Abstract
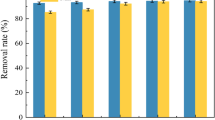
We evaluated the sorptive properties of mordenite zeolite (MOR), a copper terephthalate metal–organic framework (MOF), and graphene oxide (GO) and their potential use in treating acid rock drainage (ARD) containing Fe3+, Cu2+, Mn2+, Zn2+, Pb2+, and Cd2+ ions. MOR was prepared via a hydrothermal method, MOF was prepared via a solvothermal method, and few-layered GO nanosheets were synthesized using Hummers’ method. The aqueous contaminants were removed by chemico-physical sorption and ion exchange in batch tests. It proved possible to dramatically improve removal efficiency and sorptive capacity by optimizing experimental conditions. Magnetic MOF crystals were more efficient in removing metals than the MOR and GO. Sorption tests using ARD from the Sungun copper mine and a multi-component solution containing cationic metal species revealed that both GO nanosheets and magnetic MOF have great potential for ARD treatment.
Zusammenfassung
Untersucht wurden die Sorptionseigenschaften des Zeolithminerals Mordenit (MOR), eines Kupfer-Terephtalats aus der Klasse der metallorganischen Gerüstverbindungen (MOF) und von Graphenoxid (GO), sowie deren Potential zur Behandlung von Sauerwasser (ARD) mit Gehalten an Fe3+, Cu2+, Mn2+, Zn2+, Pb2+und Cd2+. MOR wurde mittels Hydrothermalsynthese, MOF unter Nutzung einer Solvothermalmethode hergestellt. Die Synthese der dünnen GO-Nanoschichten erfolgte entsprechend der Methode nach Hummer. Die Wasserschadstoffe wurden in Batch-Tests durch physikochemische Sorption und Ionenaustausch abgereichert. Es konnte gezeigt werden, dass sich Abreinigungsvermögen und Sorptionskapazität der getesteten Materialien durch Optimierung der experimentellen Bedingungen erheblich verbessern lassen. Die magnetischen MOF-Kristalle wiesen in Bezug auf die Entfernung der Schwermetalle bessere Ergebnisse auf als MOR und GO. Sorptionstests mit Sauerwasser von der Sungun-Kupfermine sowie mit einer kationische Metallspezies enthaltenden Mehrkomponentenlösung ergaben, dass sowohl GO-Nanoschichten als auch magnetisches MOF ein großes Potential zur Sauerwasserbehandlung besitzen.
Resumen
Evaluamos las propiedades sortivas de zeolita mordenita (MOR), un sistema orgánico metálico –tereftalato de cobre- (MOF), un óxido de grafeno (GO) y sus potenciales usos en el tratamiento de drenaje ácido de roca (ARD) conteniendo iones Fe3+, Cu2+, Mn2+, Zn2+, Pb2+y Cd2+. MOR fue preparada por un método hidrotermal, MOF fue preparado por un método solvotermal y pocas capas de nanoláminas GO fueron sintetizadas usando el método de Hummers. Los contaminantes acuosos fueron removidos por sorción químico-física e intercambio iónico en estudios en batch. Se probó que pueden mejorarse significativamente las eficiencias de remoción y las capacidades sortivas, optimizando las condiciones experimentales. Los cristales magnéticos MOF fueron más eficientes en remover metales que MOR y GO. Los estudios de sorción usando ARD desde la mina de cobre Sungun y una solución multicomponente conteniendo cationes metálicos mostraron que tanto las nanoláminas GO como las MOF magnéticas tienen un gran potencial para el tratamiento de ARD.
摘要
本文评价了丝光沸石(MOR)、对苯二甲酸铜金属-有机框架材料(MOF)和氧化石墨烯(GO)的吸附特性以及它们处理含Fe3+、Cu2+、Mn2+、Zn2+、Pb2+和Cd2+的酸性岩石废水(ARD)的能力。水热法制备丝光沸石(MOR),溶剂热法制备对苯二甲酸铜金属-有机框架材料(MOF),Hummers法合成氧化石墨烯(GO)纳米片。化学-物理吸附作用和离子交换作用去除了批次试验中的水合污染物。试验证明,优化实验条件可以显著提高去除效率和吸附能力。对苯二甲酸铜金属-有机框架材料(MOF) 的磁化晶体比丝光沸石(MOR)和氧化石墨烯(GO)去除金属离子效率更高。Sungun铜矿酸性岩石废水(ARD)和含金属阳离子的多组分溶液的吸附试验证明,氧化石墨烯(GO)纳米片和对苯二甲酸铜金属-有机框架材料(MOF)磁化晶体具有巨大的处理酸性岩石废水(ARD)的潜力。.












Similar content being viewed by others
References
Chandra V, Park J, Chun Y, Lee JW, Hwang IC, Kim KS (2010) Water-dispersible magnetite-reduced graphene oxide composites for arsenic removal. ACS Nano 4:3979–3986
Erdem E, Karapinar N, Donat R (2004) The removal of heavy metal cations by natural zeolite. J Colloid Interface Sci 280:309–314
Gupta VK, Mittal A, Krishnan L, Mittal J (2006) Adsorption treatment and recovery of the hazardous dye, brilliant blue FCF, over bottom ash and de-oiled soya. J Colloid Interface Sci 293:16–26
Gupta VK, Ali I, Saini VK (2007a) Defluoridation of wastewaters using waste carbon slurry. Water Res 41:3307–3316
Gupta VK, Singh AK, Gupta B (2007b) Schiff bases as cadmium (II) selective ionophores in polymeric membrane electrodes. Anal Chem Acta 583:340–348
Gupta VK, Goyal RN, Sharma RA (2009) Novel PVC membrane based alizarin sensor and its application; determination of vanadium, zirconium and molybdenum. Int J Electrochem Sci 4:156–172
Inglezakis VJ, Loizidou MD, Grigoropoulou HP (2002) Equilibrium and kinetic ion exchange studies of Pb2+, Cr3+, Fe3+ and Cu2+ on natural clinoptilolite. Water Res 36:2784–2792
Inglezakis VJ, Loizidou MD, Grigoropoulou HP (2003) Ion exchange of Pb2+, Cu2+, Fe3+ and Cr3+ on natural clinoptilolite: selectivity determination and influence of acidity on metal uptake. J Colloid Interface Sci 261:49–54
Kalin M, Fyson A, Wheeler WN (2006) The chemistry of conventional and alternative treatment systems for the neutralization of acid mine drainage. Sci Total Environ 366:395–408
Li Y, Wu Y (2009) Coassembly of graphene oxide and nanowires for large-area nanowire alignment. J Am Chem Soc 131:5851–5857
Lipson H, Steeple H (1970) Interpretation of X-ray Powder Diffraction Patterns. Macmillan, London
Long RQ, Yang RT (2001) Carbon nanotubes as superior sorbent for dioxin removal. J Am Chem Soc 123:2058–2059
Matlock MM, Howerton BS, Atwood DA (2002) Chemical precipitation of heavy metals from acid mine drainage. Water Res 36:4757–4764
Mayer KU, Benner SG, Blowes DW (2006) Process-based reactive transport modeling of a permeable reactive barrier for the treatment of mine drainage. J Contam Hydrol 85:195–211
Mohaghegh N, Tasviri M, Rahimi E, Gholami MR (2014) Nano sized ZnO composites: preparation, characterization and application as photocatalysts for degradation of AB92 azo dye. Mater Sci Semicond Process 21:167–179
Motsi T, Rowson NA, Simmons MJH (2009) Adsorption of heavy metals from acid mine drainage by natural zeolite. Int J Miner Process 92:42–48
Namasivayam C, Yamuna RT (1999) Studies on chromium (III) removal from aqueous solution by adsorption onto biogas residual slurry and its application to tannery wastewater treatment. Water Air Soil Pollut 113:371–384
Pankaj S, Rajaram P, Tomar R (2008) Synthesis and morphological studies of nanocrystalline MOR type zeolite material. J Colloid Interface Sci 325:547–557
Peric J, Trgo M, Vukojevic-Medvidovic N (2004) Removal of zinc, copper and lead by natural zeolite—a comparison of adsorption isotherms. Water Res 38:1893–1899
R´ıos CA, Williams CD, Roberts CL (2008) Removal of heavy metals from acid mine drainage (AMD) using coal fly ash, natural clinker and synthetic zeolites. J Hazard Mater 156:23–35
Shiokawa K, Ito M, Itabashi K (1989) Crystal structure of synthetic mordenite zeolites. Zeolites 9:170–176
Sprynskyy M, Buszewski B, Terzyk AP, Namiesnik J (2006) Study of the selection mechanism of heavy metal (Pb2+, Cu2+, Ni2+ and Cd2+) adsorption on clinoptilolite. J Colloid Interface Sci 304:21–28
Stankovich S, Dikin DA, Piner RD, Kohlhaas KA, Kleinhammes A, Jia Y, Wu Y, Nguyen ST, Ruoff RS (2007) Synthesis of graphene-based nanosheets via chemical reduction of exfoliated graphite oxide. Carbon 45:1558–1565
Taty-Costodes VC, Fauduet H, Porte C, Delacroix A (2003) Removal of Cd(II) and Pb(II) ions, from aqueous solutions, by adsorption onto sawdust of Pinus sylvestris. J Hazard Mater 105:121–142
Vermaak SSP, Potgieter JH, Monama P, Grieken RV (2006) Comparison of limestone, dolomite and fly ash as pre-treatment agents for acid mine drainage. Miner Eng 19:454–462
Wang XL, Lu JL, Xing BS (2008) Sorption of organic contaminants by carbon nanotubes: influence of adsorbed organic matter. Environ Sci Technol 42:3207–3212
Zhang H, Lv X, Li Y, Wang Y, Li J (2010) P25-graphene composite as a high performance photocatalyst. ACS Nano 4:380–386
Zhao GX, Jiang L, He Y, Li JX, Dong HL, Wang XK, Hu WP (2011a) Sulfonated graphene for persistent aromatic pollutant management. Adv Mater 23:3959–3963
Zhao GX, Li J, Ren X, Chen Ch, Wang X (2011b) Few-layered graphene oxide nanosheets as superior sorbents for heavy metal ion pollution management. Environ Sci Technol 45:10454–10462
Zhao GX, Ren XM, Gao X, Tan XL, Li JX, Chen CL, Huang YY, Wang XK (2011c) Removal of Pb(II) ions from aqueous solutions on few-layered graphene oxide nanosheets. Dalton Trans 40:10945–40952
Zhou Y, Bao Q, Tang LAL, Zhong Y, Loh KP (2009) Hydrothermal dehydration for the “Green” reduction of exfoliated graphene oxide to graphene and demonstration of tunable optical limiting properties. Chem Mater 21:2950–2956
Acknowledgments
The authors are grateful to Mr. Rezai from the Sungun Copper Mine for providing an ARD wastewater sample.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rahimi, E., Mohaghegh, N. Removal of Toxic Metal Ions from Sungun Acid Rock Drainage Using Mordenite Zeolite, Graphene Nanosheets, and a Novel Metal–Organic Framework. Mine Water Environ 35, 18–28 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10230-015-0327-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10230-015-0327-7