Abstract
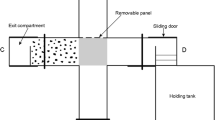
Previous studies have demonstrated that animals use multiple strategies to solve spatial tasks. We used a T-maze to examine spatial behavior in crayfish, using visual and tactile stimuli as place cues and a food-scented escape tank as reinforcement to leave the maze. In trials on a single day and across multiple days, crayfish learned to exit the maze with significantly reduced latency and with fewer turns. In addition, we examined place memory in 40-min periods with the maze closed and found that crayfish spent longer in the vicinity of a previously open exit compared to a closed exit. Probe tests were conducted using a forced-choice procedure to determine whether crayfish remembered the route out of the maze using primarily place cues or response learning. We found that approximately equal numbers of animals used each strategy, and individuals were able to switch from one strategy to the other on different test days. Males and females did not differ significantly in their performance in the place memory test, maze exit task, or probe tests. Both sexes displayed place memory for the exit location and reduced latency to exit during trials 24 h, 48 h, 72 h, and 1 week after initial training trials, suggesting that spatial memories in crayfish are relatively enduring.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alves C, Chichery R, Boal JG, Dickel L (2007) Orientation in the cuttlefish Sepia officinalis: response versus place learning. Anim Cog 10:29–36
Basil J, Sandeman D (2000) Crayfish (Cherax destructor) use tactile cues to detect and learn topographical changes in their environment. Ethology 106:247–259
Biegler R, McGregor A, Krebs JR, Healy SD (2001) A larger hippocampus is associated with longer-lasting spatial memory. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 98:6941–6944
Blokland A, Rutten K, Prickaerts J (2006) Analysis of spatial orientation strategies of male and female Wistar rats in a Morris water escape task. Behav Brain Res 171:216–224
Broadbent NJ, Squire LR, Clark RE (2006) Reversible hippocampal lesions disrupt water maze performance during both recent and remote memory tests. Learn Mem 13:187–191
Bubb DH, Lucas MC, Thom TJ (2002) Winter movements and activity of signal crayfish Pacifastacus leniusculus in an upland river, determined by radio telemetry. Hydrobiologia 483:111–119
Cheng K, Narendra A, Wehner R (2006) Behavioral ecology of odometric memories in desert ants: acquisition, retention, and integration. Behav Ecol 17:227–235
Cole MR, Clipperton A, Walt C (2007) Place versus response learning in rats. Learn Behav 35:214–224
Collett TS, Graham P, Durier V (2003) Route learning by insects. Curr Opin Neurobiol 13:718–725
Crook RJ, Hanlon RT, Basil JA (2009) Memory of visual and topographical features suggests spatial learning in nautilus (Nautilus pompilius L.). J Comp Psychol 123:264–274
Davis KM, Huber R (2007) Activity patterns, behavioural repertoires, and agonistic interactions of crayfish: a non-manipulative field study. Behaviour 144:229–247
Driscoll I, Hamilton DA, Yeo RA, Brooks WM, Sutherland RJ (2005) Virtual navigation in humans: the impact of age, sex, and hormones on place learning. Horm Behav 47:326–335
Dudchenko PA (2001) How do animals actually solve the T maze? Behav Neurosci 115:850–860
Ekstrom AD, Kahana MJ, Caplan JB, Fields TA, Isham EA, Newman EL, Fried I (2003) Cellular networks underlying human spatial navigation. Nature 425:184–188
Etienne AS, Jeffery KJ (2004) Path integration in mammals. Hippocampus 14:180–192
Foucaud J, Burns JG, Mery F (2010) Use of spatial information and search strategies in a water maze analog in Drosophila melanogaster. PLoS ONE 5:e15231. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0015231
Hazlett B, Rittschof D, Rubenstein D (1974) Behavioral biology of the crayfish Orconectes virilis. I. Home range. Am Midl Nat 92:301–319
Healy SD, Bacon IE, Haggis O, Harris AP, Kelley LA (2009) Explanations for variation in cognitive ability: behavioural ecology meets comparative cognition. Behav Process 80:288–294
Hudina S, Maguire I, Klobucar GIV (2008) Spatial dynamics of the noble crayfish (Astacus astacus L.) in the Paklenica National Park. Knowl Managt Aquat Ecosyst 388. doi:10.1051/kmae:2008001
Hvorecny LM, Grudowski JL, Blakeslee CJ, Simmons TL, Roy PR, Brooks JA, Hanner RM, Beigel ME, Karson MA, Nichols RH, Holm JB, Boal JG (2007) Octopuses (Octopus bimaculoides) and cuttlefishes (Sepia pharaonis, S. officinalis) can conditionally discriminate. Anim Cogn 10:449–459
Jacobs LF, Gaulin SJC, Sherry DF, Hoffman GE (1990) Evolution of spatial cognition: sex-specific patterns of spatial behavior predict hippocampal size. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 87:6349–6352
Jonasson Z (2005) Meta-analysis of sex differences in rodent models of learning and memory: a review of behavioral and biological data. Neurosci Biobehav R 28:811–825
Jones CM, Braithwaite VA, Healy SD (2003) The evolution of sex differences in spatial ability. Behav Neurosci 117:403–411
Jozet-Alves C, Moderan J, Dickel L (2008) Sex differences in spatial cognition in an invertebrate: the cuttlefish. Proc R Soc B 275:2049–2054
Kesner RP, Bolland BL, Dakis M (1993) Memory for spatial locations, motor responses, and objects: triple dissociation among the hippocampus, caudate nucleus, and extrastriate visual cortex. Exp Brain Res 93:462–470
Knierim JJ, Hamilton DA (2011) Framing spatial cognition: neural representations of proximal and distal frames of reference and their roles in navigation. Physiol Rev 91:1245–1279
Li H, Cooper RL (2001) Spatial familiarity in the blind cave crayfish, Orconectes australis packardi. Crustaceana 74:417–433
Lopez J, Pereira de Vasconcelos A, Cassel J-C (2008) Environmental cue saliency influences the vividness of a remote spatial memory in rats. Neurobiol Learn Mem 90:285–289
McMahon A, Patullo BW, Macmillan DL (2005) Exploration in a T-maze by the crayfish Cherax destructor suggests bilateral comparison of antennal tactile information. Biol Bull 208:183–188
Menzel R, De Marco RJ, Greggers U (2006) Spatial memory, navigation and dance behaviour in Apis mellifera. J Comp Physiol A 192:889–903
Narendra A, Cheng K, Wehner R (2007) Acquiring, retaining and integrating memories of the outbound distance in the Australian desert ant Melophorus bagoti. J Exp Biol 210:570–577
Odling-Smee L, Braithwaite VA (2003) The influence of habitat stability on landmark use during spatial learning in the three-spined stickleback. Anim Behav 65:701–707
Odling-Smee LC, Boughman JW, Braithwaite VA (2008) Sympatric species of three spine stickleback differ in their performance in a spatial learning task. Behav Ecol Sociobiol 62:1935–1945
Packard MG, McGaugh JL (1996) Inactivation of hippocampus or caudate nucleus with lidocaine differentially affects expression of place and response learning. Neurobiol Learn Mem 65:65–72
Paul CM, Magda G, Abel S (2009) Spatial memory: theoretical basis and comparative review on experimental methods in rodents. Behav Brain Res 203:151–164
Pleskacheva MG (2009) Behavior and spatial learning in radial mazes in birds. Neurosci Behav Physiol 39:725–739
Pol-Bodetto S, Jeltsch-David H, Lecourtier L, Rusnac N, Mam-Lam-Fook C, Cosquer B, Geiger K, Cassel J-C (2011) The double-H maze test, a novel, simple, water-escape memory task: acquisition, recall of recent and remote memory, and effects of systemic muscarinic or NMDA receptor blockade during training. Behav Brain Res 218:138–151
Postma A, Jager G, Kessels RPC, Koppeschaar HPF, van Honk J (2004) Sex differences for selective forms of spatial memory. Brain Cogn 54:24–34
Putz G, Heisenberg M (2002) Memories in Drosophila heat-box learning. Learn Mem 9:349–359
Restle F (1957) Discrimination of cues in mazes: a resolution of the “place-vs.-response” question. Psychol Rev 64:217–228
Sanchis-Segura C, Spanagel R (2006) Behavioural assessment of drug reinforcement and addictive features in rodents: an overview. Addict Biol 11:2–38
Shettleworth SJ (2010) Cognition, evolution, and behavior. Oxford Univ Press, New York
Shuranova Z, Burmistrov Y, Abramson CI (2005) Habituation to a novel environment in the crayfish Procambarus cubensis. J Crustacean Biol 25:488–494
Sitaraman D, Zars M, LaFerriere H, Chen Y-C, Sable-Smith A, Kitamoto T, Rottinghaus GE, Zars T (2008) Serotonin is necessary for place memory in Drosophila. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 105:5579–5584
Smulders TV, Gould KL, Leaver LA (2010) Using ecology to guide the study of cognitive and neural mechanisms of different aspects of spatial memory in food-hoarding animals. Phil Trans R Soc B 365:883–900
Sovrano VA, Bisazza A, Vallortigara G (2003) Modularity as a fish (Xenotoca eiseni) views it: conjoining geometric and nongeometric information for spatial reorientation. J Exp Psychol Anim B 29:199–210
Spritzer MD, Daviau ED, Coneeny MK, Engelman SM, Prince WT, Rodriguez-Wisdom KN (2011) Effects of testosterone on spatial learning and memory in adult rats. Horm Behav 59:484–496
Stein RA (1976) Sexual dimorphism in crayfish chelae: functional significance linked to reproductive activities. Can J Zool 54:220–227
Stein RA, Magnuson JJ (1976) Behavioral response of crayfish to a fish predator. Ecology 57:751–761
Texeira CM, Pomedli SR, Maei HR, Kee N, Frankland P (2006) Involvement of anterior cingulated cortex in the expression of remote spatial memory. J Neurosci 26:7555–7564
Tierney AJ (Ed) (2003) The crayfish nervous system: from histology to function. [Special issue]. Microsc ResTechniq 60
Tierney AJ, Lee J (2011) Spatial learning in a T-maze by the crayfish Orconectes rusticus. J Comp Psychol 125:31–39
Vallortigara G (1996) Learning of colour and position cues in domestic chicks: male are better at position, females at colour. Behav Process 36:289–296
VanderSal ND, Hebets EA (2007) Cross-modal effects on learning: a seismic stimulus improves color discrimination learning in a jumping spider. J Exp Biol 210:3689–3695
Vorhees CV, Williams MT (2006) Morris water maze: procedures for assessing spatial and related forms of memory. Nat Protoc 1:848–858
Wallraff HG (2005) Avian navigation: pigeon homing as a paradigm. Spring, Berlin
Wehner R (2009) The architecture of the desert ant’s navigational toolkit (Hymenoptera: Formicidae). Myrmecol News 12:85–96
Wessnitzer J, Managan M, Webb B (2008) Place memory in crickets. Proc R Soc B 275:915–921
White NM, McDonald RJ (2002) Multiple parallel memory systems in the brain of the rat. Neurobiol Learn Mem 77:125–184
Wolbers T, Hegarty M (2010) What determines our navigational abilities? Trends Cogn Sci 14:138–146
Ziegler PE, Wehner R (1997) Time-courses of memory decay in vector-based and landmark-based systems of navigation in desert ants, Cataglyphis fortis. J Comp Physiol A 181:13–20
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tierney, A.J., Andrews, K. Spatial behavior in male and female crayfish (Orconectes rusticus): learning strategies and memory duration. Anim Cogn 16, 23–34 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10071-012-0547-1
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10071-012-0547-1