Abstract
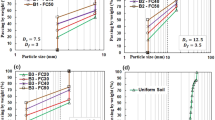
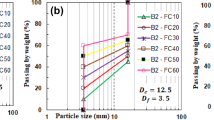
Binary granular soils, mixtures of carbonate sands and nonplastic fines, are widely used for constructions of foundation, airport and embankment in island and coast. Impact load (e.g., sea wave, aircraft landing, pile driving and dynamic compaction during foundation, et al.) is frequently exerted to the mixtures. It is therefore of extreme importance to investigate the evolutions of particle size distribution, particle breakage and volumetric deformation of the mixtures under impact load due to that the grains of carbonate sands are easily to be crushed, which may significant affect its mechanical behavior. Three mixtures (i.e., 100% carbonate plus 0% fines (by dry weight), 90% carbonate plus 10% fines and 80% carbonate plus 20% fines) were prepared to analyze the effect of fines content on particle breakage and volumetric deformation under impact load. It was observed that a unique fractal grading could be obtained for all the mixtures when the blow number was large enough (\(N>20,000\)). The void ratio of the mixtures converged to be a constant ultimate value as the mixture reached the fractal state. The volumetric strain and relative particle breakage with respect to the blow number could be described by hyperbolic functions, indicating that the volumetric strain and relative particle breakage progressively increased to ultimate values with increasing the blow number.















Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- t :
-
Test time
- N :
-
Blow number
- \(I_D \) :
-
Relative density
- \(f_c \) :
-
Fines content (%)
- \(e_0 \) :
-
Initial void ratio
- h :
-
Specimen height (mm)
- \(h_0 \) :
-
Initial specimen height (mm)
- F :
-
Percentage finer (%)
- d :
-
Grain diameter (mm)
- \(d_{\mathrm{M}} \) :
-
Maximum grain diameter (mm)
- \(\alpha \) :
-
Fractal dimensions
- \(\varepsilon _v \) :
-
Volumetric strain (%)
- \(\varepsilon _u \) and \(N_{\varepsilon 0} \) :
-
Two fitting parameters
- \(e_0 \) :
-
Initial void ratio
- e :
-
Current void ratio
- \(B_{\mathrm{p}} \) and \(B_{\mathrm{t}} \) :
-
Breakage potential and total breakage, respectively
- \(B_{\mathrm{r}} \) :
-
Relative breakage index (%)
- \(B_u \) and \(N_{b0} \) :
-
Fitting parameter
References
Coop, M.R., Sorensen, K.K., Bodas Freitas, T., et al.: Particle breakage during shearing of a carbonate sand. Geotechnique 54, 157–163 (2004)
Yamamuro, J.A., Bopp, P.A., Lade, P.V.: One-dimensional compression of sands at high pressures. J. Geotech. Geoenviron. Eng. 122, 147–154 (1996)
Miao, G., Airey, D.: Breakage and ultimate states for a carbonate sand. Geotechnique 63, 1221–1229 (2013)
Shipton, B., Coop, M.R.: On the compression behaviour of reconstituted soils. Soils Found. 52, 668–681 (2012)
Tarantino, A., Hyde, A.F.L.: An experimental investigation of work dissipation in crushable materials. Geotechnique 55, 575–584 (2005)
Asadzadeh, M., Soroush, A.: Direct shear testing on a rockfill material. Arab. J. Sci. Eng. 34, 379–396 (2009)
Nimbalkar, S., Indraratna, B.: Improved performance of ballasted rail track using geosynthetics and rubber shockmat. J. Geotech. Geoenviron. Eng. pp 04016031–04016031 (2016)
Cheng, Y.P., Nakata, Y., Bolton, M.D.: Discrete element simulation of crushable soil. Geotechnique 53, 633–641 (2003)
Bagherzadeh Kh, A., Mirghasemi, A.A., Mohammadi, S.: Numerical simulation of particle breakage of angular particles using combined DEM and FEM. Powder Technol. 205, 15–29 (2011)
Indraratna, B., Thakur, P.K., Vinod, J.S.: Experimental and numerical study of railway ballast behavior under cyclic loading. Int. J. Geomech. 10, 136–144 (2010)
Lobo-Guerrero, S., Vallejo, L.E., Vesga, L.F.: Visualization of crushing evolution in granular materials under compression using DEM. Int. J. Geomech. 6, 195–195 (2006)
Maeda, K., Sakai, H., Kondo, A., et al.: Stress-chain based micromechanics of sand with grain shape effect. Granular Matter 12, 499–505 (2010)
Wang, J., DEM Yan, H.: analysis of energy dissipation in crushable soils. Soils Found. 52, 644–657 (2012)
Zhou, W., Yang, L., Ma, G., et al.: DEM analysis of the size effects on the behavior of crushable granular materials. Granular Matter 18, 1–11 (2016)
Huang, J.Y., Hu, S.S., Xu, S.L., et al.: Fractal crushing of granular materials under confined compression at different strain rates. Int. J. Impact Eng 106, 259–265 (2017)
Mcdowell, G.R., Bolton, M.D., Robertson, D.: The fractal crushing of granular materials. J. Mech. Phys. Solids 44, 2079–2102 (1996)
Mcdowell, G.R., Bolton, M.D.: On the micromechanics of crushable aggregates. Geotechnique 48, 667–679 (1998)
Mcdowell, G.R., Daniell, C.M.: Fractal compression of soil. Geotechnique 51, 173–176 (2001)
Yan, W.M., Shi, Y.: Evolution of grain grading and characteristics in repeatedly reconstituted assemblages subject to one-dimensional compression. Geotech. Lett. 4, 223–229 (2014)
Xiao, Y., Liu, H., Xiao, P., et al.: Fractal crushing of carbonate sands under impact loading. Geotech. Lett. 6, 199–204 (2016)
Ben-Nun, O., Einav, I.: The role of self-organization during confined comminution of granular materials. Philos. Trans. A Math. Phys. Eng. Sci. 368, 231–47 (2010)
De Bono, J.P., Mcdowell, G.R.: On the micro mechanics of one-dimensional normal compression. Geotechnique 63, 895–908 (2013)
De Bono, J., Mcdowell, G.: Particle breakage criteria in discrete-element modelling. Geotechnique 66, 1014–1027 (2016)
Mcdowell, G.R., De Bono, J.P., Yue, P., et al.: Micro mechanics of isotropic normal compression. Geotech. Lett. 3, 166–172 (2013)
Einav, I.: Breakage mechanics-Part I: Theory. J. Mech. Phys. Solids 55, 1274–1297 (2007)
Muir Wood, D. & Maeda, K.: Changing grading of soil: effect on critical states. Acta Geotech. 3, 3–14 (2008)
Xu, Y., Feng, X., Zhu, H., et al.: Fractal model for rockfill shear strength based on particle fragmentation. Granular Matter 17, 753–761 (2015)
Shahnazari, H., Rezvani, R.: Effective parameters for the particle breakage of calcareous sands: An experimental study. Eng. Geol. 159, 98–105 (2013)
Wang, X.Z., Jiao, Y.Y., Wang, R., et al.: Engineering characteristics of the calcareous sand in Nansha Islands. South China Sea. Eng. Geol. 120, 40–47 (2011)
Salgado, R., Bandini, P., Karim, A.: Shear strength and stiffness of silty sand. J. Geotech. Geoenviron. Eng. 126, 451–462 (2000)
Thevanayagam, S., Shenthan, T.: Undrained fragility of clean sands, silty sands, and sandy silts. J. Geotech. Geoenviron. Eng. 128, 849–859 (2002)
Xiao, Y., Sun, Y., Liu, H., et al.: Model predictions for behaviors of sand-nonplastic-fines mixtures using equivalent-skeleton void-ratio state index. Sci. China Tech. Sci. 60, 878–892 (2017). doi:10.1007/s11431-016-9024-9
Shipton, B., Coop, M.R.: Transitional behaviour in sands with plastic and non-plastic fines. Soils Found. 55, 1–16 (2015)
Xiao, Y., Coop, M.R., Liu, H., et al.: Transitional behaviors in well-graded coarse granular soils. J. Geotech. Geoenviron. Eng. 142, 06016018 (2016)
Ladd, R.S.: Preparing test specimens using undercompaction. Geotech. Test. J. 1, 16–23 (1978)
Polito, C.P., Martin Ii, J.R.: Effects of nonplastic fines on the liquefaction resistance of sands. J. Geotech. Geoenviron. Eng. 127, 408–415 (2001)
Yang, S., Lacasse, S., Sandven, R.: Determination of the transitional fines content of mixtures of sand and non-plastic fines. Geotech. Test. J. 29, 102–107 (2006)
Polito, C.P., Green, R.A., Lee, J.: Pore pressure generation models for sands and silty soils subjected to cyclic loading. J. Geotech. Geoenviron. Eng. 134, 1490–1500 (2008)
Papadopoulou, A.I., Tika, T.M.: The effect of fi nes plasticity on monotonic undrained shear strength and liquefaction resistance of sands. Soil Dyn. Earthq. Eng. 88, 191–206 (2016)
Chiu, C.F., Fu, X.J.: Interpreting undrained instability of mixed soils by equivalent intergranular state parameter. Geotechnique 58, 751–755 (2008)
Belkhatir, M., Arab, A., Schanz, T., et al.: Laboratory study on the liquefaction resistance of sand-silt mixtures: effect of grading characteristics. Granular Matter 13, 599–609 (2011)
Tyler, S.W., Wheatcraft, S.W.: Fractal scaling of soil particle-size distributions: analysis and limitations. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 56, 362–369 (1992)
Tyler, S.W., Wheatcraft, S.W.: Application of fractal mathematics to soil water retention estimation. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 53, 987–996 (1989)
Russell, A.R.: A compression line for soils with evolving particle and pore size distributions due to particle crushing. Geotech. Lett. 1, 5–9 (2011)
Ueng, T.S., Chen, T.J.: Energy aspects of particle breakage in drained shear of sands. Geotechnique 50, 65–72 (2000)
Xiao, Y., Liu, H., Chen, Y., et al.: Strength and deformation of fockfill material based on large-scale triaxial compression tests. II: Influence of particle breakage. J. Geotech. Geoenviron. Eng. 140, 04014071 (2014)
Zhang, Y.D., Buscarnera, G.: Prediction of breakage-induced couplings in unsaturated granular soils. Geotechnique 65, 135–140 (2015)
Ovalle, C., Dano, C., Hicher, P.-Y., et al.: Experimental framework for evaluating the mechanical behavior of dry and wet crushable granular materials based on the particle breakage ratio. Can. Geotech. J. 52, 587–598 (2015)
Zhang, C., Nguyen, G.D., Kodikara, J.: An application of breakage mechanics for predicting energy-size reduction relationships in comminution. Powder Technol. 287, 121–130 (2016)
Hardin, B.O.: Crushing of soil particles. J. Geotech. Eng. 111, 1177–1192 (1985)
Xiao, Y., Liu, H., Desai, C.S., Sun, Y., Liu, H.: Effect of intermediate principal-stress ratio on particle breakage of rockfill material. J. Geotech. Geoenviron. Eng. 142, 06015017 (2016)
Xiao, Y., Liu, H., Chen, Q., Ma, Q., Xiang, Y., Zheng, Y.: Particle breakage and deformation of carbonate sands with wide range of densities during compression loading process. Acta Geotech. (2017). doi:10.1007/s11440-017-0580-y
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to acknowledge the financial support from the 111 Project (Grant No. B13024), the National Science Foundation of China (Grant Nos. 51509024, 51678094), the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities (Grant No. 106112015CDJXY200008) and the Project funded by China Postdoctoral Science Foundation (Grant No. 2016M590864).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
The Authors are most thankful for editor’s and two reviewers’ valuable comments for improving this paper.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xiao, Y., Liu, H., Chen, Q. et al. Evolution of particle breakage and volumetric deformation of binary granular soils under impact load. Granular Matter 19, 71 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10035-017-0756-z
Received:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10035-017-0756-z