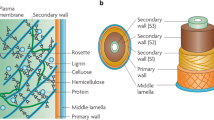
Abstract.
In nature, cellulose, lignocellulose and lignin are major sources of plant biomass; therefore, their recycling is indispensable for the carbon cycle. Each polymer is degraded by a variety of microorganisms which produce a battery of enzymes that work synergically. In the near future, processes that use lignocellulolytic enzymes or are based on microorganisms could lead to new, environmentally friendly technologies. This study reviews recent advances in the various biological treatments that can turn these three lignicellulose biopolymers into alternative fuels. In addition, biotechnological innovations based on natural delignification and applied to pulp and paper manufacture are also outlined.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Electronic Publication
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pérez, J., Muñoz-Dorado, J., de la Rubia, T. et al. Biodegradation and biological treatments of cellulose, hemicellulose and lignin: an overview. Int Microbiol 5, 53–63 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10123-002-0062-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10123-002-0062-3