Abstract
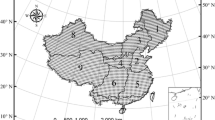
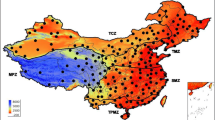
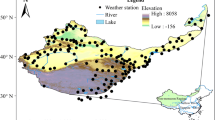
Based on daily maximum and minimum temperature data from 437 weather stations over China, this study examined the spatiotemporal change of temperature extremes in China from 1960 to 2011. Results showed a general downward trends in the occurrence of cold days (TX10) and nights (TN10) (base period 1961–1990), but upward tendency on the occurrence of warm days (TX90) and nights (TN90), the temperatures of coldest day (TXn), coldest night (TNn), warmest day (TXx), and warmest night (TNx) in China and most climate regions. At the national scale, TX10 and TN10 have significantly decreased by −1.89 and −4.39 days/decade, and TX90 and TN90 have significantly increased by 2.49 and 4.72 days/decade from 1960 to 2011. The national average trends for TXn, TNn, TXx, and TNx were 0.28, 0.54, 0.17, and 0.27 °C/decade, respectively. The temporal changes of extremes indices showed that changes in cold (warm) relative indices may be primarily related to that of corresponding winter (summer) Tmax and Tmin, respectively. Regionally, the magnitudes of changes in extreme indices decreased from the north to south of China. However, we found significant increase of warm extremes, especially warm days and nights in Southeast China. For most climate regions, the trend magnitudes in warm days/nights were larger than that in cold days/nights, but the trend in coldest temperature was much higher than that in warmest temperature. The trend magnitudes in minimum temperature indices were larger than those based on daily maximum temperature, explaining the faster increase of Tmin than Tmax in China.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alexander LV, Zhang X, Peterson TC, Caesar J, Gleason B, Klein Tank A, Haylock M, Collins D, Trewin B, Rahimzadeh F, Tagipour A, Ambenje P, Rupa Kumar K, Revadekar J, Griffiths G, Vincent L, Stephenson D, Burn J, Aguilar E, Brunet M, Taylor M, New M, Zhai P, Rusticucci M, Vazquez-Aguirre JL (2006) Global observed changes in daily climate extremes of temperature and precipitation. J Geophys Res 111:D05109
Dai A, Trenberth KE, Karl TR (1999) Effects of clouds, soil moisture, precipitation, and water vapor on diurnal temperature range. J Clim 12:2451–2473
DeGaetano AT, Allen RJ (2002) Trends in twentieth-century temperature extremes across the United States. J Clim 15:3188–3205
Donat MG, Alexander LV, Yang H, Durre I, Vose R, Dunn RJH, Willett KM, Aguilar E, Brunet M, Caesar J, Hewitson B, Jack C, Klein Tank AMG, Kruger AC, Marengo JA, Peterson TC, Renom M, Oria Rojas C, Rusticucci M, Salinger J, Elrayah AS, Sekele SS, Srivastava AK, Trewin B, Villarroel C, Vincent LA, Zhai P, Zhang X, Kitching S (2013) Updated analyses of temperature and precipitation extreme indices since the beginning of the twentieth century: the HadEX2 dataset. J Geophys Res 118:2098–2118
Du HB, ZF W, Li M, Jin YH, Zong SW, Meng XJ (2013) Characteristics of extreme daily minimum and maximum temperature over Northeast China, 1961–2009. Theor Appl Climatol 111:161–171
Durre I, Wallace JM, Lettenmaier DP (2000) Dependence of extreme daily maximum temperatures on antecedent soil moisture in the contiguous United States during summer. J Clim 13:2641–2651
Easterling DR, Horton B, Jones PD, Peterson TC, Karl TR, Parker DE, Salinger MJ, Razuvayev V, Plummer N, Jamason P, Folland CK (1997) Maximum and minimum temperature trends for the globe. Science 277:364–367
Easterling DR, Meehl GA, Parmesan C, Changnon SA, Karl TR, Mearns LO (2000) Climate extremes: observations, modeling, and impacts. Science 289:2068–2074
Gong DY, Pan YZ, Wang JA (2004) Changes in extreme daily mean temperatures in summer in eastern China during 1955–2000. Theor Appl Climatol 77:25–37
Halsnæs K, Kaspersen PS, Drews M (2015) Key drivers and economic consequences of high-end climate scenarios: uncertainties and risks. Clim Res 64:85–98
Jiang Z, Song J, Li L, Chen W, Wang Z, Wang J (2012) Extreme climate events in China: IPCC-AR4 model evaluation and projection. Clim Chang 110:385–401
Katz RW, Brown BG (1992) Extreme events in a changing climate: variability is more important than averages. Clim Chang 21:289–302
Kendall MG (1975) Rank correlation measures. Charles Griffin, London
Li Z, He Y, Wang P, Theakstone WH, An W, Wang F, Lu A, Zhang W, Cao W (2012) Changes of daily climate extremes in southwestern China during 1961–2008. Glob Planet Chang 80:255–272
Liu B, Xu M, Henderson M, Qi Y, Li Y (2004) Taking China’s temperature: daily range, warming trends, and regional variations, 1955–2000. J Clim 17:4453–4462
Liu B, Xu M, Henderson M, Qi Y (2005) Observed trends of precipitation amount, frequency, and intensity in China, 1960–2000. J Geophys Res 110:D08103
Liu B, Henderson M, Xu M (2008) Spatiotemporal change in China’s frost days and frost-free season, 1955–2000. J Geophys Res 113:D12104
Liu B, Henderson M, Zhang Y, Xu M (2009) Spatiotemporal change in China’s climatic growing season: 1955–2000. Clim Chang 99:93–118
Liu B, Henderson M, Xu M, Zhang Y (2011) Observed changes in precipitation on the wettest days of the year in China, 1960–2000. Int J Climatol 31:487–503
Mann HB (1945) Nonparametric tests against trend. Econometrica 13:245–259
Mearns LO, Katz RW, Schneider SH (1984) Extreme high-temperature events: changes in their probabilities with changes in mean temperature. J Appl Meteorol 23:1601–16132
Nicholls N (2001) Commentary and analysis: the insignificance of significance testing. Bull Am Meteorol Soc 82:981–986
Qi Y, Henderson M, Xu M, Chen J, Shi P, He C, Skinner GW (2004) Evolving core-periphery interactions in a rapidly expanding urban landscape: the case of Beijing. Landscape Ecol 19:375–388
Qian W, Lin X (2004) Regional trends in recent temperature indices in China. Clim Res 27:119–134
Qian Y, Gong D, Fan J, Leung LR, Bennartz R, Chen D, Wang W (2009) Heavy pollution suppresses light rain in China: observations and modeling. J Geophys Res 114:D00K02
Ren GY, Zhou YQ (2014) Urbanization effect on trends of extreme temperature indices of national stations over mainland China, 1961–2008. J Clim 27:2340–2360
Shen D, Varis O (2001) Climate change in China. Ambio 30:381–383
Shen X, Liu B, Li G, Wu Z, Jin Y, Yu P, Zhou D (2014) Spatiotemporal change of diurnal temperature range and its relationship with sunshine duration and precipitation in China. J Geophys Res 119:13163–13179
Song C, Pei T, Zhou C (2014) The role of changing multiscale temperature variability in extreme temperature events on the eastern and central Tibetan Plateau during 1960–2008. Int J Climatol 34:3683–3701
Toreti A, Desiato F (2008) Changes in temperature extremes over Italy in the last 44 years. Int J Climatol 28:733–745
Wang B, Zhang M, Wei J, Wang S, Li S, Ma Q, Li X, Pan S (2013) Changes in extreme events of temperature and precipitation over Xinjiang, Northwest China, during 1960–2009. Quatern Int 298:141–151
Wang Y, Ren F, Zhang X (2014) Spatial and temporal variations of regional high temperature events in China. Int J Climatol 34:3054–3065
Wu C, Huang G, Yu H, Chen Z, Ma J (2014) Spatial and temporal distributions of trends in climate extremes of the Feilaixia catchment in the upstream area of the Beijiang River Basin, South China. Int J Climatol 34:3161–3178
Yan ZW, Jones PD, Davies TD, Moberg A, Bergstrom H, Camuffo D, Cocheo C, Maugeri M, Demaree GR, Verhoeve T, Thoen E, Barriendos M, Rodriguez R, Martin-Vide J, Yang C (2002) Trends of extreme temperatures in Europe and China based on daily observations. Clim Chang 53:355–392
Yang J, Ren C, Jiang Z (2008) Characteristics of extreme temperature event and its response to regional warming in Northwest China in past 45 years. Chin Geogra Sci 18:70–76
You Q, Kang S, Aguilar E, Yan Y (2008) Changes in daily climate extremes in the eastern and central Tibetan Plateau during 1961–2005. J Geophys Res 113:D7
You Q, Kang S, Aguilar E, Pepin N, Flügel WA, Yan Y, Zhang Y, Huang J (2011) Changes in daily climate extremes in China and their connection to the large scale atmospheric circulation during 1961–2003. Clim Dyn 36:2399–2417
Yu Z, Li X (2014) Recent trends in daily temperature extremes over northeastern China (1960–2011). Quatern Int 380:35–48
Zhai P, Pan X (2003) Trends in temperature extremes during 1951–1999 in China. Geophys Res Lett 30:17
Zhai P, Sun A, Ren F, Liu X, Gao B, Zhang, Q (1999) Changes of climate extremes in China. In: Weather and Climate Extremes, Springer Netherlands.
Zhang Q, Xiao M, Singh VP, Wang Y (2016) Spatiotemporal variations of temperature and precipitation extremes in the Poyang Lake basin, China. Theor Appl Climatol 124:855–864
Zhou Y, Ren G (2012) Change in extreme temperature event frequency over mainland China, 1961-2008. Clim Res 50:125
Zhou L, Dickinson RE, Tian Y, Fang J, Li Q, Kaufmann RK, Tucker C, Myneni RB (2004) Evidence for a significant urbanization effect on climate in China. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 101:9540–9544
Zhou L, Dai A, Dai Y, Vose RS, Zou CZ, Tian Y, Chen H (2009) Spatial dependence of diurnal temperature range trends on precipitation from 1950 to 2004. Clim Dyn 32:429–440
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 41601048).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shen, X., Liu, B., Lu, X. et al. Spatial and temporal changes in daily temperature extremes in China during 1960–2011. Theor Appl Climatol 130, 933–943 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00704-016-1934-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00704-016-1934-3