Abstract
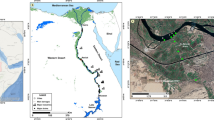
This study estimated the inputs of four paddy herbicides in the entire river inflow reaching Lake Biwa, the largest lake in Japan, which serves as a water resource for 14 million people. The Uso River and the Hino River, the main contaminated rivers among the inflow rivers, were selected as daily and hourly monitoring sites to provide data on the seasonal trends in the concentration and load of herbicides and to determine the effect of rainfall events on load. The monitoring was also performed four times in 15 inflow rivers. The total input to the lake was calculated from the loads during fine weather conditions and additional loads during rainfall events. The former based on the lumped load from the two rivers and by prorating for the 15 rivers, and the latter was estimated from the relation between precipitation and increased load rate. The annual losses of herbicide from the basin to Lake Biwa were estimated to be 14.5% for bromobutide, 3.0% for pretilachlor, 5.2% for molinate, and 8.8% for simetryn. The loads caused by rainfall events accounted for 9%–18% of the total annual loads.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
TA Albanis TG Dains MK Kourgia (1994) ArticleTitleTransportation of pesticides in estuaries of the Axios, Loudias and Aliakmon Rivers (Thermaikos Gulf), Greece Sci Total Environ 156 IssueID1 11–22 Occurrence Handle10.1016/0048-9697(94)90416-2
LK Armbrust (1999) ArticleTitlePhotochemical processes influencing pesticide degradation in rice paddies J Pestic Sci 24 69–73
NT Besta RL Huhnke JH Stiegler (1997) ArticleTitleAtrazine runoff from conservation tillage systems J Soil Water Cons 52 44–48
KL Crepeau KM Kuivila (2000) ArticleTitleRice pesticide concentrations in the Colusa Basin Drain and the Sacramento River, California, 1990–1993 J Environ Qual 29 926–935
SA Cryer LJ Rotston PL Havens (1998) ArticleTitleUtilizing simulated weather patterns to predict runoff exceedence probabilities for highly sorbed pesticides Environ Pollut 103 211–218 Occurrence Handle10.1016/S0269-7491(98)00119-5
JM Dabrowski SKC Peall AJ Reinecke M Liess R Schulz (2002) ArticleTitleRunoff-related pesticide input into the Lourens River, South Africa Water Air Soil Pollut 135 265–283 Occurrence Handle10.1023/A:1014705931212
Fukushima M, Yamaguchi Y, Yamada A (1995) Temporal trend of pesticide pollution in river water as a source of potable water. IWSA Specialized Conference on Advanced Treatment and Integrated Water System Management into the 21th Century, Osaka, Japan, May 15–17, 1995:158–163
InstitutionalAuthorNameHokkaido Institute of Environmental Science (2000) Study on pesticide movement in environment and decrease of influence on environment (in Japanese) Hokkaido Institute of Environmental Science Sapporo, Hokkaido
K Inao Y Ishii Y Kobara Y Kitamura (2001) ArticleTitlePrediction of pesticide behavior in paddy fields by water balance on the water management using Pesticide Paddy Field Model (PADDY) J Pestic Sci 26 229–235
K Inao Y Ishii Y Kobara Y Kitamura (2003) ArticleTitleLandscape-scale simulation of pesticide behavior in river basin due to runoff from paddy field using Pesticide Paddy Field Model (PADDY) J Pestic Sci 28 24–32 Occurrence Handle10.1584/jpestics.28.24
T Inoue S Ebise (1999) ArticleTitleRunoff characteristics of pesticides from paddy fields to lake (in Japanese) Res Rep Natl Inst Environ Stud Jpn 144 49–57
Integrated Planning of Water Resource Quality, Department of Environmental Engineering, Kyoto University (2000) Symposium on integration of basin management and applications to decision making and actual environment. Integrated Planning of Water Resource Quality, Otsu, Japan, March 11, 2000, pp 103–105
Y Ishii (1984) ArticleTitlePollution by pesticides of estuaries in Aichi Prefecture and opinion on safety use of pesticides (in Japanese) Ecol Chem 7 IssueID2 19–31
Japan Meteorological Agency (2004) http://www.jma.go.jp/
InstitutionalAuthorNameJapan Static Association (2002) Japan statistical yearbook, 52nd edn Japan Static Association Tokyo, Japan
J Kanazawa (Eds) (1996) Characteristics and toxicites of pesticide in the environment (in Japanese) Godo Publishers Tokyo
K Kibe H Takano T Kameya K Urano (2000) ArticleTitleEstimation of runoff load of simetryn from paddy fields by a new fate model (in Japanese) J Jpn Soc Water Environ 23 IssueID6 343–351
T Kunimatsu (1997) ArticleTitleChemical characters of water quality in Lake Biwa Environmental Conservation Engineering 26 IssueID8 480–484
T Kunimatsu M Sudo (1997) ArticleTitleMeasurement and evaluation of nutrient runoff loads from mountainous forested lands (in Japanese) J Jpn Soc Water Environ 20 IssueID12 810–815
InstitutionalAuthorNameLake Biwa Research Institute (1989) Data book of world lake environments Lake Biwa Research Institute and International Lake Environment Committee Otsu
S Maru (1985) ArticleTitleMonitoring survey of pesticides in river water within Chiba Prefecture (in Japanese) Ecol Chem 8 IssueID3 3–10
Mullins JA, Carsel RF, Scarbrough HE, Ivery AM (1993) PRZM-2, a model for predicting pesticide fate in the crop root and unsaturated soil zones, users manual for release 2.0. EPA/600/R-93/046. Technical Report. Environmental Research Laboratory, US Environmental Protection Agency, Athens, GA
M Nakamura M Kobayashi K Hasegawa (1982) ArticleTitleThe effect of return flow irrigation on balance of water pollution material in paddy fields (2) (in Japanese Bull Shiga Pref Agric Exp Stn 24 79–86
A Numabe T Inoue S Ebise (1992) ArticleTitleEstimation on the runoff amounts of pesticides applied after transplanting on rice plant by drainage river (in Japanese) J Jpn Soc Water Environ 15 IssueID10 662–671
WE Pereira FD Hostettler (1993) ArticleTitleNonpoint source contamination of the Mississippi River and its tributaries by herbicides Environ Sci Technol 27 IssueID8 1542–1552 Occurrence Handle10.1021/es00045a008
Y Sasagawa S Matsui H Yamada (1996) ArticleTitleRun-off herbicides from paddy fields around the southern basin of Lake Biwa (in Japanese) J Jpn Soc Water Environ 19 IssueID7 547–556
K Sasaki T Tsukioka J Terasawa S Shimizu (1994) ArticleTitleRiver water monitoring survey for pesticides and estimation on the runoff amounts from agricultural fields (in Japanese) Res Rep Natl Inst Environ Stud Jpn 133 57–65
MD Scrunshaw JN Lester (1995) ArticleTitleOrganochlorine contamination in sediments of the inner Thames Estuary J Chart Inst Water Environ Manage 9 519–525
Shiga Prefecture (2002) Information of precipitation in Shiga prefecture Shiga Prefecture Otsu
M Sudo T Kunimatsu (1992) ArticleTitleCharacteristics of pesticide runoff from golf links Water Sci Tech 25 IssueID11 85–92
M Sudo T Kunimatsu T Okubo (2002a) ArticleTitleConcentration and loading of pesticide residues in Lake Biwa basin (Japan) Water Res 36 315–329 Occurrence Handle10.1016/S0043-1354(01)00196-8
M Sudo T Okubo T Kunimatsu S Ebise M Nakamura R Kaneki (2002b) ArticleTitleInflow and outflow of agricultural chemicals in Lake Biwa Lakes Reserv Res Manage 7 301–308 Occurrence Handle10.1046/j.1440-1770.2002.00195.x
M Sudo T Kawachi Y Hida T Kunimatsu (2004) ArticleTitleSpatial distribution and seasonal changes of pesticides in Lake Biwa, Japan Limnology 5 IssueID2 77–86 Occurrence Handle10.1007/s10201-003-0115-0
Y Takahasi Y Wada Y Odanaka H Furuno (2000) ArticleTitleField-scale runoff study for three pesticides under natural rainfall J Pestic Sci 25 140–143
A Tanabe H Mitobe K Kawata A Yasuhara T Shibamoto (2001) ArticleTitleSeasonal and spatial studies on pesticide residues in surface waters of the Shinano River in Japan J Agric Food Chem 49 3847–3852 Occurrence Handle10.1021/jf010025x Occurrence Handle11513677
T Tsuda M Kojima H Harada A Nakajima S Aoki (1997) ArticleTitleHerbicides in water and fish from rivers flowing into Lake Biwa Toxicol Environ Chem 61 243–249
RD Wauchope (1978) ArticleTitleThe pesticide content of surface water draining from agricultural fields – a review J Environ Qual 7 IssueID4 459–472
RD Wauchope (1992) ArticleTitleEnvironmental risk assessment of pesticides: Improving simulation model credibility Weed Technol 6 753–759
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sudo, M., Okubo, T. & Kaneki, R. Paddy herbicide inputs in the entire river inflow reaching Lake Biwa, Japan. Limnology 6, 91–99 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10201-005-0145-x
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10201-005-0145-x