Abstract
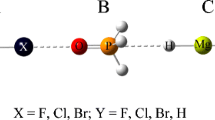
In this work we investigate the nature of the Cl···N interactions in complexes formed between substituted ammonium [NHn(X3-n) (with n = 0, 1, 2, 3 and X = −CH3, −F] as Lewis bases and F−Cl molecule as Lewis acid. They have been chosen as a study case due to the wide range of variation of their binding energies, BEs. Møller-Plesset [MP2/6-311++G(2d,2p)] calculations show that the BEs for this set of complexes lie in the range from 1.27 kcal/mol (in F−Cl···NF3) to 27.62 kcal/mol [in F−Cl···N(CH3)3]. The intermolecular distribution of the electronic charge density and their L(r) = −¼∇2ρ(r) function have been investigated within the framework of the atoms in molecules (AIM) theory. The intermolecular interaction energy decomposition has also been analyzed using the reduced variational space (RVS) method. The topological analysis of the L(r) function reveals that the local topological properties measured at the (3,+1) critical point [in L(r) topology] are good descriptors of the strength of the halogen bonding interactions. The results obtained from energy decomposition analysis indicate that electrostatic interactions play a key role in these halogen bonding interactions. These results allow us to establish that, when the halogen atom is bonded to a group with high electron-withdrawing capacity, the electrostatic interaction between the electron cloud of the Lewis base and the halogen atom unprotected nucleus of the Lewis acid produces the formation and determines the geometry of the halogen bonded complexes. In addition, a good linear relationship has been established between: the natural logarithm of the BEs and the electrostatic interaction energy between electron charge distribution of N atom and nucleus of Cl atom, denoted as V e-n(N,Cl) within the AIM theory.

Interaction energy components for FCl···NH3 complex in function of the chlorinenitrogen separation distance.




Similar content being viewed by others
Reference
Brinck T, Murray JS, Politzer P (1992) Int J Quantum Chem, Quantum Biol Symp 19:57–64
Auffinger P, Hays FA, Westhof E, Ho PS (2004) Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 101:16789–16794
Politzer P, Lane P, Concha MC, Ma Y, Murray JS (2007) J Mol Model 13:305–311
Politzer P, Murray JS, Concha MC (2007) J Mol Model 13:643–650
Tomura M (2009) Chem Phys 359:126–131
Stevens WJ, Fink WH (1987) Chem Phys Lett 139:15–22
Riley KE, Hobza P (2008) J Chem Theory Comput 4:232–242
Jeziorski B, Moszynski R, Szalewicz K (1994) Chem Rev 94:1887–1930
Alkorta I, Blanco F, Elguero J (2009) Struct Chem 20:63–71
Glendening ED (2005) J Phys Chem A 109:11936
Li Q, Yuan H, Jing B, Liu Z, Li W, Cheng J, Gong B, Sun J (2010) THEOCHEM 942:145–148
Bader RFW (1990) Atoms in molecules. A quantum theory. Clarendon, Oxford
Popelier P (2000) Atoms in molecules, an introduction. Prentice-Hall, Manchester
Matta CF, Boyd RJ (2007) The quantum theory of atoms in molecules: from solid state to DNA and drug design. Wiley-VCH, Weinheim
Lu Y-X, Zou J-W, Wand Y-H, Yu Q-S, Jiang Y-J, Zhao W-N (2007) Chem Phys Lett 449:6–10
Eskandari K, Zariny H (2010) Chem Phys Lett 492:9–13
Lu Y-X, Zou J-W, Wand Y-H, Yu Q-S (2006) THEOCHEM 767:139–142
Lu Y-X, Zou J-W, Wand Y-H, Yu Q-SJ (2006) THEOCHEM 776:83–87
Blanco F, Alcorta I, Solimannejad M, Elguero J (2009) J Phys Chem A 113:3237–3244
Xu L, Zou J-W, Lu Y-L, Yu Q-S, Zhang N (2009) THEOCHEM 897:12–16
Xu L, Zou J-W, Wang Y-H, Yu Q-S (2007) Int J Quant Chem 107:1479–1486
Lu Y-X, Zou J-W, Wang Y-H, Yu Q-S (2007) Chem Phys 334:1–7
Zhang X, Zeng Y, Li X, Meng L, Zheng S (2011) Struct Chem 22:567–576
Duarte DJR, Vallejos MM, Peruchena NM (2010) J Mol Model 16:737–748
Boys SF, Bernardi F (1970) Mol Phys 19:553–559
Su P, Li H (2009) J Chem Phys 131:014102–014102
Blieger-König F, Schönbohn J (2000) AIM2000 Program package, version 2.0 Copyright 2002, chemical adviser by Bader RFW. Büro fur Innovative Software Strieibel Blieger-König, Germany
AIMAll (Version 11.12.19), Todd A. Keith, TK Gristmill Software, Overland Park KS, USA, 2011 (aim.tkgristmill.com)
Frisch MJ et al. (2003) Gaussian 03, Revision E.01. Gaussian Inc, Wallingford
Bondi A (1964) J Phys Chem 68:441–451
Bui TTT, Dahaoui S, Lecomte C, Desiraju GR, Espinosa E (2009) Angew Chem Int Ed 48:3838–3841
Martinez Amezaga NJ, Pamies SC, Peruchena NM, Sosa GL (2010) J Phys Chem A 114:552–562
Bader RFW, Essén H (1984) J Chem Phys 80:1943–1960
Rozas I, Alkorta I, Elguero J (2000) J Am Chem Soc 122:11154–11161
Popelier PLA (2000) Coord Chem Rev 197:169–189
Acknowledgments
The authors acknowledge SECYT-UNNE (Secretaría de Ciencia y Tecnología – Universidad Nacional del Nordeste), Grant PICTO (Proyecto de Investigación Científica y Tecnológica Orientado) 089 and PIP CONICET (Proyecto de Investigación Plurianual–Consejo Nacional de Investigaciones Científicas y Técnicas) 095, for financial support. Darío Jorge Roberto Duarte is fellows of CONICET UNNE and Nélida Maria Peruhena is a career researcher of CONICET, Argentine.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
ESM 1
(DOC 137 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Duarte, D.J.R., Sosa, G.L. & Peruchena, N.M. Nature of halogen bonding. A study based on the topological analysis of the Laplacian of the electron charge density and an energy decomposition analysis. J Mol Model 19, 2035–2041 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00894-012-1624-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00894-012-1624-8