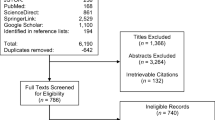
Abstract
There is no doubt that an abundance of factors exists that makes learning with serious games successful. Research articles reporting on these factors, however, tend to focus on select serious game elements and do not combine all salient factors for successful learning with serious games. Addressing this gap is a necessity for the success of serious games and may even alleviate long-standing debates about pedagogy over enjoyment, how much realism is enough or whether artificial intelligence is worth the cost. This article examines existing academic literature from 2000 to 2015, extracting shared serious game success factors that have had an encouraging impact on gameful learning experiences. As such, we subsequently aim to withdraw the field from a perpetual spiral of does-my-game-work research toward more worthwhile why-does-my-game-not-work research. Qualitative content analysis through the constant comparison method (CCM) analyzed a total of 63 articles from a variety of recognized electronic libraries and databases. Through this analysis, we reveal five central serious game themes: backstory and production; realism; artificial intelligence and adaptivity; interaction; and feedback and debriefing, all of which require deliberate intertwining with pedagogical content to ensure successful learning. This review unravels each of the five themes into their constituent factors and consequently presents the factors as practical guidelines that serious games producers should strive to include in their game productions. Applying these recommendations whenever serious games are considered will provide a foundation for effective gameful learning experiences.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abt CC (1970) Serious games. Viking Press, New York
Admiraal W, Huizenga J, Heemskerk I, Kuiper E, Volman M, ten Dam G (2014) Gender-inclusive game-based learning in secondary education Int J Incl Educ 18:1208–1218. doi:10.1080/13603116.2014.885592
Akl EA, Sackett K, Pretorius R, Erdley S, Bhoopathi PS, Mustafa R, Schunemann HJ (2008) Educational games for health professionals Cochrane Database Syst Rev:20. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD006411.pub2
Alamri A, Hassan MM, Hossain MA, Al-Qurishi M, Aldukhayyil Y, Hossain MS (2014) Evaluating the impact of a cloud-based serious game on obese people. Comput Hum Behav 30:468–475. doi:10.1016/j.chb.2013.06.021
Annetta LA, Mangrum J, Holmes S, Collazo K, Cheng M-T (2009a) Bridging realty to virtual reality: investigating gender effect and student engagement on learning through video game play in an elementary school classroom Int J. Sci Educ 31:1091–1113
Annetta LA, Minogue J, Holmes SY, Cheng MT (2009b) Investigating the impact of video games on high school students’ engagement and learning about genetics. Comput Educ 53:74–85. doi:10.1016/j.compedu.2008.12.020
Annetta L, Lamb R, Minogue J, Folta E, Holmes S, Vallett D, Cheng R (2014) Safe science classrooms: teacher training through serious educational games. Inf Sci 264:61–74. doi:10.1016/j.ins.2013.10.028
Arnab S et al (2013) The development approach of a pedagogically-driven serious game to support Relationship and Sex Education (RSE) within a classroom setting. Comput Educ 69:15–30. doi:10.1016/j.compedu.2013.06.013
Barab S, Pettyjohn P, Gresalfi M, Volk C, Solomou M (2012) Game-based curriculum and transformational play: designing to meaningfully positioning person, content, and context. Comput Educ 58:518–533. doi:10.1016/j.compedu.2011.08.001
Baranowski T et al (2011) Video game play, child diet, and physical activity behavior change: a randomized clinical trial. Am J Prev Med 40:33–38. doi:10.1016/j.amepre.2010.09.029
Bedwell WL, Pavlas D, Heyne K, Lazzara EH, Salas E (2012) Toward a Taxonomy Linking Game Attributes to Learning: An Empirical Study Simulation & Gaming 43:729–760
Bellotti F, Berta R, De Gloria A, Primavera L (2009) Enhancing the educational value of video games. Computers in Entertainment 7:1–18. doi:10.1145/1541895.1541903
Bellotti F, Berta R, De Gloria A, D’Ursi A, Fiore V (2012) A serious game model for cultural heritage Journal on Computing and Cultural. Heritage 5:1–27
Bhoopathi PS, Sheoran R, Adams CE (2007) Educational games for mental health professionals: a Cochrane review The International Journal Of Psychiatric. Nurs Res 12:1497–1502
Blakely G, Skirton H, Cooper S, Allum P, Nelmes P (2009) Educational gaming in the health sciences: systematic review. J Adv Nurs 65:259–269. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2648.2008.04843.x
Boeije H (2002) A purposeful approach to the constant comparative method in the analysis of qualitative interviews. Qual Quant 36:391–409. doi:10.1023/A:1020909529486
Boyle E, Connolly TM, Hainey T (2011) The role of psychology in understanding the impact of computer games. Entertainment Computing 2:69–74. doi:10.1016/j.entcom.2010.12.002
Breuer J, Bente G (2010) Why so serious? On the relation of serious games and learning Eludamos Journal for Computer Game Culture 4:7–24
Brom C, Sisler V, Slavik R (2010) Implementing digital game-based learning in schools: augmented learning environment of ‘Europe 2045’. Multimedia Syst 16:23–41. doi:10.1007/s00530-009-0174-0
Brom C, Preuss M, Klement D (2011) Are educational computer micro-games engaging and effective for knowledge acquisition at high-schools? A quasi-experimental study Computers & Education 57:1971–1988. doi:10.1016/j.compedu.2011.04.007
Buttussi F, Pellis T, Vidani AC, Pausler D, Carchietti E, Chittaro L (2013) Evaluation of a 3D serious game for advanced life support retraining. Int J Med Inform 82:798–809. doi:10.1016/j.ijmedinf.2013.05.007
Byun J, Loh CS (2015) Audial engagement: effects of game sound on learner engagement in digital game-based learning environments. Comput Hum Behav 46:129–138. doi:10.1016/j.chb.2014.12.052
Cheng M-T, Annetta L (2012) Students’ learning outcomes and learning experiences through playing a serious educational game J Biol Educ 46:203–213
Cheng M-T, Su T, Huang W-Y, Chen J-H (2014) An educational game for learning human immunology: what do students learn and how do they perceive? British Journal of Educational Technology 45:820–833
Cheng M-T, Lin Y-W, She H-C (2015) Learning through playing Virtual Age: exploring the interactions among student concept learning, gaming performance, in-game behaviors, and the use of in-game characters. Comput Educ 86:18–29. doi:10.1016/j.compedu.2015.03.007
Chittaro L, Buttussi F (2015) Assessing knowledge retention of an immersive serious game vs. a traditional education method in aviation safety. IEEE Trans Visual Comput Graphics 21:529–538. doi:10.1109/tvcg.2015.2391853
Chittaro L, Sioni R (2015) Serious games for emergency preparedness: evaluation of an interactive vs. a non-interactive simulation of a terror attack. Comput Hum Behav 50:508–519. doi:10.1016/j.chb.2015.03.074
Connolly TM, Stansfield M, Hainey T (2011) An alternate reality game for language learning: aRGuing for multilingual motivation. Comput Educ 57:1389–1415. doi:10.1016/j.compedu.2011.01.009
Connolly TM, Boyle EA, MacArthur E, Hainey T, Boyle JM (2012) A systematic literature review of empirical evidence on computer games and serious games. Comput Educ 2012:661–686. doi:10.1016/j.compedu.2012.03.004
Cook DA et al (2013) Comparative effectiveness of instructional design features in simulation-based education: systematic review and meta-analysis. Med Teach 35:e844–e875. doi:10.3109/0142159X.2012.714886
Couceiro RM, Papastergiou M, Kordaki M, Veloso AI (2013) Design and evaluation of a computer game for the learning of Information and Communication Technologies (ICT) concepts by physical education and sport science students. Education and Information Technologies 18:531–554. doi:10.1007/s10639-011-9179-3
Crookall D (2014) Engaging (in) gameplay and (in) debriefing Simulation & Gaming
Csikszentmihalyi M (2008) Flow: The psychology of optimal experience, 2nd edn. Harper Perennial, New York
De Freitas S, Ketelhut DJ (2014) Introduction for the Journal of Information Sciences special issue on serious games. Inf Sci 264:1–3. doi:10.1016/j.ins.2014.01.036
DeSmet A et al (2014) A meta-analysis of serious digital games for healthy lifestyle promotion. Prev Med 69:95–107. doi:10.1016/j.ypmed.2014.08.026
Dickey MD (2011) Murder on Grimm Isle: the impact of game narrative design in an educational game-based learning environment. British Journal of Educational Technology 42:456–469. doi:10.1111/j.1467-8535.2009.01032.x
Dondlinger MJ (2007) Educational video game design: A review of the literature Journal of applied educational technology 4:21–31
Donnelly CM, McDaniel MA (1993) Use of analogy in learning scientific concepts Journal of Experimental Psychology: learning. Memory, and Cognition 19:975–987. doi:10.1037/0278-7393.19.4.975
Echeverría A, García-Campo C, Nussbaum M, Gil F, Villalta M, Améstica M, Echeverría S (2011) A framework for the design and integration of collaborative classroom games. Comput Educ 57:1127–1136. doi:10.1016/j.compedu.2010.12.010
Feinstein AH, Cannon HM (2002) Constructs of simulation evaluation Simulation and Gaming 33:425–440. doi:10.1177/1046878102238606
Garris R, Ahlers R, Driskell JE (2002) Games, motivation, and learning: A research and practice model Simulation and Gaming 33:441–467 doi:10.1177/1046878102238607
Gee JP (2005) Good video games and good learning Phi Kappa Phi Forum:33
Gentner D, Holyoak KJ (1997) Reasoning and learning by analogy: introduction. Am Psychol 52:32–34. doi:10.1037/0003-066X.52.1.32
Giessen HW (2015) Serious Games Effects: an Overview. Procedia - Social and Behavioral Sciences 2015:2240–2244. doi:10.1016/j.sbspro.2015.01.881
González-González C, Blanco-Izquierdo F (2012) Designing social videogames for educational uses. Comput Educ 58:250–262. doi:10.1016/j.compedu.2011.08.014
González-González C, Toledo-Delgado P, Collazos-Ordoñez C, González-Sánchez J (2014) Design and analysis of collaborative interactions in social educational videogames. Comput Hum Behav 31:602–611. doi:10.1016/j.chb.2013.06.039
Hainey T (2007) Reviews: games and Simulations in Online Learning: Research and Development Frameworks Int J. Inf Manage 27:438. doi:10.1016/j.ijinfomgt.2007.08.008
Hämäläinen R (2008) Designing and evaluating collaboration in a virtual game environment for vocational learning. Comput Educ 50:98–109. doi:10.1016/j.compedu.2006.04.001
Hämäläinen R (2011) Using a game environment to foster collaborative learning: a design-based study Technology. Pedagogy and Education 20:61–78. doi:10.1080/1475939X.2011.554010
Hong J-C, Hwang M-Y, Chen Y-J, Lin P-H, Huang Y-T, Cheng H-Y, Lee C-C (2013a) Using the saliency-based model to design a digital archaeological game to motivate players’ intention to visit the digital archives of Taiwan’s natural science museum. Comput Educ 66:74–82. doi:10.1016/j.compedu.2013.02.007
Hong JC, Tsai CM, Ho YJ, Hwang MY, Wu CJ (2013b) A comparative study of the learning effectiveness of a blended and embodied interactive video game for kindergarten students Interact Learn Environ 21:39–53. doi:10.1080/10494820.2010.542760
Hong J-C, Lin M-P, Hwang M-Y, Tai K-H, Kuo Y-C (2015) Comparing animated and static modes in educational gameplay on user interest, performance and gameplay anxiety. Comput Educ 88:109–118. doi:10.1016/j.compedu.2015.04.018
Huizenga J, Admiraal W, Akkerman S, ten Dam G (2009) Mobile game-based learning in secondary education: engagement, motivation and learning in a mobile city game. J Comput Assist Learn 25:332–344. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2729.2009.00316.x
Hunicke R, LeBlanc M, Zubek R (2004) MDA: A formal approach to game design and game research. Paper presented at the AAAI Workshop on Challenges in Game AI, San Jose
Hwang G-J, Wu P-H, Chen C-C (2012a) An online game approach for improving students’ learning performance in web-based problem-solving activities. Comput Educ 59:1246–1256. doi:10.1016/j.compedu.2012.05.009
Hwang GJ, Sung HY, Hung CM, Huang I, Tsai CC (2012b) Development of a personalized educational computer game based on students’ learning styles. Education Tech Research Dev 60:623–638. doi:10.1007/s11423-012-9241-x
Hwang G-J, Yang L-H, Wang S-Y (2013a) A concept map-embedded educational computer game for improving students’ learning performance in natural science courses. Comput Educ 69:121–130. doi:10.1016/j.compedu.2013.07.008
Hwang GJ, Sung HY, Hung CM, Yang LH, Huang I (2013b) A knowledge engineering approach to developing educational computer games for improving students’ differentiating knowledge. British Journal of Educational Technology 44:183–196. doi:10.1111/j.1467-8535.2012.01285.x
Hwang GJ, Chiu LY, Chen CH (2015) A contextual game-based learning approach to improving students’ inquiry-based learning performance in social studies courses. Comput Educ 81:13–25. doi:10.1016/j.compedu.2014.09.006
Hyungsup Y (2014) A study on an analysis of success factors of a serious game: in case of “Anti-Aging Village” International Journal of Multimedia and Ubiquitious Engineering 9:205–214 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.14257/ijmue.2014.9.7.17
Johnson CI, Mayer RE (2010) Applying the self-explanation principle to multimedia learning in a computer-based game-like environment. Comput Hum Behav 26:1246–1252. doi:10.1016/j.chb.2010.03.025
Jonassen DH (1994) Thinking technology: toward a constructivist design model. Educational Technology 34:34–37
Ke F (2008) A case study of computer gaming for math: engaged learning from gameplay? Comput Educ 51:1609–1620. doi:10.1016/j.compedu.2008.03.003
Ke F, Abras T (2013) Games for engaged learning of middle school children with special learning needs. British Journal of Educational Technology 44:225–242
Ke F, Grabowski B (2007) Gameplaying for maths learning: cooperative or not? British Journal of Educational Technology 38:249–259. doi:10.1111/j.1467-8535.2006.00593.x
Ketamo H, Kiili K (2010) Conceptual change takes time: Game based learning cannot be only supplementary amusement Journal of Educational Multimedia and Hypermedia 19:399–419
Kickmeier-Rust MD, Albert D (2010) Micro-adaptivity: protecting immersion in didactically adaptive digital educational games. J Comput Assist Learn 26:95–105
Kiili K (2005) Content creation challenges and flow experience in educational games: the IT-Emperor case. The Internet and Higher Education 8:183–198. doi:10.1016/j.iheduc.2005.06.001
Kiili K, Perttula PTA (2012) Exerbraining for schools: combining body and brain training. Procedia Computer Science 15:163–173. doi:10.1016/j.procs.2012.10.068
Kitchenham B (2007) Guidelines for performing systematic literature reviews in software engineering. Technical report, EBSE Technical Report EBSE-2007-01
Knight JF et al (2010) Serious gaming technology in major incident triage training: a pragmatic controlled trial. Resuscitation 81:1175–1179. doi:10.1016/j.resuscitation.2010.03.042
Kriz CW, Hense JU (2006) Theory-oriented evaluation for the design of and research in gaming and simulation Simulation and Gaming 37:268–283. doi:10.1177/1046878106287950
Kuk K, Milentijević I, Rančić D, Spalević P (2012) Pedagogical agent in Multimedia Interactive Modules for Learning – MIMLE Expert Syst Appl 39:8051–8058 doi:10.1016/j.eswa.2012.01.138
Mayo JA (2001) Using analogies to teach conceptual applications of developmental theories. Journal of Constructivist Psychology 14:187–213. doi:10.1080/10720530126292
McHugh ML (2012) Interrater reliability: The kappa statistic Biochemia Medica 22:276–282
Mcmahon M, Henderson S (2011) Enhancing nutritional learning outcomes using within a simulation and pervasive game-based strategy. Paper presented at the AACE Edmedia Conference 2011
Michael DR, Chen SL (2006) Serious games: Games that educate, train, and inform. Thomson, Boston
Minovic M, Milovanovic M, Starcevic D (2011) Modelling Knowledge and Game Based Learning: Model Driven Approach J Univers Comput Sci 17:1241–1260
Mortara M, Catalano CE, Bellotti F, Fiucci G, Houry-Panchetti M, Petridis P (2014) Learning cultural heritage by serious games. Journal of Cultural Heritage 15:318–325
Moseley A, Whitton N, Iacovides I, McAndrew P, Scanlon E, Aczel J (2014) The Gaming Involvement and Informal Learning Framework Simulation & Gaming 45:611–626
Niedenthal S (2009) What we talk about when we talk about game aesthetics. EBSCOhost. http://hdl.handle.net/2043/13326 Accessed June 2, 2015
Norman G, Dore K, Grierson L (2012) The minimal relationship between simulation fidelity and transfer of learning. Med Educ 46:636–647. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2923.2012.04243.x
Osterman KF (1998) Using Constructivism and Reflective Practice To Bridge the Theory/Practice Gap. American Educational Research Association, San Diego
Papastergiou M (2009a) Digital game-based learning in high school computer science education: impact on educational effectiveness and student motivation. Comput Educ 52:1–12. doi:10.1016/j.compedu.2008.06.004
Papastergiou M (2009b) Exploring the potential of computer and video games for health and physical education: a literature review. Comput Educ 53:603–622. doi:10.1016/j.compedu.2009.04.001
Peters VAM, Vissers GAN (2004) A Simple Classification Model for Debriefing Simulation Games Simulation & Gaming 35:70–84
Petridis P, Dunwell I, De Freitas S, Panzoli D (2010) An engine selection methodology for high fidelity serious games, pp 27–34. doi:10.1109/VS-GAMES.2010.26
Prensky M (2001) Fun, play and games: what makes games engaging. In: Digital game-based learning. McGraw-Hill, pp 1–31
Riffe D, Lacy S, Fico FG (1998) Analyzing media messages: Using quantitative content analysis in research. LEA’s communications series (general theory). Lawrence Erlbaum Associates Publishers, Mahwah, NJ, US
Rodriguez DM, Teesson M, Newton NC (2014) A systematic review of computerised serious educational games about alcohol and other drugs for adolescents. Drug Alcohol Rev 33:129–135. doi:10.1111/dar.12102
Russell SJ, Norvig P (2014) Artificial intelligence: a modern approach. Pearson Education Limited, Pearson custom library. Harlow (Third edition, Pearson new international edition)
Sacfung A, Sookhanaphibarn K, Choensawat W (2014) Serious game for fire safety evacuation plan. Adv Mater Res 931–932:583–587.10.4028/http://www.scientific.net/AMR.931-932.583 doi:
Sadler TD, Romine WL, Menon D, Ferdig RE, Annetta L (2015) Learning biology through innovative curricula: a comparison of game- and nongame-based approaches. Sci Educ 99:696. doi:10.1002/sce.21171
Schmitz B, Klemke R, Specht M (2014) The impact of coupled games on the learning experience of learners at-risk: An empirical study Pervasive Mob Comput 14:57–65. doi:10.1016/j.pmcj.2013.09.002
Schmitz B, Klemke R, Walhout J, Specht M (2015a) Attuning a mobile simulation game for school children using a design-based research approach. Comput Educ 81:35–48. doi:10.1016/j.compedu.2014.09.001
Schmitz B, Schuffelen P, Kreijns K, Klemke R, Specht M (2015b) Putting yourself in someone else’s shoes: the impact of a location-based, collaborative role-playing game on behaviour. Comput Educ 85:160–169. doi:10.1016/j.compedu.2015.02.012
Serrano-Laguna Á, Torrente J, Moreno-Ger P, Fernández-Manjón B (2014) Application of learning analytics in educational videogames. Entertainment Computing 5:313–322. doi:10.1016/j.entcom.2014.02.003
Sherry JL (2013) The Challenge of Audience Reception: A Developmental Model for Educational Game Engagement Digital Games: A Context for Cognitive Developments 139:11–20. doi:10.1002/cad.20027
Sitzmann T (2011) A meta-analytic examination of the instructional effectiveness of computer-based simulation games Pers Psychol 64:489–528
Soflano M, Connolly T, Hainey T (2015a) An application of adaptive games-based learning based on learning style to teach SQL. Comput Educ 86:192–211. doi:10.1016/j.compedu.2015.03.015
Soflano M, Connolly T, Hainey T (2015b) Learning style analysis in adaptive GBL application to teach SQL. Comput Educ 86:105–119. doi:10.1016/j.compedu.2015.02.009
Squire KD (2013) Video game-based learning: an emerging paradigm for instruction. Performance Improvement Quarterly 26:101–130
Susi T, Johannesson M, Backlund P (2007) Serious games—An overview. Technical Report No. HS-IKI-TR-07-001, University of Skövde, Skövde
Thompson D, Baranowski T, Buday R, Baranowski J, Thompson V, Jago R, Griffith M (2010) Serious video games for health: How behavioral science guided the development of a serious video game Simulation & Gaming 41:587–606
Torrente J, Moreno-Ger P, Martinez-Ortiz I, Fernandez-Manjon B (2009) Integration and deployment of educational games in e-learning environments: The learning object model meets educational gaming Educ Technol Soc 12:359–371
Torrente J, Del Blanco A, Serrano-Laguna A, Vallejo-Pinto JA, Moreno-Ger P, Fernandez-Manjon B (2014) Towards a low cost adaptation of educational games for people with disabilities Comput Sci. Inf Syst 11:369–391. doi:10.2298/csis121209013t
Van der Spek ED, Van Oostendorp H, Meyer JJC (2013) Introducing surprising events can stimulate deep learning in a serious game. British Journal of Educational Technology 44:156–169. doi:10.1111/j.1467-8535.2011.01282.x
Van Eck R (2006a) Digital Game-Based Learning: It’s Not Just the Digital Natives Who Are Restless EDUCAUSE Review 41:16–18
Van Eck R (2006b) The effect of contextual pedagogical advisement and competition on middle-school students’ attitude toward mathematics and mathematics instruction using a computer-based simulation game. Journal of Computers in Mathematics and Science Teaching 25:165–195
Vandercruysse S, Vandewaetere M, Clarebout G (2012) Game-based learning: a review on the effectiveness of educational games. In: Handbook of Research on Serious Games as Educational, Business and Research Tools. pp 628–647. doi:10.4018/978-1-4666-0149-9.ch032
Verpoorten D, Castaigne J-L, Westera W, Specht M (2014) A quest for meta-learning gains in a physics serious game. Education and Information Technologies 19:361–374
Virvou M, Katsionis G (2008) On the usability and likeability of virtual reality games for education: the case of VR-ENGAGE. Comput Educ 50:154–178. doi:10.1016/j.compedu.2006.04.004
Virvou M, Katsionis G, Manos K (2005) Combining software games with education: Evaluation of its educational effectiveness Educ Technol Soc 8:54–65
Visschedijk GC, Van der Hulst AH (2012) Hoe realistisch moet een serious game zijn? Op zoek naar de optimale fidelity. Homo Ludens Magazine:96–111
Vygotsky LS (1978) Mind in society: the development of higher psychological processes
Webster D, Celik O (2014) Systematic review of Kinect applications in elderly care and stroke rehabilitation Journal Of Neuroengineering And. Rehabilitation 11:108. doi:10.1186/1743-0003-11-108
Westera W, Nadolski RJ, Hummel HGK, Wopereis IGJH (2008) Serious Games for Higher Education: a Framework for Reducing Design Complexity. J Comput Assist Learn 24:420–432
Whitton N (2011) Encouraging Engagement in Game-Based Learning International Journal of Game-Based Learning (IJGBL) 1:75–84
Whitton N (2013) Games for Learning International Review of Qualitative Research 6:424–439 doi:10.1525/irqr.2013.6.3.424
Wiemeyer J (2010) Serious Games—The challenges for computer science in sport International Journal of Computer Science in Sport 9:65–74
Wouters P, van Nimwegen C, van Oostendorp H, van der Spek ED (2013) A meta-analysis of the cognitive and motivational effects of serious games. J Educ Psychol 105:249–265. doi:10.1037/a0031311
Zin NAM, Yue WS (2013) Design and evaluation of history Digital Game Based Learning (DGBL) software. J Next Gen Inf Technol 4:9–24 doi:10.4156/jnit.vol4.issue4.2
Zyda M (2005) From visual simulation to virtual reality to games. Computer 38:25–32
Acknowledgments
This work is based on research support, in part, by the National Research Foundation of South Africa. Any opinion, findings and conclusions or recommendations expressed in this material are those of the authors, and therefore, the NRF does accept any liability in regard thereto. We also wish to acknowledge the effort of the librarians of the North-West University.
Author contributions
All authors contributed to this article, in content and in form. WSR and ASB wrote the manuscript. VL assisted the mechanics of the systematic literature review. AW assisted with inter-reliability and quality assurance. All authors contributed equally to the editing of the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest with respect to the authorship and/or publication of this article.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ravyse, W.S., Seugnet Blignaut, A., Leendertz, V. et al. Success factors for serious games to enhance learning: a systematic review. Virtual Reality 21, 31–58 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10055-016-0298-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10055-016-0298-4