Abstract
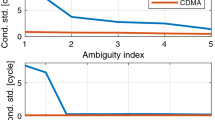
We will focus on single-frequency single-baseline real-time kinematic (RTK) combining four Code Division Multiple Access (CDMA) satellite systems. We will combine observations from the Chinese BeiDou Navigation Satellite System (BDS), European Galileo, American Global Positioning System (GPS) and the Japanese Quasi-Zenith Satellite System (QZSS). To further strengthen the underlying model, attention will be given to overlapping frequencies between the systems. If one can calibrate the inter-system biases, a common pivot satellite between the respective systems can be used to parameterize double-differenced ambiguities. The LAMBDA method is used for ambiguity resolution. The instantaneous (single-epoch) single-frequency RTK performance is evaluated by a formal as well as an empirical analysis, consisting of ambiguity dilution of precision (ADOP), bootstrapped and integer least-squares success rates and positioning precisions. The time-to-correct-fix in some particular cases when instantaneous RTK is not possible will also be analyzed. To simulate conditions with obstructed satellite visibility or when low-elevation multipath is present, various elevation cut-off angles between 10 and 40° will be used. Four days of real data are collected in Perth, Western Australia. It will be shown that the four-system RTK model allows for improved integer ambiguity resolution and positioning performance over the single-, dual- or triple-systems, particularly for higher cut-off angles.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Cao W, O’Keefe K, Cannon M (2008) Evaluation of COMPASS ambiguity resolution performance using geometric-based techniques with comparison to GPS and Galileo. In: Proceedings of ION-GNSS-2008, Institute of Navigation, Savannah, GA, 16–19 September, pp 1688–1697
Chen H, Huang Y, Chiang K, Yang M, Rau R (2009) The performance comparison between GPS and BeiDou-2/COMPASS: a perspective from Asia. J Chin Inst Eng 32(5):679–689
Deng C, Tang W, Liu J, Shi C (2013) Reliable single-epoch ambiguity resolution for short baselines using combined GPS/BeiDou system. GPS Solut. doi:10.1007/s10291-013-0337-5
Euler HJ, Goad Cg (1991) On optimal filtering of GPS dual frequency observations without using orbit information. Bull Geod 65:130–143
Gibbons G (2013) GNSS News. Inside GNSS, p 1
Grelier T, Ghion A, Dantepal J, Ries L, DeLatour A, Issler JL, Avila-Rodriguez J, Wallner S, Hein G (2007) Compass signal structure and first measurements. In: Proceedings of ION-GNSS-2007, Institute of Navigation, Fort Worth, TX, September, pp 3015–3024
He L, Ge M, Wang J, Wickert J, Schuh H (2013a) Experimental study on the precise orbit determination of the BeiDou navigation satellite system. Sensors 13(3):2911–2928. doi:10.3390/s130302911
He H, Li J, Yang Y, Xu J, Guo H, Wang A (2013b) Performance assessment of single- and dual-frequency BeiDou/GPS single-epoch kinematic positioning. GPS Solut. doi:10.1007/s10291-013-0339-3
JAXA (2013) Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA), navigation service interface specification for QZSS (IS-QZSS), V1.5 Tech. Rep., March 27, 2013
Li W, Teunissen PJG, Zhang B, Verhagen S (2013a) Precise point positioning using GPS and Compass observations. In: Sun et al (eds) Lect Notes in Electrical Engineering, Chap 33, vol 2, pp 367–378
Li X, Ge M, Zhang H, Nischan T, Wickert J (2013b) The GFZ real-time GNSS precise positioning service system and its adaption for COMPASS. J Adv Space Res 51(6):1008–1018
Li J, Yang Y, Xu J, He H, Guo H, Wang A (2013c) Performance analysis of single-epoch dual-frequency RTK by BeiDou navigation satellite system. In: Sun et al (eds) Lecture notes in Electrical Engineering, Chap 12, vol 3, pp 133–143
Melgard T, Tegedor J, de Jong K, Lapucha D, Lachapelle G (2013) Interchangeable integration of GPS and Galileo by using a common system clock in PPP. In: Proceedings of ION-GNSS-2013, Institute of Navigation, Nashville, TN, 16–20 September, pp 1198–1206
Mirgorodskaya T (2013) GLONASS government policy, status and modernization plans. In: Proceedings of international global navigation satellite systems (IGNSS) symposium, Golden Coast, 16–18 July
Montenbruck O, Hauschild A, Hessels U (2011) Characterization of GPS/GIOVE sensor stations in the CONGO network. GPS Solut 15(3):193–205
Montenbruck O, Hauschild A, Steigenberger P, Hugentobler U, Teunissen PJG, Nakamura S (2013) Initial assessment of the COMPASS/BeiDou-2 regional navigation satellite system. GPS Solut 17(2):211–222
Nadarajah N, Teunissen PJG, Raziq N (2013) BeiDou inter-satellite-type bias evaluation and calibration for mixed receiver attitude determination. Sensors 13(7):9435–9463
Odijk D, Teunissen PJG (2008) ADOP in closed form for a hierarchy of multi-frequency single-baseline GNSS models. J Geod 82:473–492
Odijk D, Teunissen PJG (2013a) Characterization of between-receiver GPS-Galileo inter-system biases and their effect on mixed ambiguity resolution. GPS Solut 17(4):521–533
Odijk D, Teunissen PJG (2013b) Estimation of differential inter-system biases between the overlapping frequencies of GPS, Galileo, BeiDou and QZSS. In: 4th International colloquium scientific and fundamental aspects of the Galileo programme, 4–6 December, Prague, Czech Republic
Odolinski R, Teunissen PJG, Odijk D (2013) An analysis of combined COMPASS/BeiDou-2 and GPS single- and multiple-frequency RTK positioning. In: Proceedings of ION PNT 2013, Honolulu, Hawaii, April 23–25, pp 69–90
Shi C, Zhao Q, Li M, Tang W, Hu Z, Lou Y, Zhang H, Niu X, Liu J (2012) Precise orbit determination of Beidou Satellites with precise positioning. Sci China Earth Sci 55:1079–1086. doi:10.1007/819s11430-012-4446-8
Shi C, Zhao Q, Hu Z, Liu J (2013) Precise relative positioning using real tracking data from COMPASS GEO and IGSO satellites. GPS Solut 17(1):103–119. doi:10.1007/s10291-012-0264-x
Steigenberger P, Hugentobler U, Hauschild A, Montenbruck O (2013) Orbit and clock analysis of COMPASS GEO and IGSO satellites. J Geod 87(6):515–525. doi:10.1007/s00190-013-0625-4
Teunissen PJG (1985) Generalized inverses, adjustment, the datum problem and S-transformations. In: Grafarend EW, Sanso F (eds) Optimization of geodetic networks. Springer, Berlin, pp 11–55
Teunissen PJG (1990) An integrity and quality control procedure for use in multi sensor integration. In: Proceedings of ION-GPS-1990, Colorado Spring, CO, pp 513–522, also published in: vol VII of GPS Red Book Series: Integrated systems, ION Navigation, 2012
Teunissen PJG (1995) The least squares ambiguity decorrelation adjustment: a method for fast GPS integer estimation. J Geod 70:65–82
Teunissen PJG (1997) A canonical theory for short GPS baselines. Part I: the baseline precision, Part II: the ambiguity precision and correlation, Part III: the geometry of the ambiguity search space, Part IV: precision versus reliability. J Geod 71(6):320–336, 71(7):389–401, 71(8):486–501, 71(9):513–525
Teunissen PJG (1998) Success probability of integer GPS ambiguity rounding and bootstrapping. J Geod 72:606–612
Teunissen PJG (1999) An optimality property of the integer least-squares estimator. J Geod 73:587–593
Teunissen PJG, de Jonge P, Tiberius C (1996) The volume of the GPS ambiguity search space and its relevance for integer ambiguity resolution. In: Proceedings of ION-GPS-1996, vol 9, pp 889–898
Teunissen PJG, Odijk D, Zhang B (2010) PPP-RTK: results of CORS network-based PPP with integer ambiguity resolution. J Aeronaut Astronaut Aviation Ser A 42(4):223–230
Teunissen PJG, Odolinski R, Odijk D (2013) Instantaneous BeiDou+GPS RTK positioning with high cut-off elevation angles. J Geod. doi:10.1007/s00190-013-0686-4
Yang Y, Li J, Xu J, Tang J, Guo H, He H (2011) Contribution of the compass satellite navigation system to global PNT users. Chin Sci Bull 56(26):2813–2819
Acknowledgments
This work has been executed in the framework of the Positioning Program of the Cooperative Research Centre for Spatial Information (CRC-SI). The second author is the recipient of an Australian Research Council (ARC) Federation Fellowship (project number FF0883188). All this support is gratefully acknowledged.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Odolinski, R., Teunissen, P.J.G. & Odijk, D. Combined BDS, Galileo, QZSS and GPS single-frequency RTK. GPS Solut 19, 151–163 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10291-014-0376-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10291-014-0376-6