB Klemp (1997) ArticleTitleThe resolution dependence of explicitly modeled convective systems Mon Wea Rev 125 527–548 Occurrence Handle10.1175/1520-0493(1997)125<0527:TRDOEM>2.0.CO;2
JW Wilson NA Crook CK Mueller (1998) ArticleTitleNowcasting thunderstorms: a status report Bull Amer Meteor Soc 79 2079–2099 Occurrence Handle10.1175/1520-0477(1998)079<2079:NTASR>2.0.CO;2
Zampieri M (2004) Comparison among first, second and third order CBL models. Proc. 16th Symp. on Boundary Layer and Turbulence, Portland, Maine
M Zampieri P Malguzzi A Buzzi (2005) ArticleTitleSensitivity of quantitative precipitation forecasts to boundary layer parameterization: a flash flood case study in the Western Mediterranean Natural Hazard Earth Sys Sci 5 603–612 Occurrence Handle10.5194/nhess-5-603-2005
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Davolio, S., Buzzi, A. & Malguzzi, P. High resolution simulations of an intense convective precipitation event. Meteorol. Atmos. Phys. 95, 139–154 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00703-006-0200-0
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00703-006-0200-0