Abstract
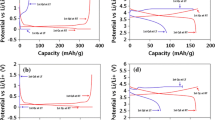
The activation characteristics and the effects of current densities on the formation of a separate LiCoO2 and graphite electrode were investigated and the behavior also was compared with that of the full LiCoO2/graphite batteries using various electrochemical techniques. The results showed that the formation current densities obviously influenced the electrochemical impedance spectrum of Li/graphite, LiCoO2/Li, and LiCoO2/graphite cells. The electrolyte was reduced on the surface of graphite anode between 2.5 and 3.6 V to form a preliminary solid electrolyte interphase (SEI) film of anode during the formation of the LiCoO2/graphite batteries. The electrolyte was oxidized from 3.95 V vs Li+/Li on the surface of LiCoO2 to form a SEI film of cathode. A highly conducting SEI film could be formed gradually on the surface of graphite anode, whereas the SEI film of LiCoO2 cathode had high resistance. The LiCoO2 cathode could be activated completely at the first cycle, while the activation of the graphite anode needed several cycles. The columbic efficiency of the first cycle increased, but that of the second decreased with the increase in the formation current of LiCoO2/graphite batteries. The formation current influenced the cycling performance of batteries, especially the high-temperature cycling performance. Therefore, the batteries should be activated with proper current densities to ensure an excellent formation of SEI film on the anode surface.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Itagaki M, Yotsuda S, Kobari N, Watanabe K, Kinoshita S, Ueb M (2006) Electrochim Acta 51:1629
Wang C, Appleby AJ, Little FE (2001) Electrochim Acta 46:1793
Zhang S, Shi P (2004) Electrochim Acta 49:1475
Zhang SS, Xu K, Jow TR (2004) Electrochim Acta 49:1057
Lee H-H, Wang Y-Y, Wan C-C, Yang M-H, Wu H-C, Shieh D-T (2004) J Power Sources 134:118
Jiang J, Dahn JR (2004) Electrochim Acta 49:4599
Matsui M, Dokko K, Kanamura K (2008) J Power Sources 177:184
Lee S-B, Pyun S-I (2002) Carbon 40:2333
Zhang SS, Xu K, Jow TR (2004) J Power Sources 130:281
Dedryvère R, Martinez H, Leroy S, Lemordant D, Bonhomme F, Biensan P, Gonbeau D (2007) J Power Sources 174:462
Zhang SS, Xu K, Jow TR (2006) Electrochim Acta 51:1636
He Y-B, Tang Z-Y, Song Q-S, Xie H, Liu Y-G, Xu Q (2008) J Electrochem Soc 155:A481
Peleda E, Golodnitsky D, Ulusa A, Yufita V (2004) Electrochim Acta 50:391
Nobili F, Tossici R, Croce F, Scrosati B, Marassi R (2001) J Power Sources 94:238
Croce F, Nobili F, Deptula A, Lada W, Tossici R, D’Epifanio A, Scrosati B, Marassi R (1999) Electrochem Commun 1:605
Umeda M, Dokko K, Fujita Y, Mohamedi M, Uchida I, Selman JR (2001) Electrochim Acta 47:885
Fey GTK, Yo WH, Chang YC (2002) J Power Sources 105:82
Itagaki M, Kobari N, Yotsuda S, Watanabe K, Kinoshita S, Ue M (2005) J Power Sources 148:78
Zhang SS, Xu K, Jow TR (2002) J Electrochem Soc 149:A1521
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by China Postdoctoral Science Foundation (no. 20100470296), Guangdong Province Energy and Environmental Materials Innovation R&D Team Plan and Dongguan McNair Technology Co., Ltd., China.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
He, YB., Li, B., Yang, QH. et al. Effects of current densities on the formation of LiCoO2/graphite lithium ion battery. J Solid State Electrochem 15, 1977–1985 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10008-010-1220-8
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10008-010-1220-8