Abstract
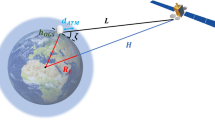
Free-space laser communication offers an attractive alternative for transferring high-bandwidth data when fiber optic cable is neither practical nor feasible. However, there are a variety of deleterious features of the atmospheric channel that may lead to serious signal fading, and even the complete loss of signal altogether. Physical obstructions—such as birds, insects, tree limbs, or other factors—can temporarily or permanently block the laser line-of-sight. Platform/building motion due to wind, differential heating and cooling, or ground motion over time can result in serious misalignment of fixed-position laser communication systems. But most importantly of all, absorption and scattering due to particulate matter in the atmosphere may significantly decrease the transmitted optical signal, while random atmospheric distortions due to optical turbulence can severely degrade the wave-front quality of a signal-carrying laser beam, causing intensity fading and random signal losses at the receiver.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
R.M. Goody and Y.L. Yung, Atmospheric Radiation: Theoretical Basis, 2nd ed. (Oxford University Press, 1989).
M.E. Thomas and D.D. Duncan, Atmospheric Transmission, The Infrared and Electro-Optical Systems Handbook, Vol. 2 (SPIE Press, 1993).
A.S. Jursa, Ed., Handbook of Geophysics and the Space Environment (Air Force Geophysics Laboratory, 1985).
G.P. Anderson, F.X. Kneizys, J.H. Chetwind, J. Wand, M.L. Hoke, L.S. Rothman, L.M. Kimball, R.A. McClatchey, E.P. Shettle, S.A. Clough, W.O. Gallery, L.W. Abreu, J.E.A. Selby, "FASCODE/MODTRAN/LOWTRAN: Past/Present/Future", 18th Annual Review Conference on Atmospheric Transmission Models, 1995.
ONTAR Corporation (http://www.ontar.com/).
K.T. Whitby and B. Cantrell, "Atmospheric aerosols--characteristics and measurements," Proc. Intern. Conf. on Environ. Sensing and Assessment, Las Vegas, Nevada, 14-19 September (IEEE, New York, 1976).
H.C. van de Hulst, Light Scattering by Small Particles (John Wiley & Sons, 1957).
C.F. Bohren and D.R. Huffman, Absorption and Scattering of Light by Small Particles (John Wiley & Sons, 1983).
D. Deirmendjian, Electromagnetic Scattering on Spherical Polydispersions (Elsevier, 1969).
E.J. McCartney, Optics of the Atmosphere; Scattering by Molecules and Particles, (John Wiley & Sons, 1976).
S.G. Gathman, "Optical properties of the marine aerosol as predicted by the Navy aerosol model," Opt. Eng. 22, 57-62 (1983).
A.M.J. van Eijk, "The ANAM-3.0 development," (TNO-The Netherlands Organisation for Applied Scientific Research Report FEL-01-C187, 2001).
A. Deepak and H.E. Gerber, "Report of the experts meeting on aerosols and their climatic effects", WCP-55, 1983.
M. Hess, P. Koepke, I. Schult, "Optical Properties of Aerosols and Clouds: The Software Package OPAC", Bull. Amer. Met. Soc. 79, 831-844 (1998).
E.P. Shettle and R.W. Fenn, "Models for the aerosols of the lower atmosphere and the effects of humidity variations on their optical properties", AFGL-TR-79-0214, 1979.
G.A. d'Almeida, P. Koepke, and E.P. Shettle, Atmospheric Aerosols: Global Climatology and Radiative Characteristics (A. Deepak Publishing, 1991)
A.N. Kolmogorov, "The local structure of turbulence in an incompressible viscous fluid for very large Reynolds numbers," C. R. Acad. Sci. U.R.S.S. 30, 301-305 (1941).
A.N. Kolmogorov, "Dissipation of energy in the locally isotropic turbulence," C. R. Acad. Sci. U.R.S.S. 32, 16-18 (1941).
A.M. Obukhov, "On the energy distribution in the spectrum of a turbulent flow, C. R. Acad. Sci. U.R.S.S. 32, 19-21 (1941).
A.M. Obukhov, "On the energy distribution in the spectrum of a turbulent flow," Izv., Akad. Nauk SSSR, Ser. Geogra. Geofiz. 5, 453-466 (1941).
A.M. Yaglom, "Laws of small-scale turbulence in atmosphere and ocean (in commemoration of the 40th anniversary of the theory of locally isotropic turbulence)," Izv., Atmos. Oceanic Phy. 17, 919-935 (1981).
A.N. Kolmogorov, "A refinement of previous hypotheses concerning local structure of turbulence in a viscous incompressible fluid at high Reynolds number," J. Fluid Mech. 13, 82-85 (1962).
V.I. Tatarskii, The Effects of the Turbulent Atmosphere on Wave Propagation (National Technical Information Service, Springfield, Va., 1971).
R.J. Hill and S.F. Clifford, "Modified spectrum of atmospheric temperature fluctuations and its application to optical propagation," J. Opt. Soc. Am. 68, 892-899 (1978).
L.C. Andrews, "An analytical model for the refractive index power spectrum and its application to optical scintillations in the atmosphere," J. Mod. Opt. 39, 1849-1853 (1992).
G.D. Nastrom and F.D. Eaton, "The coupling of gravity waves and turbulence and turbulence at White Sands, New Mexico from radar observations," J. Appl. Meteorol., 32 (1), 81-87 (1993).
G.D. Nastrom and F.D. Eaton, "Variations of winds and turbulence seen by the 50-MHz radar at White Sands Missile Range, New Mexico," J. Appl. Meteorol., 34 (10), 2135-2148 (1995).
M.C. Roggemann and B.M. Welsh, Imaging Through Turbulence (CRC Press, Boca Raton, FL, 1996), p. 320.
J.W. Hardy, Adaptive Optics for Astronomical Telescopes (Oxford University Press, New York, NY, 1998), p. 448.
Y. Han Oh, J.C. Ricklin, E. Oh, S. Doss-Hammel and F.D. Eaton, "Estimating optical turbulence effects on free-space laser communication: modeling and measurements at ARL's A_LOT facility," SPIE, 5550, 247-255 (2004).
W.B. Miller, J.C. Ricklin and W.J. Stewart, An Optical Turbulence Code for the Surface Boundary Layer (Army Research Laboratory, ASL-TR-0220, 1987).
W.B. Miller and J.C. Ricklin, A Module for Imaging Through Optical Turbulence (Army Research Laboratory, ASL-TR-0221-27, 1990).
H. Rachele and A. Tunick, "Energy balance model for imagery and electromagnetic propagation," J Appl Meteorol, 33, 964-976 (1994).
R.W. Smith, J.C. Ricklin, K.E. Cranston and J.P. Cruncleton, "Comparison of a model describing propagation through optical turbulence (PROTURB) with field data," SPIE, 2222, 780-789 (1994).
A. Ishimaru, Wave Propagation and Scattering in Random Media (Academic, New York, 1978), Vol. II, Appendix C.
J.A. Businger, "Turbulent Transfer in the Atmospheric Surface Layer," in Workshop on Micrometeorology, D. Haugen, Ed. (American Meteorological Society, Boston, MA, 1973).
N. Busch, "On the Mechanics of Atmospheric Turbulence," in Workshop on Micrometeorology, D. Haugen, Ed. (American Meteorological Society, Boston, MA, 1973).
H.A. Panofsky and J.A. Dutton, Atmospheric Turbulence: Models and Methods for Engineering Applications (John Wiley & Sons, New York, 1984).
M. Liu, D. Durran, P. Mundkur, M. Yocke and J. Ames, The Chemistry, Dispersion and Transport of Air Pollutants Emitted From Fossil Fuel Plants in California: Data Analysis and Emission Impact Model (National Technical Information Service, PB-264-822, 1976).
F.V. Hansen, A Fractional Stability Category Scheme (Atmospheric Sciences Laboratory Technical Report ASL-TR-0275, 1990).
E.C. Kung, "Climatology of aerodynamic roughness parameter and energy dissipation in the planetary boundary layer of the northern hemisphere," in Studies of the Effects of Variations in Boundary Conditions on the Atmospheric Boundary Layer (Annual Report, Contract DA-36-039-AMC-00878, Dept. of Meteorology, Univ. of Wisconsin, Madison, Wisconsin, 1963).
Characterization of Wind Speed in the Lowest Layers of the Atmosphere Near the Ground: Strong Winds (Engineering Sciences Data Unit Ltd, London, UK, EDSU 72026, 1972).
L.O. Myrup and J. Ranziere, A Consistent Scheme for Estimating Diffusivities to be Used in Air Quality Models (NTIC, Springfield, VA, PB-272-284, 1976).
A.S. Smedman-Hogstrom and U. Hogstrom, "Practical method of determining wind frequency distributions for the lowest m from routine meteorological data," J. Appl. Meteorol., 17 (7), 942-954 (1977).
C.D. MacArthur and P.A. Hains, The Roughness Length Associated With Regions of Heterogeneous Vegetation and Elevation (Army Research Laboratory, ASL-CR-82-0206-1, 1982).
S.F. Clifford, "The classical theory of wave propagation in a turbulent medium," in Laser Beam Propagation in the Atmosphere, J. Strohbehn, ed. (Springer, New York, 1978).
A.S. Monin and A.M. Yaglom, Statistical Fluid Mechanics (MIT Press, Cambridge, MA, 1971). V.L. Mironov, Laser beam propagation in turbulence atmosphere (Nauka, Moscow, 1981), p. 246.
V.L. Mironov, Laser beam propagation in turbulence atmosphere (Nauka, Moscow, 1981), p. 246.
A.S. Gurvich, A.I. Kon, V.L. Mironov, and S.S. Khmelevtsov, Laser radiation in turbulent atmosphere (Nauka, Moscow, 1976), p. 227.
V.A. Banakh, ed., High-power laser beams in a randomly inhomogeneous atmosphere (SO RAN Publ., Novosibirsk, 1998), p. 341.
M.E. Gracheva and A.S. Gurvich, "Simple models of turbulence," Izv. Akad. Nauk SSSR, Fiz. Atm. Okeana 16(10), 1107-1111 (1980).
M.G. Miller and P.L. Zieske, Turbulence environmental characterization (Rome Air Development Center, Griffiss Air Force Base, NY, RADC-TR-79-131, 1979).
R.R. Parenti and R.J. Sasiela, "Laser-guide-star systems for astronomical applications," J. Opt. Soc. Am. A, 11(1), 288-309 (1994).
R.E. Hufnagel, "Variations of atmospheric turbulence," in Digest of topical meeting on optical propagation through turbulence (Optical Society of America, Washington, D.C., 1974), p. WA1.
G.C. Valley, "Isoplanatic degradation of tilt correction and short-term imaging systems," Appl. Opt. 19(4), 574-577 (1980).
B.G. Zollars, "Atmospheric-turbulence compensation experiments using synthetic beacons," in Selected Papers on Adaptive Optics for Atmospheric Compensation (SPIE Press, 1994), Vol. MS92, pp. 564-588.
D.P. Greenwood, "Bandwidth specification for adaptive optics systems," J. Opt. Soc. Am., 67(3), 390-393 (1977).
T.E. Van Zandt, J.L. Green, K.S. Gage, and W.L. Clark, Vertical profiles of refractivity turbulence structure constant: Comparison of observations by the Sunset radar with a new theoretical model, Radio Science, 13, 819-829 (1978).
T.E. Van Zandt, K.S. Gage, and J.M. Warnock, An improve model for the calculation of profiles of wind, temperature, and humidity, Preprints Twentieth Conference on Radar Meteorology, American Meteorological Society, Boston MA, 129-135 (1981).
J.M. Warnock, T.E. Van Zandt, and J.L. Green, A statistical model to estimate mean values of parameters of turbulence in the free atmosphere, Preprints 7th symposium on turbulence and diffusion, Nov 12-15, 1985, Boulder, CO, AMS, Boston, MA, 156-159.
E.M. Dewan, R.E. Good, B. Beland, and J. Brown, A model for Cn2 (optical turbulence) profiles using radiosonde data, (PL-TR-93-2043, Environmental Research Papers, No. 1121, Phillips Laboratory, Hanscom AFB, MA, 1993).
W.B. Miller, J.C. Ricklin and L.C. Andrews, "Log-amplitude variance and wave structure function: a new perspective for Gaussian beams," J. Opt. Soc. Am. A, 10 (4), 661-672 (1993).
L.C. Andrews, W.B. Miller and J.C. Ricklin, "Geometrical representation of Gaussian beams propagating through complex optical systems," Appl. Opt., 32 (30), 5918-5929 (1993).
L.C. Andrews and R.L. Phillips, Laser Beam Propagation Through Random Media (SPIE Press, Bellingham, 1998).
L.C. Andrews, R.L. Phillips, and C.Y. Hopen, Laser Beam Scintillation With Applications (SPIE Press, Bellingham, 2001).
J.C. Ricklin and F.M. Davidson, "Atmospheric turbulence effects on a partially coherent Gaussian beam: implications for free-space laser communication," J. Opt. Soc. Am. A, 19 (9), 1794-1803 (2002).
J.C. Ricklin and F.M. Davidson, "Atmospheric optical communication with a Gaussian Schell beam," J. Opt. Soc. Am. A, 20 (5), 856-866 (2003).
V.I. Tatarskii, Wave Propagation in a Turbulent Medium (McGraw-Hill Book Company, Inc., New York, 1961).
F. Dios, J.A. Rubio, A. Rodriguez and A. Comeron, "Scintillation and beam-wander analysis in an optical ground station-satellite uplink," Appl. Opt., 43 (12), 3866-3873 (2004).
R.L. Fante, "Electromagnetic beam propagation in turbulent media: an update," Proc. IEEE, 68 (11), 1424-1443 (1980).
R.J. McIntyre, "The distribution of gains in uniformly multiplying avalanche photodiodes," IEEE Trans. Electron. Dev., 19 (6), 703-713 (1972).
J.H. Churnside and C.M. McIntyre, "Averaged threshold receiver for direct detection of optical communications through the lognormal atmospheric channel," Appl. Opt., 16 (10), 2669-2676 (1977).
R.M. Gagliardi and S. Karp, Optical Communications (Wiley-Interscience, New York, 1995).
A.R. Weeks, J. Xu, R.R. Phillips, L.C. Andrews, C.M. Stickley, G. Sellar, J.S. Stryjewsky and J.E. Harvey, "Experimental verification for an eight-element multiple-aperture equal-gain coherent laser receiver for laser communications," Appl. Opt., 37 (21), 4782-4788 (1998).
R.K. Tyson, "Adaptive optics and ground-to-space laser communications," Appl. Opt., 35 (19), 3640-3646 (1996).
B.M. Levine, E.A. Martinsen, A. Wirth, A. Jankevics, M. Toledo-Quinones, F. Landers and T.L. Bruno, "Horizontal line-of-sight turbulence over near-ground paths and implications for adaptive optics corrections in laser communications," Appl. Opt., 37 (21), 4553-4560 (1998).
R.K. Tyson, "Bit-error rate for free-space adaptive optics laser communications," J. Opt. Soc. Am. A, 19 (4), 753-758 (2002).
R.K. Tyson, "Indirect measurement of a laser communications bit-error-rate reduction with low-order adaptive optics," Appl. Opt., 42 (21), 4239-4243 (2003).
R.J. List, Smithsonian Meteorological Tables (Smithsonian Institute, Washington, DC, 1951).
F.B. Smith, "A Scheme for estimating the vertical dispersion of a plume from a source near the ground," Proc. of the Third Meeting of the Expert Panel on Air Pollution Modeling (NATO Committee on the Challenges of Modern Society, Paris, France, 2-3 October, 1972).
F.B. Smith, "The relation between Pasquill stability P and Kazanski-Monin stability (in neutral and unstable conditions," Atmos. Environ., 13 (6), 879-881 (1979).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ricklin, J., Hammel, S., Eaton, F. et al. Atmospheric channel effects on free-space laser communication. J Optic Comm Rep 3, 111–158 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10297-005-0056-y
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10297-005-0056-y