Abstract
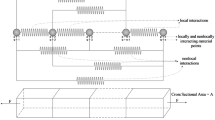
Many studies have used patient-specific finite element models to estimate the stress environment in atherosclerotic plaques, attempting to correlate the magnitude of stress to plaque vulnerability. In complex geometries, few studies have incorporated the anisotropic material response of arterial tissue. This paper presents a fibre remodelling algorithm to predict the fibre architecture, and thus anisotropic material response in four patient-specific models of the carotid bifurcation. The change in fibre architecture during disease progression and its affect on the stress environment in the plaque were predicted. The mean fibre directions were assumed to lie at an angle between the two positive principal strain directions. The angle and the degree of dispersion were assumed to depend on the ratio of principal strain values. Results were compared with experimental observations and other numerical studies. In non-branching regions of each model, the typical double helix arterial fibre pattern was predicted while at the bifurcation and in regions of plaque burden, more complex fibre architectures were found. The predicted change in fibre architecture in the arterial tissue during plaque progression was found to alter the stress environment in the plaque. This suggests that the specimen-specific anisotropic response of the tissue should be taken into account to accurately predict stresses in the plaque. Since determination of the fibre architecture in vivo is a difficult task, the system presented here provides a useful method of estimating the fibre architecture in complex arterial geometries.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alastrue V, Garcia A, Pena E, Rodriguez JF, Martinez MA, Doblare M (2010) Numerical framework for patient-specific computational modelling of vascular tissue. Int J Numer Meth Bio 26(1): 35–51
Ateshian GA (2007) Anisotropy of fibrous tissues in relation to the distribution of tensed and buckled fibers. J Biomech Eng 129(2): 240–249. doi:10.1115/1.2486179
Cheng GC, Loree HM, Kamm RD, Fishbein MC, Lee RT (1993) Distribution of circumferential stress in ruptured and stable atherosclerotic lesions. A structural analysis with histopathological correlation. Circulation 87(4): 1179–1187
Creane A, Maher E, Sultan S, Hynes N, Kelly DJ, Lally C (2010) Finite element modelling of diseased carotid bifurcations generated from in vivo computerised tomographic angiography. Comput Biol Med 40(4): 419–429. doi:10.1016/j.compbiomed.2010.02.006
Delfino A, Stergiopulos N, Moore JE Jr, Meister JJ (1997) Residual strain effects on the stress field in a thick wall finite element model of the human carotid bifurcation. J Biomech 30(8): 777–786. doi:S0021929097000250 [pii]
Driessen NJB, Bouten CVC, Baaijens FPT (2005) Improved prediction of the collagen fiber architecture in the aortic heart valve. J Biomech Eng T Asme 127(2): 329–336. doi:10.1115/1.1865187
Driessen NJB, Cox MAJ, Bouten CVC, Baaijens FPT (2008) Remodelling of the angular collagen fiber distribution in cardiovascular tissues. Biomech Model Mechan 7(2): 93–103. doi:10.1007/s10237-007-0078-x
Driessen NJB, Wilson W, Bouten CVC, Baaijens FPT (2004) A computational model for collagen fibre remodelling in the arterial wall. J Theor Biol 226(1): 53–64. doi:10.1016/j.jtbi.2003.08.004
Finlay HM, Whittaker P, Canham PB (1998) Collagen organization in the branching region of human brain arteries. Stroke 29(8): 1595–1601
Flamini V, Kerskens C, Moerman KM, Simms CK, Lally C (2010) Imaging arterial fibres using diffusion tensor imaging-feasibility study and preliminary results. Eurasip J Adv Sig Pr. doi:10.1155/2010/904091
Freed AD (2008) Anisotropy in hypoelastic soft-tissue mechanics, i: theory. J Mech Mater Struct 3(5): 911–928
Freed AD, Einstein DR, Vesely I (2005) Invariant formulation for dispersed transverse isotropy in aortic heart valves—an efficient means for modeling fiber splay. Biomech Model Mechan 4(2-3): 100–117. doi:10.1007/s10237-005-0069-8
Gao H, Long Q (2008) Effects of varied lipid core volume and fibrous cap thickness on stress distribution in carotid arterial plaques. J Biomech 41(14): 3053–3059. doi:10.1016/j.jbiomech.2008.07.011
Gao H, Long Q, Graves M, Gillard JH, Li ZY (2009) Carotid arterial plaque stress analysis using fluid-structure interactive simulation based on in-vivo magnetic resonance images of four patients. J Biomech 42(10): 1416–1423. doi:10.1016/j.jbiomech.2009.04.010
Gasser TC, Ogden RW, Holzapfel GA (2006) Hyperelastic modelling of arterial layers with distributed collagen fibre orientations. J R Soc Interface 3(6): 15–35. doi:10.1098/rsif.2005.0073
Glagov S, Zarins C, Giddens DP, Ku DN (1988) Hemodynamics and atherosclerosis. Insights and perspectives gained from studies of human arteries. Arch Pathol Lab Med 112(10): 1018–1031
Grytz R, Meschke G (2010) A computational remodeling approach to predict the physiological architecture of the collagen fibril network in corneo-scleral shells. Biomech Model Mechanobiol 9(2): 225–235. doi:10.1007/s10237-009-0173-2
Grytz R, Meschke G, Jonas JB (2010) The collagen fibril architecture in the lamina cribrosa and peripapillary sclera predicted by a computational remodeling approach. Biomech Model Mechanobiol. doi:10.1007/s10237-010-0240-8
Hardie AD, Kramer CM, Raghavan P, Baskurt E, Nandalur KR (2007) The impact of expansive arterial remodeling on clinical presentation in carotid artery disease: a multidetector ct angiography study. Am J Neuroradiol 28(6): 1067–1070. doi:10.3174/Ajnr.A0508
Hariton I, deBotton G, Gasser TC, Holzapfel GA (2007a) Stress-driven collagen fiber remodeling in arterial walls. Biomech Model Mechanobiol 6(3): 163–175. doi:10.1007/s10237-006-0049-7
Hariton I, deBotton G, Gasser TC, Holzapfel GA (2007b) Stress-modulated collagen fiber remodeling in a human carotid bifurcation. J Theor Biol 248(3): 460–470. doi:10.1016/j.jtbi.2007.05.037
Hayashi K, Mani V, Nemade A, Aguiar S, Postley JE, Fuster V, Fayad ZA (2010) Variations in atherosclerosis and remodeling patterns in aorta and carotids. J Cardiovasc Magn R 12: 10. doi:10.1186/1532-429x-12-10
Holzapfel GA, Gasser TC, Ogden RW (2000) A new constitutive framework for arterial wall mechanics and a comparative study of material models. J Elast 61(1–3): 1–48
Holzapfel GA, Gasser TC, Stadler M (2002) A structural model for the viscoelastic behavior of arterial walls: continuum formulation and finite element analysis. Eur J Mech A Solids 21(3): 441–463. doi:10.1016/s0997-7538(01)01206-2
Holzapfel GA, Ogden RW (2010) Constitutive modelling of arteries. P Roy Soc A Math Phy 466(2118): 1551–1596. doi:10.1098/rspa.2010.0058
Humphrey JD, Eberth JF, Dye WW, Gleason RL (2009) Fundamental role of axial stress in compensatory adaptations by arteries. J Biomech 42(1): 1–8. doi:10.1016/j.jbiomech.2008.11.011
Kingsley PB (2006) Introduction to diffusion tensor imaging mathematics: part i. Tensors, rotations, and eigenvectors. Concepts Magn Reson Part A 28A(2): 101–122. doi:10.1002/cmr.a.20048
Kiousis DE, Rubinigg SF, Auer M, Holzapfel GA (2009) A methodology to analyze changes in lipid core and calcification onto fibrous cap vulnerability: the human atherosclerotic carotid bifurcation as an illustratory example. J Biomech Eng 131(12): 121002. doi:10.1115/1.4000078
Kuhl E, Holzapfel GA (2007) A continuum model for remodeling in living structures. J Mater Sci 42(21): 8811–8823. doi:10.1007/s10853-007-1917-y
Li ZY, Howarth S, Trivedi RA, JM UK-I, Graves MJ, Brown A, Wang L, Gillard JH (2006) Stress analysis of carotid plaque rupture based on in vivo high resolution mri. J Biomech 39(14): 2611–2622. doi:10.1016/j.jbiomech.2005.08.022
Li ZY, Howarth SP, Tang T, Graves MJ, J UK-I, Trivedi RA, Kirkpatrick PJ, Gillard JH (2007) Structural analysis and magnetic resonance imaging predict plaque vulnerability: a study comparing symptomatic and asymptomatic individuals. J Vasc Surg 45(4): 768–775. doi:10.1016/j.jvs.2006.12.065
Maher E, Creane A, Sultan S, Hynes N, Lally C, Kelly DJ (2009) Tensile and compressive properties of fresh human carotid atherosclerotic plaques. J Biomech 42(16): 2760–2767. doi:10.1016/j.jbiomech.2009.07.032
Miehe C (1996) Numerical computation of algorithmic (consistent) tangent moduli in large-strain computational inelasticity. Comput Method Appl M 134(3–4): 223–240
Mortier P, Holzapfel GA, De Beule M, Van Loo D, Taeymans Y, Segers P, Verdonck P, Verhegghe B (2010) A novel simulation strategy for stent insertion and deployment in curved coronary bifurcations: comparison of three drug-eluting stents. Ann Biomed Eng 38(1): 88–99. doi:10.1007/s10439-009-9836-5
Nagel T, Kelly DJ (2010) Mechano-regulation of mesenchymal stem cell differentiation and collagen organisation during skeletal tissue repair. Biomech Model Mech 9(3): 359–372. doi:10.1007/s10237-009-0182-1
O’Connell MK, Murthy S, Phan S, Xu C, Buchanan J, Spilker R, Dalman RL, Zarins CK, Denk W, Taylor CA (2008) The three-dimensional micro- and nanostructure of the aortic medial lamellar unit measured using 3d confocal and electron microscopy imaging. Matrix Biol 27(3): 171–181. doi:10.1016/j.matbio.2007.10.008
Patel DJ, Janicki JS, Carew TE (1969) Static anisotropic elastic properties of aorta in living dogs. Circ Res 25(6): 765–779
Pierce DM, Trobin W, Raya JG, Trattnig S, Bischof H, Glaser C, Holzapfel GA (2010) Dt-mri based computation of collagen fiber deformation in human articular cartilage: a feasibility study. Ann Biomed Eng 38(7): 2447–2463. doi:10.1007/s10439-010-9990-9
Rhodin JAG (1980) Architecture of the vessel wall. In: Sparks HV, Bohr DF, Somlyo AD, Geiger SR (eds) Handbook of physiology, the cardiovascular system. American Physiological Society, Bethesda, pp 1–31
Rodriguez JF, Ruiz C, Doblare M, Holzapfel GA (2008) Mechanical stresses in abdominal aortic aneurysms: influence of diameter, asymmetry, and material anisotropy. J Biomech Eng 130(2): 021023. doi:10.1115/1.2898830
Rowe AJ, Finlay HM, Canham PB (2003) Collagen biomechanics in cerebral arteries and bifurcations assessed by polarizing microscopy. J Vasc Res 40(4): 406–415. doi:10.1159/000072831
Sun W, Chaikof EL, Levenston ME (2008) Numerical approximation of tangent moduli for finite element implementations of nonlinear hyperelastic material models. J Biomech Eng 130(6): 061003. doi:10.1115/1.2979872
Taber LA, Humphrey JD (2001) Stress-modulated growth, residual stress, and vascular heterogeneity. J Biomech Eng 123(6): 528–535
Tang D, Yang C, Mondal S, Liu F, Canton G, Hatsukami TS, Yuan C (2008) A negative correlation between human carotid atherosclerotic plaque progression and plaque wall stress: in vivo mri-based 2d/3d fsi models. J Biomech 41(4): 727–736. doi:10.1016/j.jbiomech.2007.11.026
Wilson W, Driessen NJ, van Donkelaar CC, Ito K (2006) Prediction of collagen orientation in articular cartilage by a collagen remodeling algorithm. Osteoarthr Cartil 14(11): 1196–1202. doi:10.1016/j.joca.2006.05.006
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Creane, A., Maher, E., Sultan, S. et al. Prediction of fibre architecture and adaptation in diseased carotid bifurcations. Biomech Model Mechanobiol 10, 831–843 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10237-010-0277-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10237-010-0277-8