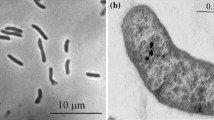
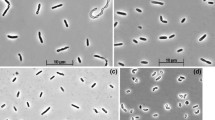
Abstract
Anaerobic enrichments with H2 as electron donor and thiosulfate/polysulfide as electron acceptor at pH 10 and 0.6 M total Na+ yielded two non sulfate-reducing representatives of reductive sulfur cycle from soda lake sediments. Strain AHT 1 was isolated with thiosulfate as the electron acceptor from north–eastern Mongolian soda lakes and strain AHT 2—with polysulfide as the electron acceptor from Wadi al Natrun lakes in Egypt. Both isolates represented new phylogenetic lineages: AHT 1—within Clostridiales and AHT 2—within the Deltaproteobacteria. Both bacteria are obligate anaerobes with respiratory metabolism. Both grew chemolithoautotrophically with H2 as the electron donor and can use thiosulfate, elemental sulfur and polysulfide as the electron acceptors. AHT 2 also used nitrate as acceptor, reducing it to ammonia. During thiosulfate reduction, AHT 1 excreted sulfite. dsrAB gene was not found in either strain. Both strains were moderate salt-tolerant (grow up to 2 M total Na+) true alkaliphiles (grow between pH 8.5 and 10.3). On the basis of the phenotypic and phylogenetic data, strains AHT 1 and AHT 2 are proposed as new genera and species Dethiobacter alkaliphilus and Desulfurivibrio alkaliphilus, respectively.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Duckworth AW, Grant WD, Jones BE, van Steenbergen R (1996) Phylogenetic diversity of soda lake alkaliphiles. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 19:181–191
Fardeau M-L, Cayol J-L, Magot M, Ollivier B (1994) Hydrogen oxidation abilities in the presence of thiosulfate as electron acceptor within the genus Thermoanaerobacter. Curr Microbiol 29:269–272
Foti M, Sorokin DY, Lomans B, Mussman M, Zakharova EE, Pimenov NV, Kuenen JG, Muyzer G (2007) Diversity, activity and abundance of sulfate-reducing bacteria in saline and hypersaline soda lakes. Appl Environ Microbiol 73:2093–2100
Hinsley AP, Berks BC (2002) Specificity of respiratory pathways involved in the reduction of sulfur compounds by Salmonella enterica. Microbiology 148:3631–3638
Hoeft SE, Kulp TR, Stolz JF, Hollibaugh JT, Oremland RS (2004) Dissimilatory arsenate reduction with sulfide as electron donor: experiments with Mono Lake water and isolation of strain MLMS-1, a chemoautotrophic arsenate respirer. Appl Environ Microbiol 70:2741–2747
Jones BE, Grant WD, Duckworth AW, Owenson GG (1998) Microbial diversity of soda lakes. Extremophiles 2:191–200
Jukes TH, Cantor CR (1969) Evolution of protein molecules. In: Munro HN (ed) Mammalian protein metabolism. Academic Press, New York, pp 21–123
Klimmek O, Kreis V, Klein C, Simon J, Wittershagen A, KroÈger A (1998) The function of the periplasmic Sud protein in polysulfide respiration of Wolinella succinogenes. Eur J Biochem 253:263–269
Marmur J (1961) A procedure for isolation of DNA from microorganisms. J Mol Biol 3:208-214
Marmur J, Doty P (1962) Determination of the base composition of deoxyribonucleic acid from microorganisms. J Mol Biol 5:109–118
Mesbah NM, Hedrick DB, Peacock AD, Rohde M, Wiegel J (2007) Natranaerobius thermophilus gen. nov., sp. nov., a halophilic, alkalithermophilic bacterium from soda lakes of the Wadi An Natrun, Egypt, and proposal of Natranaerobiaceae fam. nov. and Natranaerobiales ord. nov. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 57:2507–2512
Nielsen MB, Kjeldsen KU, Ingvorsen K (2006) Desulfitibacter alkalitolerans gen. nov., sp. nov., an anaerobic, alkalitolerant, sulfite-reducing bacterium isolated from a district heating plant. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 56:2831–2836
Pfennig N, Lippert KD (1966) Über das Vitamin B12—bedürfnis phototropher Schwefel bacterien. Arch Microbiol 55:245–256
Pikuta EV, Hoover RB, Bej AK, Marsic D, Whitman WB, Cleland D, Krader P (2003) Desulfonatronum thiodismutans sp. nov., a novel alkaliphilic, sulfate-reducing bacterium capable of lithoautotrophic growth. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 53:1327–1332
Pikuta EV, Zhilina TN, Zavarzin GA, Kostrikina NA, Osipov GA, Rainey FA (1998) Desulfonatronum lacustre gen. nov., sp. nov.: a new alkaliphilic sulfate-reducing bacterium utilizing ethanol. Microbiology 67:105–113 (Moscow, English translation)
Scholten JCM, Joye SB, Hollibaugh JT, Murrell JC (2005) Molecular analysis of the sulfate reducing and archaeal community in a meromictic soda lake (Mono Lake, California) by targeting 16S rRNA, mcrA, apsA, and dsrAB genes. Microb Ecol 50:29–39
Sorokin DY (2003) Oxidation of inorganic sulfur compounds by obligately organotrophic bacteria. Microbiology 72:641–653 (Moscow, English translation)
Sorokin DY, Banciu H, Robertson LA, Kuenen JG (2006) Haloalkaliphilic sulfur-oxidizing bacteria. In: Dworkin M, Falkow S, Rosenberg E, Schleifer KH, Stackebrandt E (eds) The Prokaryotes, vol 2: ecophysiology and biochemistry. Springer, New York, pp 969–984
Sorokin DY, Foti M, Tindall BJ, Muyzer G (2007) Desulfurispirillum alkaliphilum gen. nov. sp. nov., a novel obligately anaerobic sulfur- and dissimilatory nitrate-reducing bacterium from a full-scale sulfide-removing bioreactor. Extremophiles 11:363–370
Sorokin DY, Gorlenko VM, Namsaraev BB, Namsaraev ZB, Lysenko AM, Eshinimaev BT, Khmelenina VN, Trotsenko YA, Kuenen JG (2004a) Prokaryotic communities of the north–eastern Mongolian soda lakes. Hydrobiologia 522:235–248
Sorokin DY, Tourova TP, Antipov AN, Muyzer G, Kuenen JG (2004b) Anaerobic growth of the haloalkaliphilic denitrifying sulfur-oxidising bacterium Thialkalivibrio thiocyanodenitrificans sp. nov. with thiocyanate. Microbiology 150:2435–2442
Sorokin DY, Kuenen JG (2005a) Alkaliphilic chemolithotrophs from sodas lakes. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 52:287–295
Sorokin DY, Kuenen JG (2005b) Haloalkaliphilic sulfur-oxidizing bacteria in soda lakes. FEMS Microbiol Rev 29:685–702
Sorokin DY, Kuenen JG, Jetten M (2001) Denitrification at extremely alkaline conditions in obligately autotrophic alkaliphilic sulfur-oxidizing bacterium Thioalkalivibrio denitrificans. Arch Microbiol 175:94–101
Stach P, Einsle O, Schumacher W, Kurun E, Kroneck PMH (2000) Bacterial cytochrome c nitrite reductase: new structural and functional aspects. J Inorg Biochem 79:381–385
Taher AG (1999) Inland saline lakes of Wadi El Natrun depression, Egypt. Int J Salt Lake Res 8:149–170
Van den Bosch PLF, van Beusekom OC, Buisman CJN, Janssen AJH (2007) Sulfide oxidation at halo-alkaline conditions in a fed-batch bioreactor. Biotechnol Bioeng 97:1053–1063
Van de Peer Y, De Wachter R (1994) TREECON for Windows: a software package for the construction and drawing of evolutionary trees for the Microsoft Windows environment. Comput Applic Biosci 10:569–570
Zavarzina DG, Kolganova TV, Boulygina ES, Kostrikina NA, Tourova TP, Zavarzin GA (2006) Geoalkalibacter ferrihydriticus gen. nov. sp. nov., the first alkaliphilic representative of the family Geobacteraceae isolated from a soda lake. Microbiology 75:673–682 (Moscow, English translation)
Zavarzin GA, Zhilina TN, Kevbrin VV (1999) The alkaliphilic microbial community and its functional diversity. Mikrobiology 68:503–521 (Moscow, English translation)
Zhilina TN, Zavarzin GA, Rainey FA, Pikuta EN, Osipov GA, Kostrikina NA (1997) Desulfonatronovibrio hydrogenovorans gen. nov., sp. nov., an alkaliphilic, sulfate-reducing bacterium. Int J Syst Bacteriol 47:144–149
Zhilina TN, Zavarzina DG, Kolganova TV, Tourova TP, Zavarzin GA (2005) “Candidatus Contubernalis alkalaceticum,” an obligately syntrophic alkaliphilic bacterium capable of anaerobic acetate oxidation in a coculture with Desulfonatronum cooperativum. Microbiology 74:695–703 (Moscow, English translation)
Zhilina TN, Zavarzina DG, Kuever J, Lysenko AM, Zavarzin GA (2005) Desulfonatronum cooperativum sp.nov., a novel hydrogenotrophic, alkaliphilic, sulfate-reducing bacterium, from a syntrophic culture growing on acetate. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 55:1001–1006
Zverlov V, Klein M, Lücker S, Friedrich MW, Kellermann J, Stahl DA, Loy A, Wagner M (2005) Lateral gene transfer of dissimilatory (bi)sulfite reductase revisited. J Bacteriol 187:2203–2208
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by NWO-RFBR (47.011.2004.010), RFBR (07-04-00153) and by the Program of the Russian Academy of Sciences “Molecular and Cell Biology”.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by K. Horikoshi.
Nucleotide sequence accession number: The GenBank/EMBL accession number of the 16S rRNA gene sequence of strains AHT 1T and AHT 2T are EF422412 and EF422413.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sorokin, D.Y., Tourova, T.P., Mußmann, M. et al. Dethiobacter alkaliphilus gen. nov. sp. nov., and Desulfurivibrio alkaliphilus gen. nov. sp. nov.: two novel representatives of reductive sulfur cycle from soda lakes. Extremophiles 12, 431–439 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00792-008-0148-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00792-008-0148-8