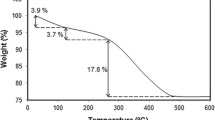
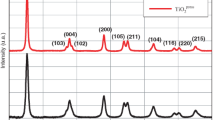
Abstract
In this work, nanocrystalline and mesoporous titania and titania/silica materials were developed, using the sol–gel method, to be applied as alternative material in solar cell devices. The materials present the silica well dispersed in the titania network, allowing efficient anchoring of the sensitizer on the TiO2 surface and enabling fast electron injection that is currently observed between ruthenium complexes and TiO2. The materials were characterized by X-ray diffraction, N2 adsorption–desorption isotherms, scanning electron microscopy, transmission electron microscopy and ultraviolet-visible spectroscopy. The ball milling processing, mainly at 500 rpm, showed to be effective in obtaining adequate textural and morphological properties of the particles, which allow getting a good packing of the photoanode. The use of sol–gel method associated to ball milling results in materials with enhanced electrical properties and high dye loading, which increase the efficiency of the solar devices being that the best device presented the solar cell efficiency 5.5 %.












Similar content being viewed by others
References
Krivtsov I, Ilkaeva M, Avdin V, Khainakov S, Garcia JR, Ordòñez S, Dìaz E, Faba L (2015) A hydrothermal peroxo method for preparation of highly crystalline silica-titania photocatalysts. J Colloid Interf Sci 444:87–96
Gupta SM, Tripathi M (2012) A review on the systhesis of TiO2 nanoparticles by solution route. Cent Eur J Chem 2:279–294
Shogh S, Mohammadpour R, Iraji zad A, Taghavinia N (2015) A new strategy on utilizing nitrogen doped TiO2 in nanostructured solar cells: embedded multifunctional N-TiO2 scattering particles in mesoporous photoanode. Mater Res Bull 72:64–69
Chou CS, Yang RY, Weng MH, Yeh CH (2008) Preparation of TiO2/dye composite particles and their applications in dye-sensitized solar cell. Powder Technol 187:181–189
Yasuda T, Ikeda S, Furukawa S (2010) Synthesis of reflective TiO2/SiO2 multilayer flakes for solar cell application. Dyes Pigments 86:278–281
Xue B, Wang H, Hu Y, Li H, Wang Z, Meng Q, Huang X, Chen L, Sato O, Fujishima A (2006) Highly efficient dye-sensitized solar cells using a composite electrolyte. C R Chimie 9:627–630
Cheng WY, Deka JR, Chiang YC, Rogeau A, Lu SY (2012) One-step, surfactant-free hydrothermal method for syntheses of mesoporous TiO2 nanoparticle aggregates and their applications in high efficiency dye-sensitized solar cells. Chem Mater 24:3255–3262
O’Regan B, Grätzel M (2001) A low-cost, high-efficiency solar cell based on dye-sensitized colloidal TiO2 films. Nature 253:737–739
Peter LM (2011) The Gratzel cell: where next? J Phys Chem Lett 2:1861–1867
Braga A, Gimenez S, Concina I, Vomiero A, Mora-Sero I (2011) Panchromatic sensitized solar cells based on metal sulfide quantum dots grown directly on nanostructured TiO2 electrodes. J Phys Chem Lett 2:454–460
Laranjo MT, Ricardi NC, Arenas LT, Benvenutti EV, Oliveira MC, Santos MJL (2014) TiO2 and TiO2/SiO2 nanoparticles obtained by sol–gel method and applied on dye sensitized solar cells. J Sol-Gel Sci Technol 72:273–281
Jung HG, Kang YS, Sun Y-K (2010) Anatase TiO2 spheres with high surface area and mesoporous structure via a hydrothermal process for dye-sensitized solar cells. Electrochim Acta 55:4637–4641
Gupta SM, Tripathi M (2011) A review of TiO2 nanoparticles. Chin Sci Bull 56:1639–1657
Kalyanasundaram K, Grätzel M (1998) Applications of functionalized transition metal complexes in photonic and optoelectronic devices. Coordin Chem Rev 77:347–414
Murali S, Lee SP, Birnie DP III (2013) The importance of silica morphology in silica-titania composites with dye sensitized solar functionality. Thin Solid Films 537:80–84
Nelson J (1999) Continuous time random walk model of electron transport in nanocrystalline TiO2 electrodes. Phys Rev B 59:15374–15380
Park K-H, Gu H-B, Jin EM, Dhayal M (2010) Using hybrid silica-conjugated TiO2 nanostructures to enhance the efficiency of dye-sensitized solar cells. Electrochim Acta 55:5499–5505
Dahoudi NA, Xi J, Cao G (2012) Silica modification of titania nanoparticles for a dye-sensitized solar cell. Electrochim Acta 59:32–38
Rho Y, Wanit M, Yeo J, Hong S, Han S, Choi J-H, Hong W-H, Lee D, Ko SH (2013) Improvement of light-harvesting efficiency in dye-sensitized solar cells using silica beads embedded in a TiO2 nanoporous structure. J Phys D Appl Phys 46:024006
Hilgendorff M, Spanhel L, Rothenhäsuler C, Müller G (1998) From ZnO colloids to nanocrystalline highly conductive films. J Electrochem Soc 145:3632–3637
Hagfeldt A, Grätzel M (2000) Molecular photovoltaics. Acc Chem Res 33:269–277
Yadav TP, Yadav RM, Singh DP (2012) Mechanical milling: a top down approach for the synthesis of nanomaterials and nanocomposites. Nanosci Technol 2:22–48
Farbod M, Khademalrasool M (2011) Synthesis of TiO2 nanoparticles by a combined sol-gel ball milling method and investigation of nanoparticle size effect on their photocatalytic activities. Powder Technol 214:344–348
Mekprasart W, Jarernboon W, Pecharapa W (2010) TiO2/CuPc hybrid nanocomposites prepared by low-energy ball milling for dye-sensitized solar cell application. Mater Sci Eng B 172:231–236
Sun Q, Zhang J, Wang P, Zheng J, Zhang X, Cui Y, Feng J, Zhu Y (2012) Sulfur-doped TiO2 nanocrystalline photoanodes for dye-sensitized solar cells. J Renew Sustain Energ 4:0231041–0231049
Wang P, Zakeeruddin SM, Comte P, Charvet R, Humphry-Baker R, Grätzel M (2003) Enhance the performance of dye-sensitized solar cells by Co-grafting amphiphilic sensitizer and hexadecylmalonic acid on TiO2 nanocrystals. J Phys Chem B 107:14336–14341
Ito S, Murakami TN, Comte P, Liska P, Grätzel C, Nazeeruddin MK, Grätzel M (2008) Fabrication of thin film dye sensitized solar cells with solar to electric power conversion efficiency over 10 %. Thin Solid Films 516:4613–4619
Choi H, Nahm C, Kim J, Moon J, Nam S, Jung D-R, Park B (2012) The effect of TiCl4-treated TiO2 compact layer on the performance of dye-sensitized solar cell. Curr Appl Phys 12:737–741
Barbé CJ, Arendse F, Comte P, Jirousek M, Lenzmann F, Shklover V, Gratzel M (1997) Nanocrystalline titanium oxide electrodes for photovoltaic applications. J Am Ceram Soc 80:3157–3171
Iler RK (1979) The chemistry of silica. Willey and Sons, New York
Frank AJ, Kopidakis N, van de Lagemaat J (2004) Electrons in nanostructured TiO2 solar cells: transport, recombination and photovoltaic properties. Coordin Chem Rev 248:1165–1179
Widiyastuti W, Lee SY, Iskandar F, Okuyama K (2009) Sintering behavior of spherical aggregated nanoparticles prepared by spraying colloidal precursor in a heated flow. Mater Sci Forum 20:318–326
Bisquert J, Vikhrenko VS (2004) Interpretation of the time constants measured by kinetic techniques in nanostructured semiconductor electrodes and dye-sensitized solar cells. J Phys Chem B 108:2313–2322
Sato N (1998) Electrochemistry at metal and semiconductor electrodes. Elsevier; Amsterdam
Zacheis GA, Gray KA, Kamat PV (2001) Radiation induced catalytic dechlorination of hexachlorobenzene on oxide surfaces. J Phys Chem B 105:4715–4720
Ito S, Nazeeruddin MK, Zakeeruddin SM, Pechy P, Comte P, Grätzel M, Mizuno T, Tanaka A, Koyanagi T (2009) Study of dye-sensitized solar cells by scanning electron micrograph observation and thickness optimization of porous TiO2 electrodes. Int J Photoenergy. doi:10.1155/2009/517609
van de Lagemaat J, Frank AJ (2001) Nonthermalized electron transport in dye-sensitized nanocrystalline TiO2 films: transient photocurrent and random-walk modeling studies. J Phys Chem B 105:11194–11205
Benkstein KD, Kopidakis N, van de Lagemaat J, Frank JA (2003) Influence of the percolation network geometry on electron transport in dye-sensitized titanium dioxide solar cells. J Phys Chem B 107:7759–7767
Son S, Hwang SH, Kim C, Yun JY, Jang J (2013) Designed synthesis of SiO2/TiO2 core/shell structure as light scattering material for highly efficient dye-sensitized solar cells. Appl Mater Interfaces 5:4815–4820
Tennakone K, Bandara J, Bandaranayake PKM, Kumara GRA, Konno A (2001) Enhanced efficiency of a dye-sensitized solar cell made from MgO-coated nanocrystalline SnO2. Jpn J Appl Phys 40:L732–L734
Zaban A, Chen SG, Chappel S, Gregg BA (2000) Bilayer nanoporous electrodes for dye-sensitized solar cells. Chem Commun 22:2231–2232
Acknowledgments
This research was supported by CNPq (process 490221/2012-2 and 477599/2013-3) and FAPERGS, Brazilian agencies. The students thank CNPq, CAPES, and FAPERGS, Brazilian agencies for the scholarships. We would also like to thank the Centre of Electron Microscopy CME UFRGS and LRNANO UFRGS.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Laranjo, M.T., Ricardi, N.C., Arenas, L.T. et al. Influence of ball milling on textural and morphological properties of TiO2 and TiO2/SiO2 xerogel powders applied in photoanodes for solar cells. J Solid State Electrochem 20, 1731–1741 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10008-016-3180-0
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10008-016-3180-0