Abstract
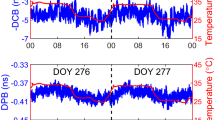
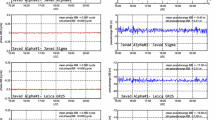
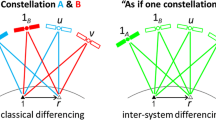
A user of heterogeneous GPS and GLONASS receiver pairs in differential positioning mode will experience ambiguity fixing challenges due to the presence of inter-channel biases. These biases cannot be canceled by differencing GLONASS observations, whether pseudorange or carrier phase. Fortunately, pre-calibration of GLONASS pseudorange and carrier phase observations can make ambiguity fixing for GPS/GLONASS positioning much easier. We propose an effective algorithm that transforms an RTK (real-time kinematic) solution in a mixed receiver baseline from a float to a fixed ambiguity solution. Carrier phase and code inter-channel biases are estimated from a zero baseline. Then, GLONASS both carrier phase and code observations are corrected accordingly. The results show that a mixed baseline can be transformed from a float (~100 %) to a fixed (more than 92 %) solution.















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Dai L, Han S, Rizos C (1999) A new data processing strategy for combined GPS/GLONASS carrier phase-based positioning. 12th International technical meeting of the satellite division of the U.S. institution of navigation, Nashville, Tennessee, 14–17 September, pp 1619–1627
Hofmann-Wellenhof B, Litchtenegger H, Wasle E (2008) GNSS—global navigation satellite systems: GPS, GLONASS, Galileo and more. Springer-Verlag, Vienna
Kozlov D, Tkachenko M, Tochilin A (2000) Statistical characterisation of hardware biases in GPS + GLONASS receivers. 13th international technical meeting of the satellite division of the U.S. institution of navigation, Salt Lake City, Utah, 19–22 September, pp 817–826
Leick A (1998) GLONASS satellite surveying. J Surv Eng 124(2):91–99
Povalyaev A (1997) Using single differences for relative positioning in GLONASS. 10th international technical meeting of the satellite division of the U.S. institution of navigation, Kansas, Missouri, 16–19 September, pp 929–934
Pratt M, Burke B, Misra P (1997) Single-epoch integer ambiguity resolution with GPS-GLONASS L1 data. 53rd Annual meeting of the institution of navigation, Albuquerque, NM, June 30–July 2, pp 691–699
Raby P, Daly P (1993) Using the GLONASS system for geodetic surveys. 6th International technical meeting of the satellite division of the institute of navigation, Salt Lake City, Utah, 22–24 September, pp 1129–1138
Rizos C (1999) Principles and practice of GPS surveying. Monograph published the school of surveying and spatial information system, UNSW, Sydney, Australia
Rizos C (2002) Network RTK research and implementation—a geodetic perspective. J GPS 1(2):144–150
Takac F (2009) GLONASS inter-frequency biases and ambiguity resolution. Inside GNSS 4(2):24–28
Takasu T, Yasuda A (2009) Development of the low-cost RTK-GPS receiver with an open source program package RTKLIB. International symposium on GPS/GNSS, Seogwipo-si Jungmun-dong, Korea, 4–6 November
Teunissen PJG (1995) The least-squares ambiguity decorrelation adjustment: a method for fast GPS integer ambiguity estimation. J Geodesy 70(1):65–82
Wang J, Leick A, Rizos C, Stewart MP (2001) GPS and GLONASS integration: modeling and ambiguity resolution issues. GPS Solut 5(1):55–64
Wanninger L (2012) Carrier phase inter-frequency biases of GLONASS receivers. J Geod 86(2):139–148
Wanninger L, Wallstab-Freitag S (2007) Combined GPS, GLONASS, and SBAS code phase and carrier phase measurements. 20th International technical meeting of the satellite division of the U.S. institution of navigation, Fort Worth, Texas, 25–28, September, pp 866–875
Yamada H, Takasu T, Kubo N, Yasuda A (2010) Evaluation and calibration of receiver inter-channel biases for RTK-GPS/GLONASS. 23rd international technical meeting of the satellite division of the institute of navigation, Portland, Oregon, 21–24 September, pp 1580–1587
Zhang S, Zhang K, Wu S, Li B (2011) Network-based RTK positioning using integrated GPS and GLONAS observations. International global navigation satellite systems society symposium-IGNSS, Sydney, Australia, 15–17 November, CD-ROM procs
Zinoviev AE (2005) Using GLONASS in combined GNSS receivers: current status. 18th International technical meeting of the satellite division of the U.S. institution of navigation, Long Beach, California, 13–16, September, pp 1046–1057
Zinoviev AE, Wieistel AV, Dolgin DA (2009) Renovated GLONASS: improved performance of GNSS receivers. 22nd international technical meeting of the satellite division of the U.S. institution of navigation, Savannah, Georgia, 22–25 September, pp 3271–3277
Acknowledgments
The first author is grateful to the scholarship provider, the Saudi Higher Education Ministry, and especially the University of Umm Al-Qura, Saudi Arabia. He is also thankful to Ultimate Positioning and Position Partners for providing receivers on loan for these investigations.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Al-Shaery, A., Zhang, S. & Rizos, C. An enhanced calibration method of GLONASS inter-channel bias for GNSS RTK. GPS Solut 17, 165–173 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10291-012-0269-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10291-012-0269-5