Abstract
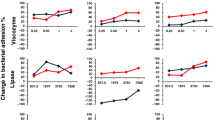
We investigated the effect of commercially available enzymes (α-amylase, α-galactosidase, papain, trypsin, and lipase) as well as proteases from deep-sea bacteria on the larval attachment of the bryozoan Bugula neritina L. The 50% effective concentrations (EC50) of the commercial proteases were 10 times lower than those of other enzymes. Crude proteases from six deep-sea Pseudoalteromonas species significantly decreased larval attachment at concentrations of 0.03 to 1 mIU ml−1. The EC50 of the pure protease from the bacterium Pseudoalteromonas issachenkonii UST041101-043 was close to 1 ng ml−1 (0.1 mIU ml−1). The protease and trypsin individually incorporated in a water-soluble paint matrix inhibited biofouling in a field experiment. There are certain correlations between production of proteases by bacterial films and inhibition of larval attachment. None of the bacteria with biofilms that induced attachment of B. neritina produced proteolytic enzymes, whereas most of the bacteria that formed inhibitive biofilms produced proteases. Our investigation demonstrated the potential use of proteolytic enzymes for antifouling defense.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Allermann K, Schneider I (2001) Antifouling paint composition comprising rosin and enzyme. PCT Patent application. WO 01/72911 A1
K Becker (1996) ArticleTitleExopolysaccharide production and attachment strength of bacteria and diatoms on substrates with different surface tensions Microb Ecol 32 23–33 Occurrence Handle10.1007/BF00170104
Bonaventura C, Bonaventura J, Hooper IR (2000) Anti-fouling methods using enzyme coatings, Dec. 7, 1999 Singapore. US Patent 5,998,200
JG Burgess KG Boyd E Armstrong Z Jiang L Yan M Berggren U May T Pisacane A Granmo DR Adams (2003) ArticleTitleThe development of a marine natural product-based antifouling paint Biofouling 19 197–205 Occurrence Handle10.1080/0892701031000061778
ME Callow JA Callow (2000) ArticleTitleSubstratum location and zoospore behaviour in the fouling alga Enteromorpha Biofouling 15 49–56
JA Callow MS Stanley R Wetherbee ME Callow (2000) ArticleTitleCellular and molecular approaches to understanding primary adhesion in Enteromorpha: an overview Biofouling 16 141–150 Occurrence Handle10.1080/08927010009378439
KE Cooksey B Wigglesworth-Cooksey (1995) ArticleTitleAdhesion of bacteria and diatoms to surfaces in the sea: a review Aquat Microb Ecol 9 87–96
AS Claire (1998) ArticleTitleTowards nontoxic antifouling J Mar Biotechnol 6 3–6
AS Clare RK Freet M McClary SuffixJr (1994) ArticleTitleOn the antennular secretion of the cyprid of Balanus amphitrite amphitrite and its role as a settlement pheromone J Mar Biol Assoc UK 74 243–250
S Dobretsov PY Qian (2002) ArticleTitleEffect of bacteria associated with the green alga Ulva reticulata on marine micro- and macrofouling Biofouling 18 217–228 Occurrence Handle10.1080/08927010290013026
S Dobretsov PY Qian (2004) ArticleTitleThe role of epibotic bacteria from the surface of the soft coral Dendronephthya sp. for the inhibition of larval settlement J Exp Mar Biol Ecol 299 35–50 Occurrence Handle10.1016/j.jembe.2003.08.011
S Dobretsov PY Qian (2006) ArticleTitleFacilitation and inhibition of larval attachment of the bryozoan Bugula neritina in association with mono-species and multi-species biofilms J Exp Mar Biol Ecol 333 263–274 Occurrence Handle10.1016/j.jembe.2006.01.019
S Dobretsov HU Dahms PY Qian (2006) ArticleTitleA review: inhibition of biofouling by marine microorganisms and their metabolites Biofouling 22 43–54 Occurrence Handle10.1080/08927010500504784
S Egan S James C Holmström S Kjelleberg (2001) ArticleTitleInhibition of algal spore germination by the marine bacterium Pseudoalteromonas tunicata FEMS Microbiol Ecol 35 67–73 Occurrence Handle10.1111/j.1574-6941.2001.tb00789.x
S Egan S James S Kjelleberg (2002) ArticleTitleIdentification and characterization of a putative transcriptional regulator controlling the expression of fouling inhibitors in Pseudoalteromonas tunicata Appl Environ Microbiol 68 372–378 Occurrence Handle10.1128/AEM.68.1.372-378.2002
N Fusetani (2004) ArticleTitleBiofouling and antifouling Nat Prod Rep 21 94–104 Occurrence Handle10.1039/b302231p
B Ghorbel A Sellami-Kamoun M Nasri (2003) ArticleTitleStability studies of protease from Bacillus cereus BG1 Enzyme Microb Technol 32 513–518 Occurrence Handle10.1016/S0141-0229(03)00004-8
C Holmström S Kjelleberg (1999) ArticleTitleMarine Pseudoalteromonas species are associated with higher organisms and produce active extracellular compounds FEMS Microbiol Ecol 30 285–293
C Holmström D Rittschof S Kjelleberg (1992) ArticleTitleInhibition of settlement by larvae of Balanus amphitrite and Cliona intestinalis by surface-colonizing marine bacterium Appl Environ Microbiol 58 2111–2115
C Holmström S Egan A Franks S McCloy S Kjelleberg (2002) ArticleTitleAntifouling activities expressed by marine surface associated Pseudoalteromonas species FEMS Microbiol Ecol 41 47–58
RA Jensen DE Morse (1988) ArticleTitleThe bioadhesive of Phragmatopoma californica tubes: a silk-like cement containing L-DOPA J Comp Phys B 158 317–324 Occurrence Handle10.1007/BF00695330
K Kamino (2001) ArticleTitleNovel barnacle underwater adhesive protein is a charged amino acid-rich protein constituted by a Cys-rich repetitive sequence Biochem J 356 503–507 Occurrence Handle10.1042/0264-6021:3560503
D Kirchman D Graham D Reish R Mitchell (1982) ArticleTitleLectins may mediate in the settlement and metamorphosis of Janua (Dexiospira) brasiliensis Grube (Polychaetea: Spirorbidae) Mar Biol Lett 3 201–222
AM Klibanov (2001) ArticleTitleImproving enzymes by using them in organic solvents Nature 409 241–246 Occurrence Handle10.1038/35051719
N Kon-ya N Shimidzu N Otaki A Yokoyama K Adachi W Miki (1995) ArticleTitleInhibitory effect of bacterial ubiquinones on the settling of barnacle, Balanus amphitrite Experientia 51 153–155 Occurrence Handle10.1007/BF01929360
SCK Lau PY Qian (2001) ArticleTitleLarval settlement in the serpulid polychaete Hydroides elegans in response to bacterial films: an investigation of the nature of putative larval settlement cue Mar Biol 138 321–328 Occurrence Handle10.1007/s002270000453
SCK Lau KKW Mak F Chen PY Qian (2002) ArticleTitleBioactivity of bacterial strains from marine biofilms in Hong Kong waters for the induction of larval settlement in the marine polychaete Hydroides elegans Mar Ecol Prog Ser 226 301–310
SCK Lau V Thiyagarajan PY Qian (2003) ArticleTitleThe bioactivity of bacterial isolates in Hong Kong waters for the inhibition of barnacle (Balanus amphitrite Darwin) settlement J Exp Mar Biol Ecol 282 43–60 Occurrence Handle10.1016/S0022-0981(02)00445-8
BJ Little PA Wagner (1997) Succession in microfouling R Nagabhushanam M Thompson (Eds) Fouling Organisms of the Indian Ocean: Biology and Control Technology Oxford and IBH New Delhi 105–134
JS Maki D Rittschof JD Costlow R Mitchell (1988) ArticleTitleInhibition of attachment of larval barnacles, Balanus amphitrite, by bacterial surface films Mar Biol 97 199–206 Occurrence Handle10.1007/BF00391303
K Matsumura M Nagano Y Kato-Yoshinaga M Yamazaki AS Clare N Fusetani (1998) ArticleTitleImmunological studies on the settlement-inducing protein complex (SIPC) of the barnacle Balanus amphitrite and its possible involvement in larva-larva interactions Proc R Soc Lond 265 1825–1830 Occurrence Handle10.1098/rspb.1998.0508
ME Pettitt SL Henry ME Callow JA Callow AS Clare (2004) ArticleTitleActivity of commercial enzymes on settlement and adhesion of cypris larvae of the barnacle Balanus amphitrite, spores of the green alga Ulva linza, and the diatom Navicula perminuta Biofouling 20 299–311 Occurrence Handle10.1080/08927010400027068
AI Railkin (2004) Marine Biofouling: Colonization Processes and Defenses CRC Press Boca Raton, FL
D Rittschof AR Schmidt IR Hooper DJ Gerhart D Gunster J Bonaventura (1991) Molecular mediation of settlement of selected invertebrate larvae MR Thompson R Sarojini R Nagabhushanam (Eds) Bioactive Compounds from Marine Organisms A.A. Balkema Rotterdam 317–328
AM Rouhi (1998) ArticleTitleThe squeeze of tributyltins Chem Eng News 27 41–42
Selvig T, Warren PP, Leavitt RL (1999) Methods for removing undesired growth from a surface. US Patent No 346535, fill. date 02.07.99
SS Shapiro MB Wilk (1965) ArticleTitleAn analysis of variance test for normality (complete samples) Biometrika 52 591–611
AP Wezel Particlevan P Wlaardingen Particlevan (2004) ArticleTitleEnvironmental risk limits for antifouling substances Aquat Toxicol 66 427–444 Occurrence Handle10.1016/j.aquatox.2003.11.003
V Vreeland JH Waite L Epstein (1998) ArticleTitleMinireview-polyphenols and oxidases in substratum adhesion by marine algae and mussels J Phycol 34 1–8 Occurrence Handle10.1046/j.1529-8817.1998.340001.x
M Wahl (1989) ArticleTitleMarine epibiosis.1. Fouling and antifouling: some basic aspects Mar Ecol Prog Ser 58 175–189
M Wahl (1997) Living attached: aufwuchs, fouling, epibiosis R Nagabhushanam M Thompson (Eds) Fouling Organisms of the Indian Ocean: Biology and Control Technology Oxford & IBH New Delhi 31–84
JH Waite (1992) ArticleTitleThe DOPA ephemera: a recurrent motif in invertebrates Biol Bull 183 178–184 Occurrence Handle10.2307/1542421
M Wiegemann (2005) ArticleTitleAdhesion in blue mussels (Mytilus edulis) and barnacles (genus Balanus): mechanisms and technical applications Aquat Sci 67 166–176 Occurrence Handle10.1007/s00027-005-0758-5
H Xiong A Nyyssölä J Jänis O Pastinen N Weymarn M Leisola O Turunen (2004) ArticleTitleCharacterization of the xylanase produced on submerged cultivation by Thermomyces lanuginosus DSM 10635 Enzyme Microb Technol 35 93–99 Occurrence Handle10.1016/j.enzmictec.2004.04.003
H Xiong L Song Y Xu M-Y Tosi S Dobretsov P-Y Qian (2007) ArticleTitleCharacterization of proteolytic bacteria from the Aleutian deep-sea and their proteases J Ind Microbiol Biotechnol 34 63–71 Occurrence Handle10.1007/s10295-006-0165-5
DM Yebra S Kiil K Dam-Johansen (2004) ArticleTitleAntifouling technology-past, present and future steps towards efficient and environmentally friendly antifouling coatings Prog Org Coat 50 75–104 Occurrence Handle10.1016/j.porgcoat.2003.06.001
JH Zar (1996) Biostatistical Analysis EditionNumber3 Prentice-Hall Upper Saddle River, NJ
F Zentz C Hellio A Valla D Broise ParticleDe La G Bremer R Labia (2002) ArticleTitleAntifouling activities of N-substituted imides: antimicrobial activities and inhibition of Mytilus edulis phenoloxidase Mar Biotechnol 4 431–440 Occurrence Handle10.1007/s10126-002-0004-2
Acknowledgments
We thank Dr. Hans-Uwe Dahms (Germany) for his useful suggestions on the manuscript; Dr. Tony Rathburn (USA) for facilitating collection of deep-sea samples; Dr. Linsheng Song (China) for his help in isolation of bacteria; and the crew, pilots, and the captain of the R/V Revelle and Jason II (USA) for their assistance. This work was supported by the West Coast National Undersea Research Center Grant UAF-04-0112 to L.A.L., a grant from China Ocean Mineral Resource Research and Development Association (COMRRDA 03/04.SC01), and a Central Allocation grant (CAS04/05.Sc01) to P.Y.Q., and partially by an Alexander von Humboldt Fellowship to S.D.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dobretsov, S., Xiong, H., Xu, Y. et al. Novel Antifoulants: Inhibition of Larval Attachment by Proteases. Mar Biotechnol 9, 388–397 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10126-007-7091-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10126-007-7091-z