Abstract
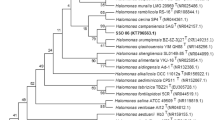
A Gram-positive, motile, endospore-forming and rod-shaped halophilic bacterial strain MSS-155 (KCTC 3788 and KCCM 41687) was isolated from a marine solar saltern of the Yellow Sea in Korea and was subjected to a polyphasic taxonomic study. This organism grew at temperature of 10.0–42.0°C with an optimum of 35°C. Strain MSS-155 grew optimally in the presence of 10% NaCl and did not grow in the absence of NaCl. The cell wall peptidoglycan type of strain MSS-155 was A4β based on l-Orn-d-Asp. Strain MSS-155 was also characterized chemotaxonomically by having menaquinone-7 (MK-7) as the predominant isoprenoid quinone and anteiso-C15:0 as the major fatty acid. The DNA G+C content was 44.0 mol%. Phylogenetic analysis based on 16S rDNA sequences showed that strain MSS-155 falls within the radiation of the cluster comprising Halobacillus species. Levels of 16S rDNA sequence similarity between strain MSS-155 and the type strains of four Halobacillus species were in the range 97.6–98.8%. Strain MSS-155 exhibited levels of DNA-DNA relatedness of 6.2–11.2% to the type strains of Halobacillus species described previously. On the basis of phenotypic properties, phylogeny, and genomic data, strain MSS-155 should be placed in the genus Halobacillus as a member of a novel species, for which we propose the name Halobacillus locisalis sp. nov.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Antón J, Llobet-Brossa E, Rodríguez-Valera F, Amann R (1999) Fluorescence in situ hybridization analysis of the prokaryotic community in habiting crystallizer ponds. Environ Microbiol 1:517–523
Antón J, Rosselló-Mora R, Rodríguez-Valera F, Amann R (2000) Extremely halophilic Bacteria in crystallizer ponds from solar salterns. Appl Environ Microbiol 66:3052–3057
Claus D, Fahmy F, Rolf HJ, Tosunoglu N (1983) Sporosarcina halophila sp. nov., an obligate, slightly halophilic bacterium from salt marsh soils. Syst Appl Microbiol 4:496–506
Cowan ST, Steel KJ (1965) Manual for the identification of medical bacteria. Cambridge University Press, London
Ezaki T, Hashimoto Y, Yabuuchi E (1989) Fluorometric deoxyribonucleic acid- deoxyribonucleic acid hybridization in microdilution wells as an alternative to membrane filter hybridization in which radioisotopes are used to determine genetic relatedness among bacterial strains. Int J Syst Bacteriol 39:224–229
Felsenstein J (1981) Evolutionary trees from DNA sequences: a maximum likelihood approach. J Mol Evol 17:368–376
Felsenstein J (1993) PHYLIP: phylogenetic inference package (version 3.5). University of Washington, Seattle, Washington
Jukes TH, Cantor CR (1969) Evolution of protein molecules. In: Munro HN (ed) Mammalian protein metabolism,vol 3. Academic Press, New York, pp 21–132
Kluge AG, Farris FS (1969) Quantitative phyletics and the evolution of anurans. Syst Zool 18:1–32
Komagata K, Suzuki K (1987) Lipids and cell-wall analysis in bacterial systematics. Methods Microbiol 19:161–203
Lanyi B (1987) Classical and rapid identification methods for medically important bacteria. Methods Microbiol 19:1–67
Leifson E (1963) Determination of carbohydrate metabolism of marine bacteria. J Bacteriol 85:1183–1184
Levring T (1946) Some culture experiments with Ulva and artificial seawater. Kungl Fysiografiska Sällsk Lund Förhandlingar 16:45–56
Litchfield CD, Gillevet PM (2002) Microbial diversity and complexity in hypersaline environments: A preliminary assessment. J Ind Microbiol Biotechnol 28:48–55
Ochsenreiter T, Pfeifer F, Schleper C (2002) Diversity of Archaea in hypersaline environments characterized by molecular-phylogenetic and cultivation studies. Extremophiles 6:267–274
Oren A (1994) The ecology of the extremely halophilic archaea. FEMS Microbiol Rev 13:415–440
Oren A (2002) Diversity of halophilic microorganisms: Environments, phylogeny, physiology, and applications. J Ind Microbiol Biotechnol 28:56–63
Rodriguez-Valera F (1986) The ecology and taxonomy of aerobic chemoorganotrophic halophilic eubacteria. FEMS Microbiol Rev 39:17–22
Rothschild LJ, Mancinelli RL (2001) Life in extreme environments. Nature 409:1092–1101
Saitou N, Nei M (1987) The neighbor-joining method: a new method for reconstructing phylogenetic trees. Mol Biol Evol 4:406–425
Sass AM, Sass H, Coolen MJL, Cypionka H, Overmann J (2001) Microbial communities in the chemocline of a hypersaline deep-sea basin (Urania basin, Mediterranean Sea). Appl Environ Microbiol 67:5392–5402
Schleifer KH, Kandler O (1972) Peptidoglycan types of bacterial cell walls and their taxonomic implications. Bacteriol Rev 36:407–477
Schlesner H, Lawson PA, Collins MD, Weiss N, Wehmeyer U, Völker H, Thomm M (2001) Filobacillus milensis gen. nov., sp. nov., a new halophilic spore-forming bacterium with Orn-d-Glu-type peptidoglycan. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 51:425–431
Shida O, Takagi H, Kadowaki K, Nakamura LK, Komagata K (1997) Transfer of Bacillus alginolyticus, Bacillus chondroitinus, Bacillus curdlanolyticus, Bacillus glucanolyticus, Bacillus kobensis, and Bacillus thiaminolyticus to the genus Paenibacillus and emended description of the genus Paenibacillus. Int J Syst Bacteriol 47:289–298
Spring S, Ludwig W, Marquez MC, Ventosa A, Schleifer K-H (1996) Halobacillus gen. nov., with description of Halobacillus litoralis sp. nov. and Halobacillus truperi sp. nov., and transfer of Sporosarcina halophilia to Halobacillus halophilus comb. nov. Int J Syst Bacteriol 46:492–496
Stackebrandt E, Goebel BM (1994) Taxonomic note: a place for DNA-DNA reassociation and 16S rRNA sequence analysis in the present species definition in bacteriology. Int J Syst Bacteriol 44:846–849
Tamaoka J, Komagata K (1984) Determination of DNA base composition by reverse-phase high-performance liquid chromatography. FEMS Microbiol Lett 25:125–128
Thompson JD, Higgins DG, Gibson TJ (1994) CLUSTAL W: improving the sensitivity of progressive multiple sequence alignment through sequence weighting, position specific gap penalties and weight matrix choice. Nucleic Acids Res 22:4673–4680
Ventosa A, Nieto JJ, Oren A (1998) Biology of moderately halophilic aerobic bacteria. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev 62:504–544
Vreeland RH, Piselli Jr. AF, McDonnough S, Meyers SS (1998) Distribution and diversity of halophilic bacteria in a subsurface salt formation. Extremophiles 2:321–331
Wainø M, Tindall BJ, Schumann P, Ingvorsen K (1999) Gracilibacillus gen. nov., with description of Gracilibacillus halotolerans gen. nov., sp. nov.; transfer of Bacillus dipsosauri to Gracilibacillus dipsosauri comb. nov., and Bacillus salexigens to the genus Salibacillus gen. nov., as Salibacillus salexigens comb. nov. Int J Syst Bacteriol 49:821–831
Wayne LG, Brenner DJ, Colwell RR, Grimont PAD, Kandler O, Krichevsky MI, Moore LH, Moore WEC, Murray RGE, Stackebrandt E, Starr MP, Trüper HG (1987) Report of the Ad Hoc Committee on Reconciliation of Approaches to Bacterial Systematics. Int J Syst Bacteriol 37:463–464
Yoon J-H, Kim H, Kim S-B, Kim H-J, Kim WY, Lee ST, Goodfellow M, Park Y-H (1996) Identification of Saccharomonospora strains by the use of genomic DNA fragments and rRNA gene probes. Int J Syst Bacteriol 46:502–505
Yoon J-H, Lee ST, Park Y-H (1998) Inter- and intraspecific phylogenetic analysis of the genus Nocardioides and related taxa based on 16S rDNA sequences. Int J Syst Bacteriol 48:187–194
Yoon J-H, Weiss N, Lee K-C, Lee I-S, Kang KH, Park Y-H (2001) Jeotgalibacillus alimentarius gen. nov., sp. nov., a novel bacterium isolated from jeotgal with l-lysine in the cell wall, and reclassification of Bacillus marinus Rüger 1983 as Marinibacillus marinus gen. nov., comb. nov. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 51:2087–2093
Yoon J-H, Kang KH, Park Y-H (2003) Halobacillus salinus sp. nov., isolated from a salt lake on the coast of the East Sea in Korea. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 53:687–693
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the 21C Frontier program of Microbial Genomics and Applications (grant MG02-0401-001-1-0-0), the NRL research program (grants M10104000294-01J000012800 and M10104000294-01J000012811) of the Ministry of Science and Technology (MOST) of the Republic of Korea, and by the research fund of Probionic Corporation of Korea.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by W.D. Grant
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yoon, JH., Kang, K.H., Oh, TK. et al. Halobacillus locisalis sp. nov., a halophilic bacterium isolated from a marine solar saltern of the Yellow Sea in Korea. Extremophiles 8, 23–28 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00792-003-0352-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00792-003-0352-5