Abstract
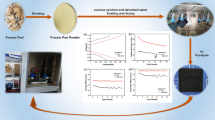
A novel method of hydrothermal ammoniated treatment on the polyacrylonitrile (PAN)-based graphite felt for vanadium redox flow battery was developed. The graphite felt was treated in a Teflon-lined stainless steel autoclave for different time at 180 °C. The content of nitrogen in the PAN graphite felt changed from 3.803% to 5.367% by adjusting treatment time to 15 h in ammonia solution, while FT-IR results indicated that nitrogenous groups were introduced. The electrochemical properties of these graphite felts were characterized by cyclic voltammetry, electrochemical impedance spectroscopy, as well as cell charge and discharge tests. The energy efficiency of the treated graphite felt reached 85% at a current density of 20 mA/cm2. The corresponding coulombic efficiency and voltage efficiency were 95.3% and 75.1%, respectively. The improvement of the electrochemical properties for the treated graphite felt might be attributed to the increase of polar nitrogenous groups of carbon fiber surface, which facilitated charge transfer between electrode and vanadium ions.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Sum E, Rychcik M, Skyllas-kazacos M (1985) J Power Sources 16:85–95
Sum E, Rychcik M (1985) J Power Sources 15:179–190
Skyllas-Kazacos M, Rychcik M, Robins RG, Fane AG (1986) J Electrochem Soc 133:1057–1058
Gattrell M, Qian J, Stewart C, Graham P, MacDougall B (2005) Electrochim Acta 51:395–407
Huang KL, Li XG, Liu SQ, Tan N, Chen LQ (2008) Renewable Energy 33:186–192
Kaneko H, Nozaki K, Wada Y, Aoki T, Negishi A (1991) Electrochim Acta 36:1191–1196
Sun B, Skyllas-Kazacos M (1991) Electrochim Acta 36:513–517
Rychcik M, Skallas-Kazacos M (1987) J Power Sources 19:45–54
Sun B, Skyllas-Kazacos M (1992) Electrochim Acta 37:1253–1260
Li XG, Huang KL, Liu SQ, Tang N, Chen LQ (2007) Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China 17:195–199
Sun B, Skyllas-Kazacos M (1992) Electrochim Acta 37:2459–2465
Wang WH, Wang XD (2007) Electrochim Acta 52:6755–6762
Maldonado S, Stevenson KJ (2005) J Phys Chem B 109:4707–4716
Shao YY, Sui JH, Yin GP, Gao YZ (2008) Appl Catal B: Environ 79:89–99
Gong KP, Du F, Xia ZH, Durstock M, Dai LM (2009) Science 323:760–764
Sidik RA, Anderson AB, Subramanian NP, Kumaraguru SP, Popov BN (2006) J Phys Chem B 110:1787–1793
Wu G, Li DY, Dai CS, Wang DL, Li N (2008) Langmuir 24:3566–3575
Saha MS, Li RY, Sun XL, Ye SY (2009) Electrochem Commun 11:438–441
Shi LP, Gao QM, Wu YH (2009) Electroanalysis 21:715–722
Shao YY, Wang YQ, Engelhard M, Wang CM et al (2010) J Power Sources 195(13):4375–4379
Chen X, Wang J, Lin M, Zhong W, Feng T, Chen J (2008) Mater Sci Eng A 492:236–242
Hsieh CT, Teng H, Chen WY, Cheng YS (2010) Carbon 48:4219–4229
Yao YL, Ding Y, Ye LS, Xia XH (2006) Carbon 44:61–66
Vukovic G, Marinkovic A, Obradovic M, Radmilovic V, Colic M, Aleksic R (2009) Appl Surf Sci 225:8067–8075
Hulicova-Jurcakova D, Kodama M, Shiraishi S, Hatori H, Zhu ZH, Lu GQ (2009) Adv Funct Mater 19:1800–1809
Shafeeyana SM, Daud WMAW, Houshmanda A, Arami-Niyaa A (2011) Appl Surf Sci 257:3936–3942
Figueiredo JL, Pereira MFR, Freitas MMA, Orfao JJM (1999) Carbon 37:1379–1389
Ros TG, van Dillen AJ, Geus JW, Koningsberger DC (2002) Chem Eur J 8:1151–1162
Yue L, Li WH, Sun FQ, Zhao LZ, Xing LD (2010) Carbon 48:3079–3090
Maldonado S, Morin S, Stevenson KJ (2006) Carbon 44:1429–1437
Oriji G, Katayama Y, Miura T (2004) Electrochim Acta 49:3091–3095
Kaneko H, Nozaki K, Wada Y, Aoki T, Negishi A, Kamimoto M (1991) Electrochim Acta 36:1191–1196
Acknowledgments
This work was financially supported by the Major State Basic Research Development Program of China (973 Program) (No. 2010CB227201) and National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 50972165).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wu, T., Huang, K., Liu, S. et al. Hydrothermal ammoniated treatment of PAN-graphite felt for vanadium redox flow battery. J Solid State Electrochem 16, 579–585 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10008-011-1383-y
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10008-011-1383-y